GPT-Runner Intellij is a
WIP
Note
Make sure to always upgrade to the latest version of
gradle-intellij-plugin.
The project-specific configuration file gradle.properties contains:
| Property name | Description |
|---|---|
pluginGroup |
Package name - after using the template, this will be set to com.github.username.repo. |
pluginName |
Plugin name displayed in the JetBrains Marketplace and the Plugins Repository. |
pluginRepositoryUrl |
Repository URL used for generating URLs by the Gradle Changelog Plugin |
pluginVersion |
The current version of the plugin in SemVer format. |
pluginSinceBuild |
The since-build attribute of the <idea-version> tag. |
pluginUntilBuild |
The until-build attribute of the <idea-version> tag. |
platformType |
The type of IDE distribution. |
platformVersion |
The version of the IntelliJ Platform IDE will be used to build the plugin. |
platformPlugins |
Comma-separated list of dependencies to the bundled IDE plugins and plugins from the Plugin Repositories. |
gradleVersion |
Version of Gradle used for plugin development. |
The properties listed define the plugin itself or configure the gradle-intellij-plugin – check its documentation for more details.
In addition, extra behaviours are configured through the gradle.properties file, such as:
| Property name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
kotlin.stdlib.default.dependency |
false |
Opt-out flag for bundling Kotlin standard library |
org.gradle.configuration-cache |
true |
Enable Gradle Configuration Cache |
org.gradle.caching |
true |
Enable Gradle Build Cache |
systemProp.org.gradle.unsafe.kotlin.assignment |
true |
Enable Gradle Kotlin DSL Lazy Property Assignment |
kotlin.incremental.useClasspathSnapshot |
false |
Temporary workaround for Kotlin Compiler OutOfMemoryError |
Some values used for the Gradle configuration shouldn't be stored in files to avoid publishing them to the Version Control System.
To avoid that, environment variables are introduced, which can be provided within the Run/Debug Configuration within the IDE, or on the CI – like for GitHub: ⚙️ Settings > Secrets.
Environment variables used by the current project are related to the plugin signing and publishing.
| Environment variable name | Description |
|---|---|
PRIVATE_KEY |
Certificate private key, should contain: -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- ... -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY----- |
PRIVATE_KEY_PASSWORD |
Password used for encrypting the certificate file. |
CERTIFICATE_CHAIN |
Certificate chain, should contain: -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... -----END CERTIFICATE---- |
PUBLISH_TOKEN |
Publishing token generated in your JetBrains Marketplace profile dashboard. |
GPT-Runner Intellij repository contains the following content structure:
.
├── .github/ GitHub Actions workflows and Dependabot configuration files
├── .run/ Predefined Run/Debug Configurations
├── build/ Output build directory
├── gradle
│ ├── wrapper/ Gradle Wrapper
│ └── libs.versions.toml Gradle version catalog
├── src Plugin sources
│ ├── main
│ │ ├── kotlin/ Kotlin production sources
│ │ └── resources/ Resources - plugin.xml, icons, messages
│ └── test
│ ├── kotlin/ Kotlin test sources
│ └── testData/ Test data used by tests
├── .gitignore Git ignoring rules
├── build.gradle.kts Gradle configuration
├── CHANGELOG.md Full change history
├── gradle.properties Gradle configuration properties
├── gradlew *nix Gradle Wrapper script
├── gradlew.bat Windows Gradle Wrapper script
├── LICENSE License, MIT by default
├── qodana.yml Qodana configuration file
├── README.md README
└── settings.gradle.kts Gradle project settings
In addition to the configuration files, the most crucial part is the src directory, which contains our implementation and the manifest for our plugin – plugin.xml.
Check our IntelliJ Platform SDK DevGuide, which contains an introduction to the essential areas of the plugin development together with dedicated tutorials.
Testing plugins is an essential part of the plugin development to make sure that everything works as expected between IDE releases and plugin refactorings. The IntelliJ Platform Plugin Template project provides integration of two testing approaches – functional and UI tests.
Most of the IntelliJ Platform codebase tests are model-level, run in a headless environment using an actual IDE instance. The tests usually test a feature as a whole rather than individual functions that comprise its implementation, like in unit tests.
Note
Run your tests using predefined Run Tests configuration or by invoking the
./gradlew checkGradle task.
The Kover – a Gradle plugin for Kotlin code coverage agents: IntelliJ and JaCoCo – is integrated into the project to provide the code coverage feature.
Code coverage makes it possible to measure and track the degree of testing of the plugin sources.
The code coverage gets executed when running the check Gradle task.
The final test report is sent to CodeCov for better results visualization.
If your plugin provides complex user interfaces, you should consider covering them with tests and the functionality they utilize.
IntelliJ UI Test Robot allows you to write and execute UI tests within the IntelliJ IDE running instance.
You can use the XPath query language to find components in the currently available IDE view.
Once IDE with robot-server has started, you can open the http://localhost:8082 page that presents the currently available IDEA UI components hierarchy in HTML format and use a simple XPath generator, which can help test your plugin's interface.
Note
Run IDE for UI tests using predefined Run IDE for UI Tests and then Run Tests configurations or by invoking the
./gradlew runIdeForUiTestsand./gradlew checkGradle tasks.
A dedicated Run UI Tests workflow is available for manual triggering to run UI tests against three different operating systems: macOS, Windows, and Linux.
Due to its optional nature, this workflow isn't set as an automatic one, but this can be easily achieved by changing the on trigger event, like in the Build workflow file.
To increase the project value, the IntelliJ Platform Plugin Template got integrated with Qodana, a code quality monitoring platform that allows you to check the condition of your implementation and find any possible problems that may require enhancing.
Qodana brings into your CI/CD pipelines all the smart features you love in the JetBrains IDEs and generates an HTML report with the actual inspection status.
Qodana inspection is configured with the qodana { ... } section in the Gradle build file and qodana.yml YAML configuration file.
Note
Qodana requires Docker to be installed and available in your environment.
To run inspections, you can use a predefined Run Qodana configuration, which will provide a full report on http://localhost:8080, or invoke the Gradle task directly with the ./gradlew runInspections command.
A final report is available in the ./build/reports/inspections/ directory.
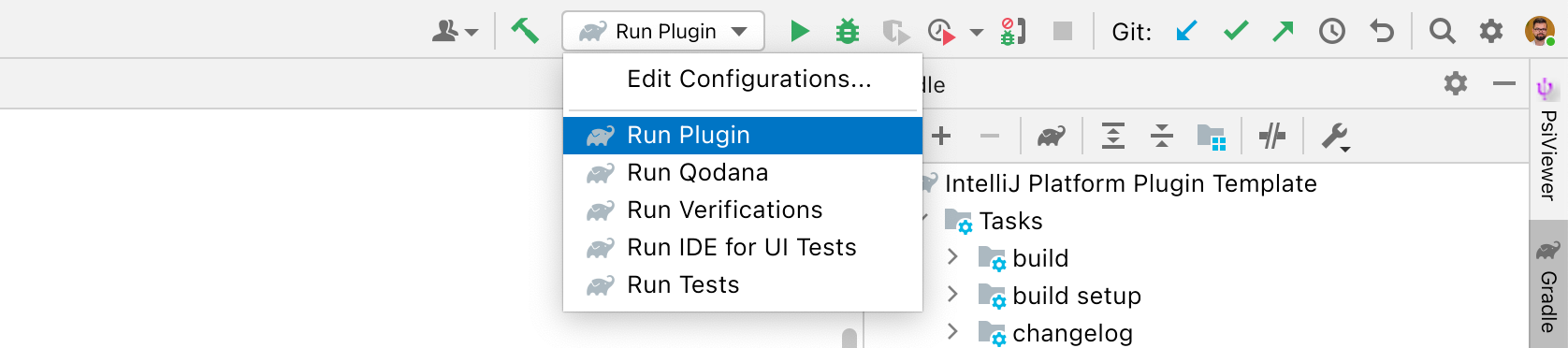
Within the default project structure, there is a .run directory provided containing predefined Run/Debug configurations that expose corresponding Gradle tasks:
| Configuration name | Description |
|---|---|
| Run Plugin | Runs :runIde Gradle IntelliJ Plugin task. Use the Debug icon for plugin debugging. |
| Run Verifications | Runs :runPluginVerifier Gradle IntelliJ Plugin task to check the plugin compatibility against the specified IntelliJ IDEs. |
| Run Tests | Runs :test Gradle task. |
| Run IDE for UI Tests | Runs :runIdeForUiTests Gradle IntelliJ Plugin task to allow for running UI tests within the IntelliJ IDE running instance. |
| Run Qodana | Runs :runInspections Gradle Qodana Plugin task. Starts Qodana inspections in a Docker container and serves generated report on localhost:8080. |
The changelog is a curated list that contains information about any new features, fixes, and deprecations. When they're provided, these lists are available in a few different places:
- the CHANGELOG.md file,
- the Releases page,
- the What's new section of JetBrains Marketplace Plugin page,
- and inside the Plugin Manager's item details.
There are many methods for handling the project's changelog. The one used in the current template project is the Keep a Changelog approach.
- IntelliJ Platform SDK Plugin SDK
- Gradle IntelliJ Plugin Documentation
- IntelliJ Platform Explorer
- Marketplace Quality Guidelines
- IntelliJ Platform UI Guidelines
- Marketplace Paid Plugins
- Kotlin UI DSL
- IntelliJ SDK Code Samples
- JetBrains Platform Slack
- JetBrains Platform Twitter
- IntelliJ IDEA Open API and Plugin Development Forum
- Keep a Changelog
- GitHub Actions