Monocular depth estimation using Feature Pyramid Network implemented in PyTorch 1.1.0
- Change your working directory to
model-test. - Unzip the
nyuv2.rarto current directory. - Download the trained model from release. Rename to
fyn_model.ptand save to current directory. - Run the Jupyter Notebook in
test.ipynb.
Note: the model I provide was trained only on a dataset containing 1k images of scenes in basements. The purpose of this model was only to test whether the network architecture works for depth estimation. The test dataset provided in model-test folder also contains only images of basements.
- Python3
- PyTorch (The version in my code is PyTorch 1.1.0)
- CUDA (It's almost impossible to train on a CPU because the network is very deep)
As the dataset is very large, I didn't provide them directly in this repository. However, you can download the depth dataset and load them with your own code.
Modify the code of the data loading part in fyn_main.py first to ensure that you can load the dataset correctly. In my original code, I store the RGB and depth images in two folders and have a pickle file to relate them, both for train dataset and test dataset.
- NYU Depth V2 Dataset: This is the dataset I used in my code for the training of the network. If you want to train on this dataset, then you can refer to my script
process_dataset.pyto process the data you download. Again, after you have processed the data, you need to check the data loading part to see if you can load the dataset correctly. - Training on other datasets: You can also use the architecture to train on other datasets, like KITTI, InteriorNet, MannequinChallenge dataset, which all contains depth map data. You will need to do the data processing and data loading step on your own. Also, although the RGB image size and depth image size might be different from NyuV2, it can still be trained using the same network architecture. Just remember the neural network takes a
Width x Height x 3RGB image as input and ouputs a1/4 Width x 1/4 Height x 1grayscale image.
After you make sure the dataset can be loaded correctly, you can run fyn_main.py to start training.
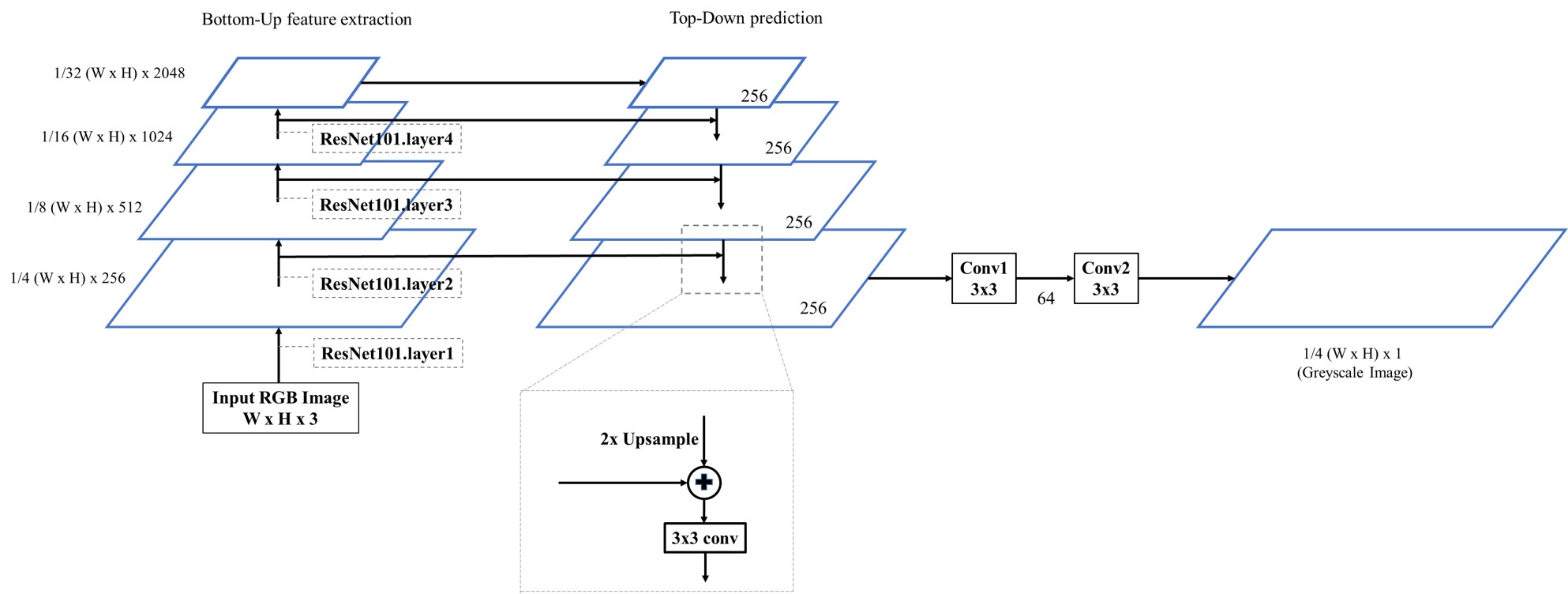
- Our architecture is basically a Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) with ResNet101 as backbone.
