/\ \ \___| |_ / \___| |__ _ _ __ _
/ \/ / _ \ __| / /\ / _ \ '_ \| | | |/ _` |
/ /\ / __/ |_ / /_// __/ |_) | |_| | (_| |
\_\ \/ \___|\__/___,' \___|_.__/ \__,_|\__, |
|___/
Purpose: Kubernetes network troubleshooting can become complex. With proper understanding of how Docker and Kubernetes networking works and the right set of tools, you can troubleshoot and resolve these networking issues. The netdebug container has a set of powerful networking tshooting tools that can be used to troubleshoot Docker networking issues. Along with these tools come a set of use-cases that show how this container can be used in real-world scenarios.
Kubernetes
If you want to spin up a throw away container for debugging.
$ kubectl run tmp-shell --rm -i --tty --image 0xgui/netdebug -- /bin/bash
And if you want to spin up a container on the host's network namespace.
$ kubectl run tmp-shell --rm -i --tty --overrides='{"spec": {"hostNetwork": true}}' --image 0xgui/netdebug -- /bin/bash
Network Problems
Many network issues could result in application performance degradation. Some of those issues could be related to the underlying networking infrastructure(underlay). Others could be related to misconfiguration at the host or Docker level. Let's take a look at common networking issues:
- latency
- routing
- DNS resolution
- firewall
- incomplete ARPs
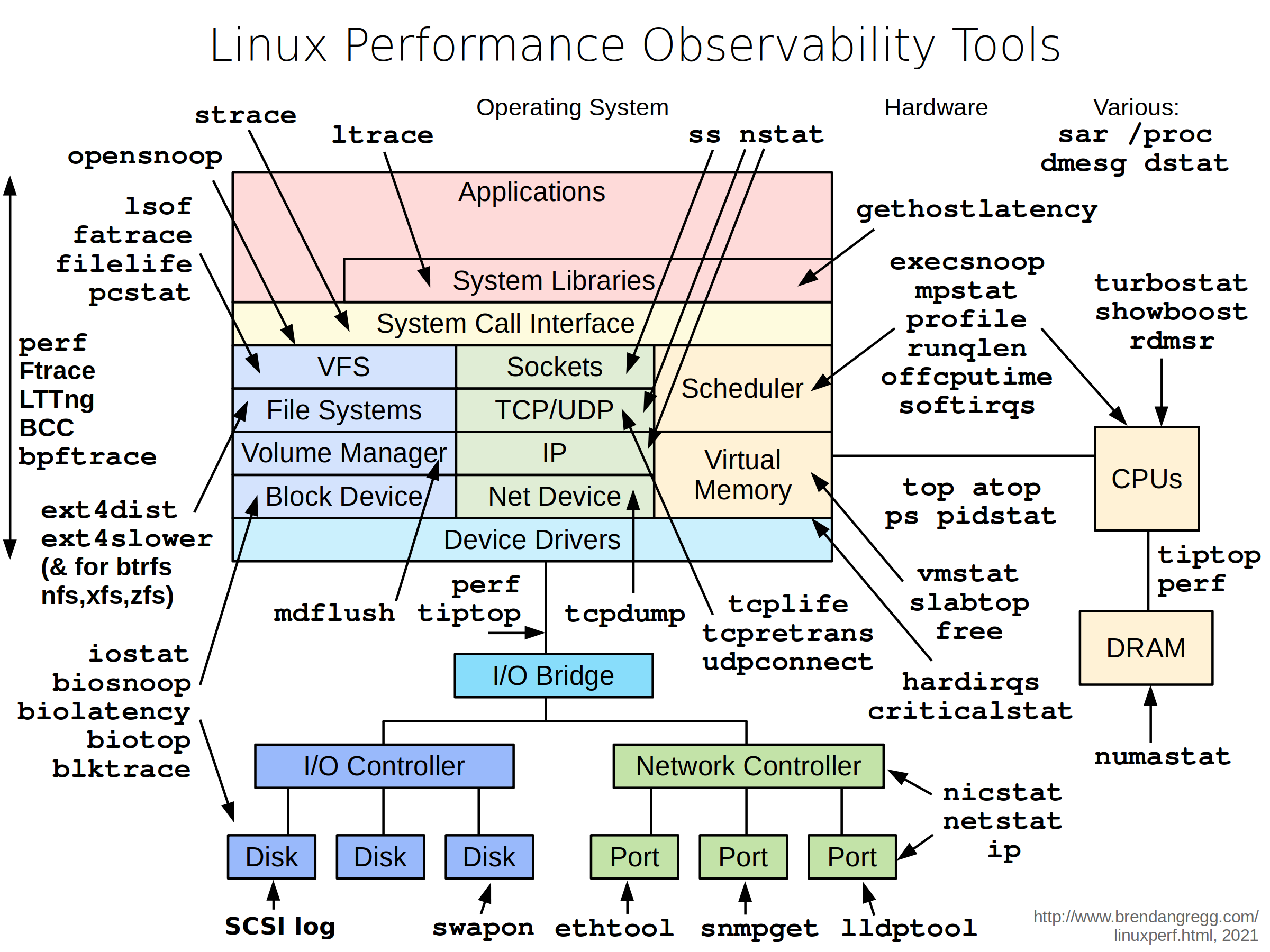
To troubleshoot these issues, netdebug includes a set of powerful tools as recommended by this diagram.
Included Packages: The following packages are included in netdebug. We'll go over some with some sample use-cases.
bash \
bind-tools \
bridge-utils \
busybox-extras \
conntrack-tools \
curl \
dhcping \
drill \
ethtool \
file\
fping \
iftop \
iperf \
iproute2 \
ipset \
iptraf-ng \
iputils \
ipvsadm \
jq \
libc6-compat \
liboping \
mtr \
net-snmp-tools \
netcat-openbsd \
nftables \
ngrep \
nmap \
openssl \
socat \
strace \
tcpdump \
tcptraceroute \
util-linux \
vim
Here's a list of use-cases that can help you understand when and how to use this container to solve networking issues in your Docker cluster. Please feel free to add your own use-case where you used netdebug to investigate, trouble-shoot, or just learn more about your environment!!!
tcpdump is a powerful and common packet analyzer that runs under the command line. It allows the user to display TCP/IP and other packets being transmitted or received over an attached network interface.
# Capturing packets on eth0 and tcp port 9999.
/ # tcpdump -i eth0 port 9999 -c 1 -Xvv
tcpdump: listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
23:14:09.771825 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 60898, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 64360)
10.0.3.5.60032 > 0e2ccbf3d608.9999: Flags [.], cksum 0x1563 (incorrect -> 0x895d), seq 222376702:222441010, ack 3545090958, win 221, options [nop,nop,TS val 2488870 ecr 2488869], length 64308
0x0000: 4500 fb68 ede2 4000 4006 37a5 0a00 0305 E..h..@.@.7.....
0x0010: 0a00 0303 ea80 270f 0d41 32fe d34d cb8e ......'..A2..M..
0x0020: 8010 00dd 1563 0000 0101 080a 0025 fa26 .....c.......%.&
0x0030: 0025 fa25 0000 0000 0000 0001 0000 270f .%.%..........'.
0x0040: 0000 0000 0000 0000 ffff d8f0 3435 3637 ............4567
0x0050: 3839 3031 3233 3435 3637 3839 3031 3233 8901234567890123
0x0060: 3435 3637 3839 3031 3233 3435 3637 3839 4567890123456789
0x0070: 3031 3233 3435 3637 3839 3031 3233 3435 0123456789012345
0x0080: 3637 3839 3031 3233 3435 3637 3839 3031 6789012345678901
0x0090: 3233 3435 3637 3839 3031 3233 3435 3637 2345678901234567
0x00a0: 3839 3031 3233 3435 3637 3839 3031 3233 8901234567890123
0x00b0: 3435 3637 3839 3031 3233 3435 3637 3839 4567890123456789
0x00c0: 3031 3233 3435 3637 3839 3031 3233 3435 0123456789012345
0x00d0: 3637 3839 3031 3233 3435 3637 3839 3031 6789012345678901
0x00e0: 3233 3435 3637 3839 3031 3233 3435 3637 2345678901234567
0x00f0: 3839 3031 3233 3435 3637 3839 3031 3233 8901234567890123
0x0100: 3435 3637 3839 3031 3233 3435 3637 3839 4567890123456789
More info on tcpdump can be found here.
Purpose: netstat is a useful tool for checking your network configuration and activity.
/ # netstat -tulpn
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.11:46727 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:9999 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
udp 0 0 127.0.0.11:39552 0.0.0.0:* -
nmap ("Network Mapper") is an open source tool for network exploration and security auditing. It is very useful for scanning to see which ports are open between a given set of hosts. This is a common thing to check for when installing Swarm or UCP because a range of ports is required for cluster communication. The command analyzes the connection pathway between the host where nmap is running and the given target address.
...
Discovered closed port 12388/tcp on 172.31.24.25
Discovered closed port 12379/tcp on 172.31.24.25
Discovered closed port 12389/tcp on 172.31.24.25
Discovered closed port 12376/tcp on 172.31.24.25
...
There are several states that ports will be discovered as:
open: the pathway to the port is open and there is an application listening on this port.closed: the pathway to the port is open but there is no application listening on this port.filtered: the pathway to the port is closed, blocked by a firewall, routing rules, or host-based rules.
Purpose: iftop does for network usage what top does for CPU usage. It listens to network traffic on a named interface and displays a table of current bandwidth usage by pairs of hosts.
ex: iftop -i eth0
Purpose: drill is a tool to designed to get all sorts of information out of the DNS.
Continuing the iperf example, we'll use drill to understand how services' DNS is resolved in Docker.
drill -V 5 perf-test-b
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, rcode: NOERROR, id: 0
;; flags: rd ; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;; perf-test-b. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
;; ADDITIONAL SECTION:
;; Query time: 0 msec
;; WHEN: Thu Aug 18 02:08:47 2016
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 0
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, rcode: NOERROR, id: 52723
;; flags: qr rd ra ; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;; perf-test-b. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
perf-test-b. 600 IN A 10.0.3.4 <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< Service VIP
;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
;; ADDITIONAL SECTION:
;; Query time: 1 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.11 <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< Local resolver
;; WHEN: Thu Aug 18 02:08:47 2016
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 56
Purpose: a simple Unix utility that reads and writes data across network connections, using the TCP or UDP protocol. It's useful for testing and troubleshooting TCP/UDP connections. netcat can be used to detect if there's a firewall rule blocking certain ports.
purpose: a collection of utilities for controlling TCP / IP networking and traffic control in Linux.
/ # ip route show
default via 192.168.65.1 dev eth0 metric 204
172.17.0.0/16 dev docker0 proto kernel scope link src 172.17.0.1
172.19.0.0/16 dev br-fd694678f5c3 proto kernel scope link src 172.19.0.1 linkdown
172.20.0.0/16 dev docker_gwbridge proto kernel scope link src 172.20.0.1
172.21.0.0/16 dev br-0d73cc4ac114 proto kernel scope link src 172.21.0.1 linkdown
172.22.0.0/16 dev br-1eb1f1e84df8 proto kernel scope link src 172.22.0.1 linkdown
172.23.0.0/16 dev br-aafed4ec941f proto kernel scope link src 172.23.0.1 linkdown
192.168.65.0/29 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.65.2
/ # ip neigh show
192.168.65.1 dev eth0 lladdr f6:16:36:bc:f9:c6 STALE
172.17.0.7 dev docker0 lladdr 02:42:ac:11:00:07 STALE
172.17.0.6 dev docker0 lladdr 02:42:ac:11:00:06 STALE
172.17.0.5 dev docker0 lladdr 02:42:ac:11:00:05 STALE
More info on iproute2 here
Swaks (Swiss Army Knife for SMTP) is a featureful, flexible, scriptable, transaction-oriented SMTP test tool. It is free to use and licensed under the GNU GPLv2.
You can use it to test and troubleshoot email servers with a crystal-clear syntax:
swaks --to user@example.com \
--from fred@example.com --h-From: '"Fred Example" <fred@example.com>' \
--auth CRAM-MD5 --auth-user me@example.com \
--header-X-Test "test email" \
--data "Example body"More info, examples and lots of documentation on Swaks here
Feel free to provide feedback and contribute networking troubleshooting tools and use-cases by opening PRs.