- FPN is an effective backbone for monocular depth estimation because of its ability to extract features and semantics at different scales. It can achieve its potential if guided by proper loss functions.
- Two consecutive 3x3 convolutions for feature processing.
- ReLU is used as activation function in the last two convolutional layers. No non-linearity in the top-down branch of FPN.
- Outputs prediction of size ¼.
- Learning rate decay is deployed during training.
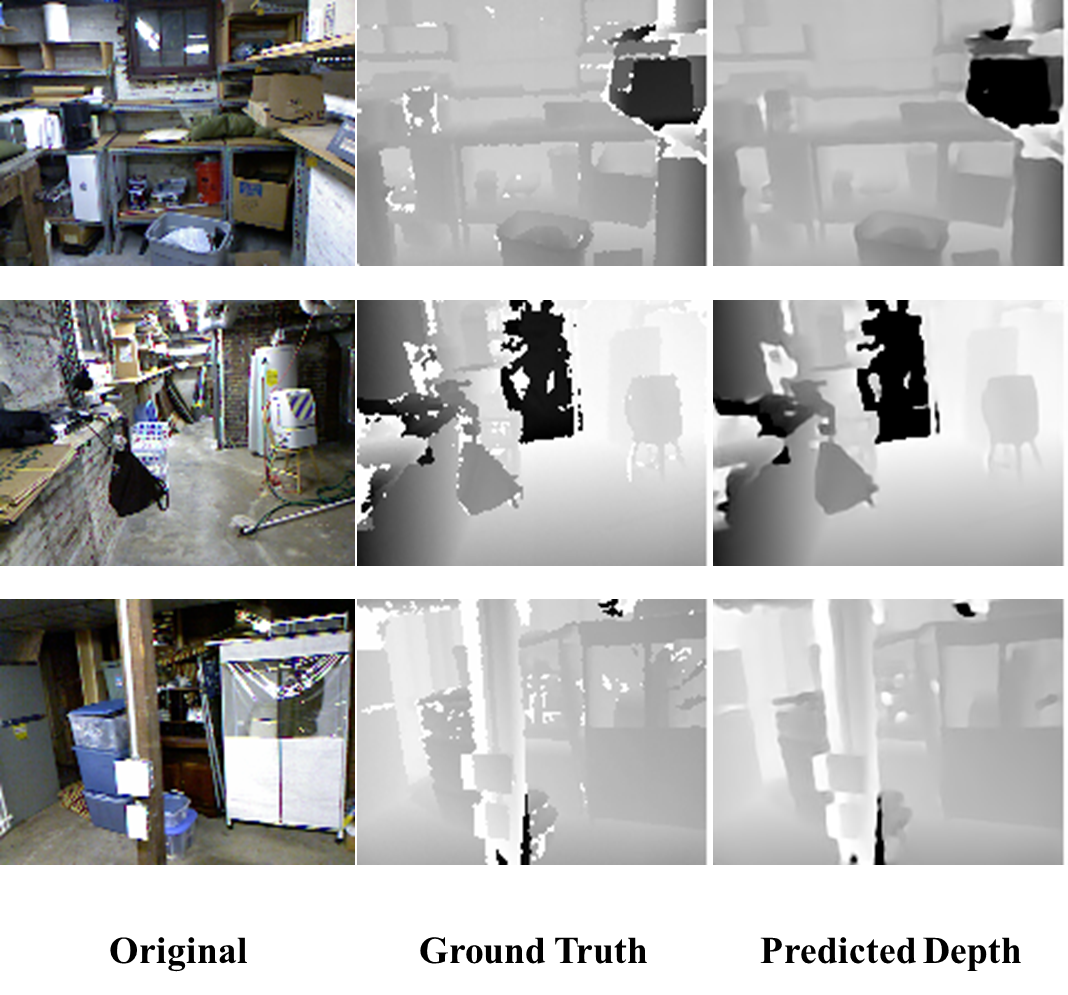
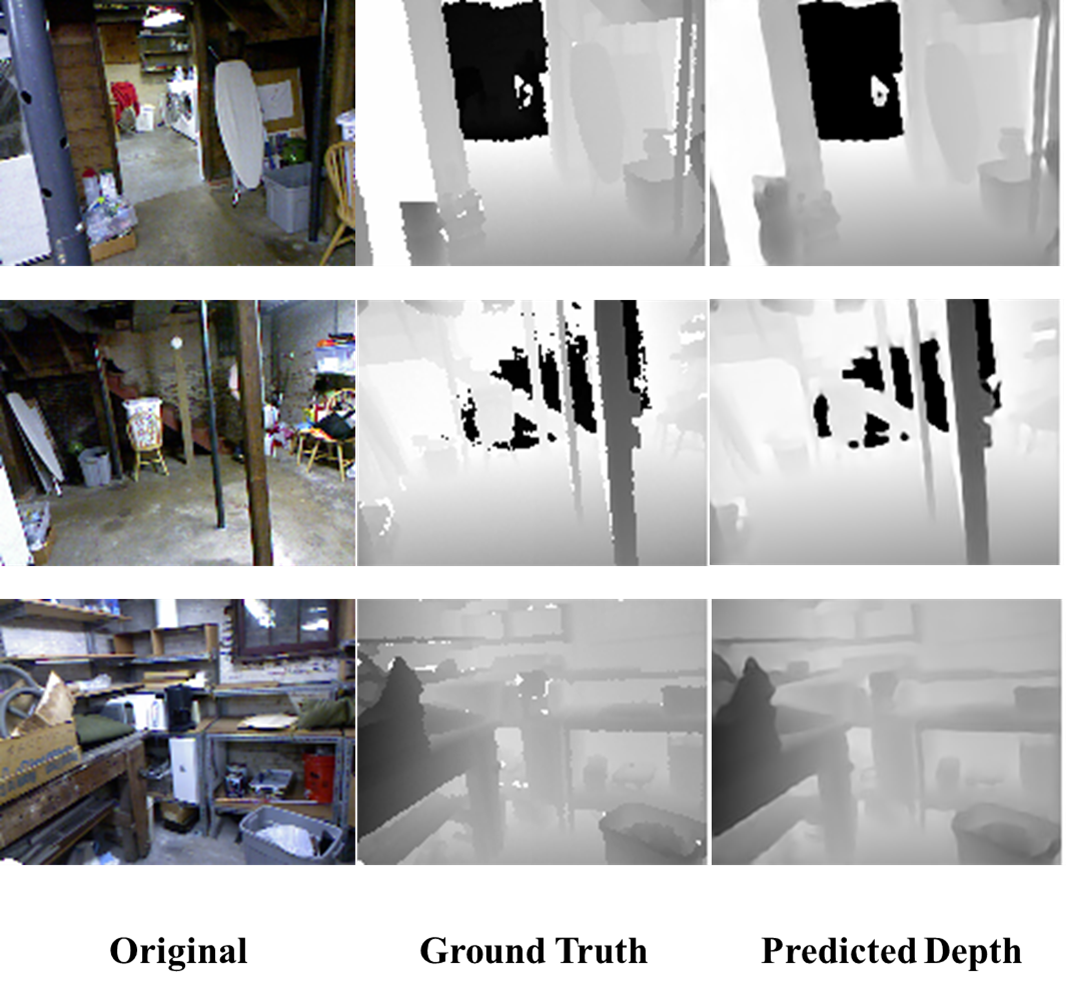
We use the NYU Depth V2 Dataset for training and testing. The RGB image and the depth image in the dataset are both of size 640x480. During training, the RGB image is loaded as 640x480 and the depth image is loaded and then resized to 160x120. The input of the network is a RGB image with size 640x480, and the output is a grayscale image of size 160x120, which is the depth map we need.
NyuV2 dataset contains images of indoor scenes, which is a limitation for depth estimation on other scenes. You can check other dataset to include more scenes in your model.
We employed a self-defined loss function in our model -- the Gradient Loss:
The gradient of depth maps is obtained by a Sobel filter; the gradient loss is the L1 norm of the difference.
Here are some results on test dataset that contains scenes of basements: