AWS Controllers for Kubernetes Hands-on
Abstract
- In the world of Infrastructure as code (IaC) there are many tools support us to create AWS resources quickly such as CDK, Pulumi, Terraform. Today I introduce AWS Controllers for Kubernetes (ACK)
- AWS Controllers for Kubernetes (ACK) lets you define and use AWS service resources directly from Kubernetes. With ACK, you can take advantage of AWS-managed services for your Kubernetes applications without needing to define resources outside of the cluster or run services that provide supporting capabilities like databases or message queues within the cluster.
- This post provides step-by-step to create AWS RDS postgres in private VPC using ACK and then access the database to prove it works.
Table Of Contents
- Introduction of ACK
- Install the ACK service controller for RDS
- Create ACK ServiceAccount base on IRSA
- Create RDS secret keys
- Create subnet group
- Create security group to allow traffic from EKS pods to the RDS
- Create DBInstance
- Access RDS through EKS pod
- Clean-up workspace
- Conclusion
🚀 Introduction of ACK
-
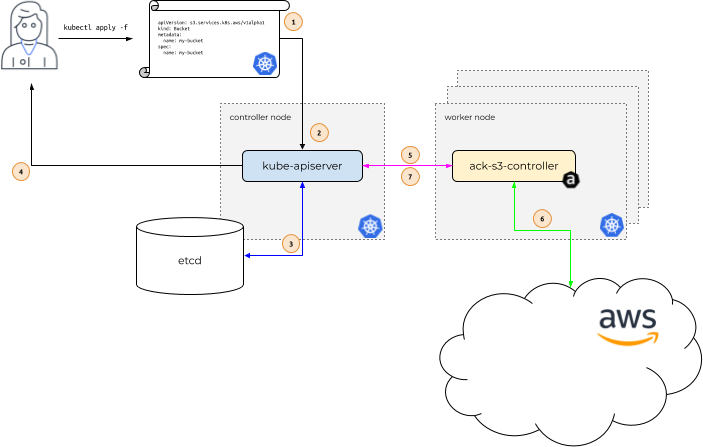
-
When to use ACK? Read here
🚀 Install the ACK service controller for RDS
-
Pre-requisite:
- EKS cluster
- OIDC for IRSA
- IAM for service account (IRSA) - Checkout Using IAM Service Account Instead Of Instance Profile For EKS Pods for how-to.
-
Install ACK for RDS
⚡ $ export HELM_EXPERIMENTAL_OCI=1 ⚡ $ helm pull oci://public.ecr.aws/aws-controllers-k8s/rds-chart --version=v0.0.17 ⚡ $ tar xf rds-chart-v0.0.17.tgz ⚡ $ helm install rds-chart --generate-name --set=aws.region=ap-northeast-2
🚀 Create ACK ServiceAccount base on IRSA
-
This step requires IAM role for service account here is ACK RDS. Note that the role needs permission to manage RDS resource. We can limit permission by restrict resource. And to protect the resource from incident of deleteing the
DBInstance(describe later), we can setDenyaction ofrds:DeleteDBInstance{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Condition": { "StringEquals": { "aws:RequestedRegion": "ap-northeast-2" } }, "Action": "rds:*", "Resource": "arn:aws:rds:ap-northeast-2:123456789012:*", "Effect": "Allow", "Sid": "CreateRds" }, { "Action": "rds:DeleteDBInstance", "Resource": "*", "Effect": "Deny", "Sid": "DenyDeleteRds" } ] } -
Generate SA yaml and update IRSA to apply, replace the IAM ARN role with yours.
ack-sa.yaml
apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/component: controller app.kubernetes.io/name: ack-rds-controller name: ack-rds-controller annotations: eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/ack-rds-controller-d1 -
Apply the manifest
kf apply -f ack-sa.yaml
🚀 Create RDS secret keys
- Best practice is to protect the RDS user password
export RDS_DB_USERNAME=rds_username export RDS_DB_PASSWORD=rds_password kubectl create secret generic rds-postgresql-user-creds \ --from-literal=username="${RDS_DB_USERNAME}" \ --from-literal=password="${RDS_DB_PASSWORD}"
🚀 Create subnet group
-
The subnet group contains all subnet of EKS private VPC
-
Get subnets from EKS VPC, replace the VPC ID and the region with yours
EKS_SUBNET_IDS=$(aws ec2 describe-subnets --filters "Name=vpc-id,Values=vpc-0eb6477bf2c8430cd" --query 'Subnets[*].SubnetId' --output text --region ap-northeast-2) -
Generate yaml file inherit ${EKS_SUBNET_IDS} above
cat <<-EOF > ack/ack-rds-subnet-groups.yaml apiVersion: rds.services.k8s.aws/v1alpha1 kind: DBSubnetGroup metadata: name: rds-postgresql-subnet-group spec: name: rds-postgresql-subnet-group description: RDS for app in EKS subnetIDs: $(printf " - %s\n" ${EKS_SUBNET_IDS}) tags: - key: stage value: development - key: owner value: dev EOF -
Apply the manifest
kf apply -f ack/ack-rds-subnet-groups.yaml
🚀 Create security group to allow traffic from EKS pods to the RDS
-
First we create a SG in the EKS VPC to attach to the RDS, replace the VPC ID with your EKS VPC ID and appropriate region
RDS_SECURITY_GROUP_ID=$(aws ec2 create-security-group \ --group-name rds-postgres-sg \ --description "SG to allow traffic from EKS pod to RDS" \ --vpc-id vpc-0eb6477bf2c8430cd \ --output text --region ap-northeast-2 ) -
Then we need to allow traffic from EKS worker nodes. There are two ways
-
In RDS SG, allow traffic from CIDR range of the EKS VPC
-
Get CIDR range of EKS VCP using command line
EKS_CIDR_RANGE=$(aws ec2 describe-vpcs --vpc-ids vpc-0eb6477bf2c8430cd --query 'Vpcs[].CidrBlock' --output text --region ap-northeast-2) -
Create ingress in the SG to allow traffic from the above CIDR
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress \ --group-id "${RDS_SECURITY_GROUP_ID}" \ --protocol tcp \ --port 5432 \ --cidr "${EKS_CIDR_RANGE}" \ --region ap-northeast-2
-
-
In RDS SG, allow traffic from the security group which is attached to all EKS nodes (in general, traffic is allowed from the network interfaces that are associated with the source security group for the specified protocol and port, read more from Understand Pods communication at
Security groups for your VPCspecifying a security group as the source for a rule)
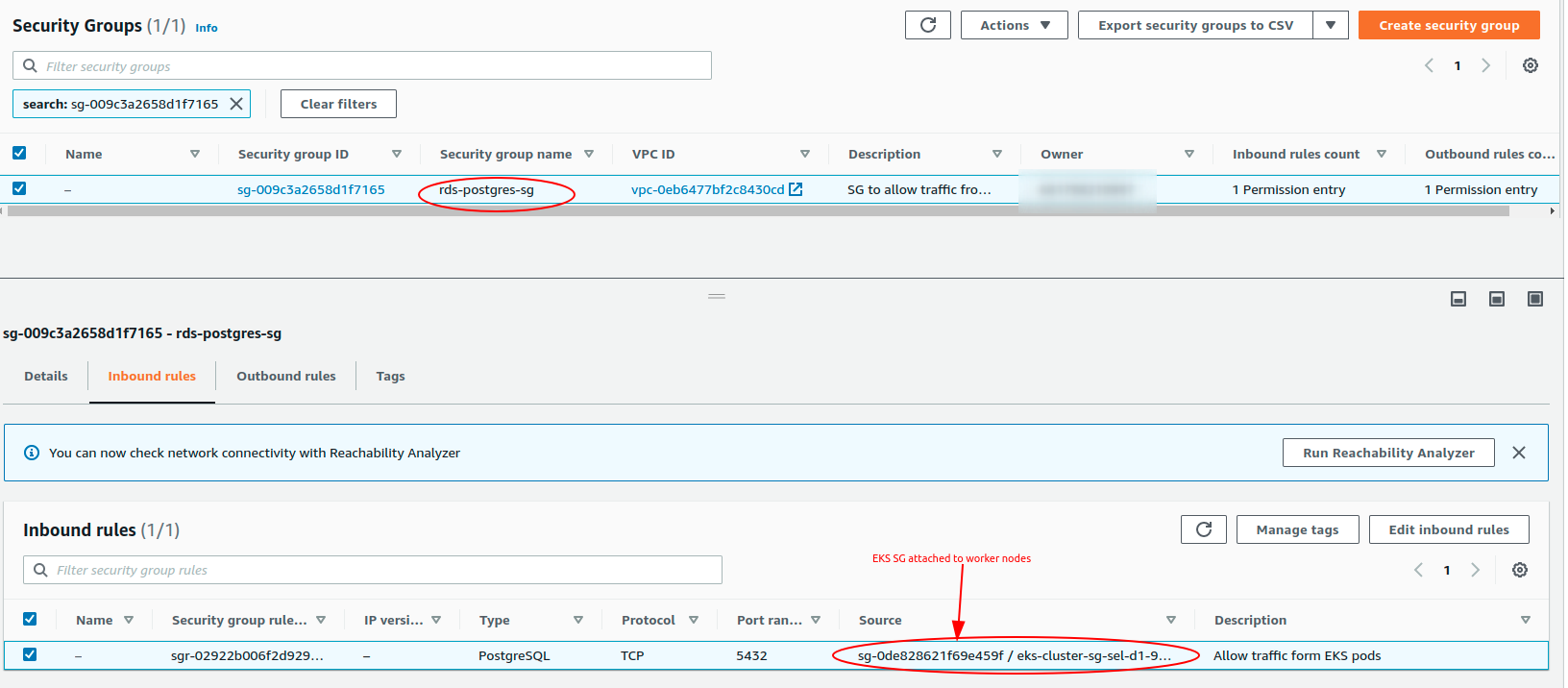
-
🚀 Create DBInstance
-
Create DBInstance manifest, replace security group ID in
vpcSecurityGroupIDswith the one you created in previous stepRDS_SECURITY_GROUP_ID. Here we select RDS instance typedb.t3.microas it is free tier, master user and password maps with the RDS secret keys created in previous step,engine: postgresversion 10ack/ack-rds-postgresql.yaml
apiVersion: rds.services.k8s.aws/v1alpha1 kind: DBInstance metadata: name: "rds-postgresql-dev" spec: allocatedStorage: 20 autoMinorVersionUpgrade: true backupRetentionPeriod: 7 dbInstanceClass: db.t3.micro dbInstanceIdentifier: "rds-postgresql-dev" dbSubnetGroupName: rds-postgresql-subnet-group engine: postgres engineVersion: "10" masterUsername: "rds_user" masterUserPassword: namespace: default name: rds-postgresql-user-creds key: password multiAZ: true publiclyAccessible: false storageEncrypted: true storageType: gp2 vpcSecurityGroupIDs: - sg-009c3a2658d1f7165 tags: - key: stage value: development - key: owner value: dev -
Apply the yaml
kf apply -f ack/ack-rds-postgresql.yaml -
Check created
DBInstance⚡ $ kf get DBInstance NAME AGE rds-postgresql-dev 1h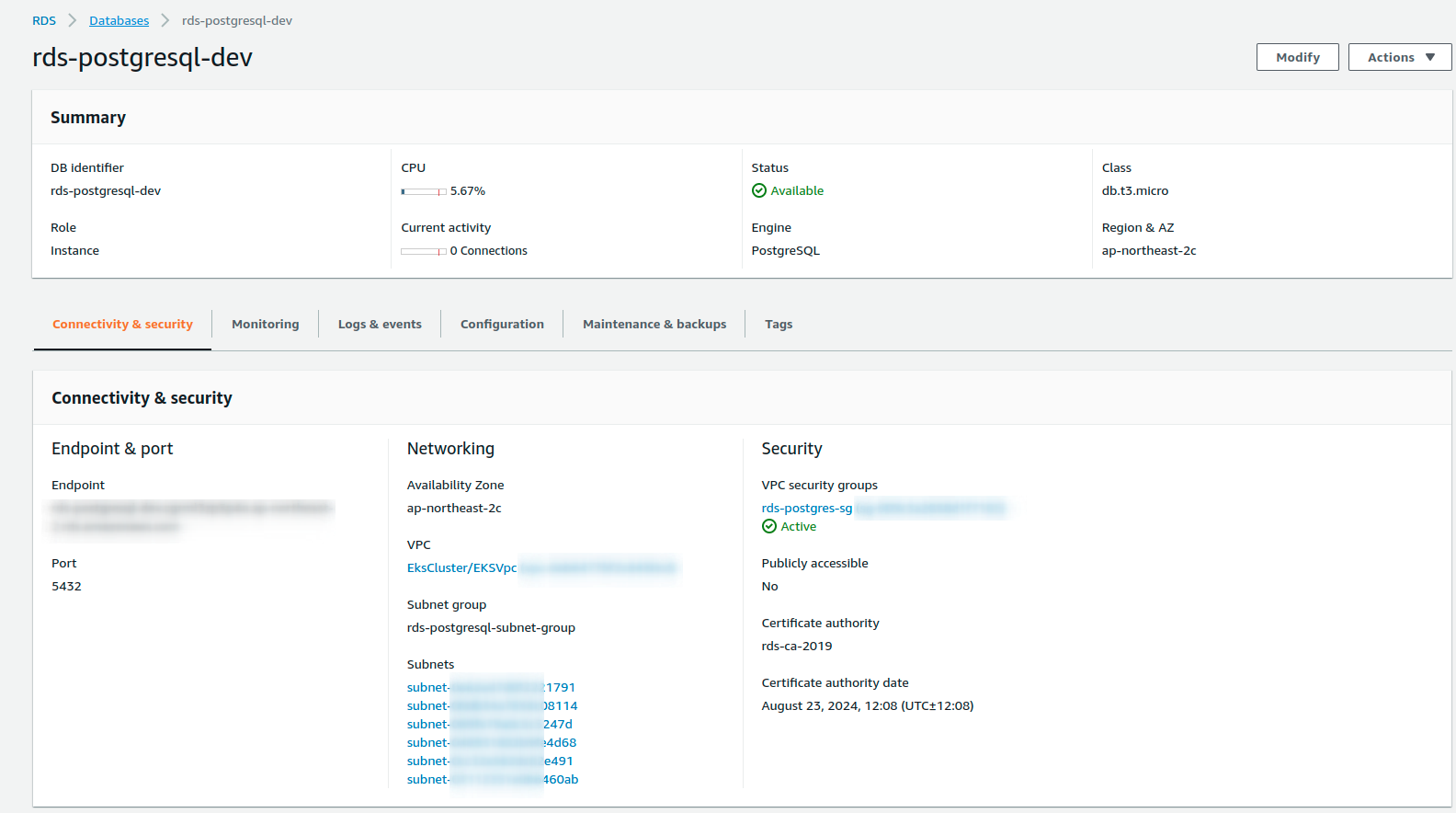
🚀 Access RDS through EKS pod
-
This step proves RDS works well and EKS pods in private VPC can read/write to the RDS use master user
-
Build
postgresql-clientdocker image and push it to ECR or any container image repositoryFROM alpine:3 RUN apk add --no-cache postgresql-client CMD while true; do sleep 5; echo psql-client; done -
Create postgresql client deployment
psql-client.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: psql-client name: psql-client spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: psql-client-deployment template: metadata: labels: app: psql-client-deployment spec: containers: - image: 123456789012.dkr.ecr.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/psql/client:latest name: psql-client -
Apply the deployment and then get pod
~ $ kf apply -f ack/psql-client.yaml deployment.apps/psql-client created ~ $ kf get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE psql-client-9d45f759-8swtr 1/1 Running 0 44m -
Go into the pod to access RDS, get RDS private endpoint in the console or using AWS CLI or using
kubectl~ $ aws rds describe-db-instances --db-instance-identifier rds-postgresql-dev --region ap-northeast-2 --query 'DBInstances[0].Endpoint.Address' "rds-postgresql-dev.xxxxxxxxxxxx.ap-northeast-2.rds.amazonaws.com" ~ $ kubectl get dbinstance rds-postgresql-dev -o jsonpath='{.status.endpoint.address}' "rds-postgresql-dev.xxxxxxxxxxxx.ap-northeast-2.rds.amazonaws.com" ~ $ kf exec -it psql-client-9d45f759-8swtr -- sh / # psql -h rds-postgresql-dev.xxxxxxxxxxxx.ap-northeast-2.rds.amazonaws.com -U rds_user -d postgres postgres=> \du List of roles Role name | Attributes | Member of --------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------- rds_user | Create role, Create DB +| {rds_superuser} | Password valid until infinity | rds_ad | Cannot login | {} rds_iam | Cannot login | {} rds_password | Cannot login | {} rds_replication | Cannot login | {} rds_superuser | Cannot login | {pg_monitor,pg_signal_backend,rds_replication,rds_password} rdsadmin | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS+| {} | Password valid until infinity | rdsrepladmin | No inheritance, Cannot login, Replication | {} postgres=> CREATE DATABASE "rds-test"; CREATE DATABASE postgres=> \l rds-test List of databases Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges ----------+--------------------+----------+-------------+-------------+------------------- rds-test | rds_user | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | (1 row)
🚀 Clean-up workspace
-
Delete
DBInstance, note that if you denyrds:DeleteDBInstancein ACK role to protect your RDS then this step requires more action such as remove the deny or delete RDS manually then force deleteDBInstance. Here assume ACK RDS role has permission of deleting the RDS⚡ $ kf delete DBInstance rds-postgresql-dev dbinstance.rds.services.k8s.aws "rds-postgresql-dev" deleted -
Delete
psql-clientdeployment⚡ $ kf delete -f ack/psql-client.yaml deployment.apps "psql-client" deleted -
Delete RDS secret key
⚡ $ kf delete secret rds-postgresql-user-creds secret "rds-postgresql-user-creds" deleted -
Delete RDS security group
⚡ $ aws ec2 delete-security-group --group-id sg-009c3a2658d1f7165 --region ap-northeast-2 -
Uninstall ACK RDS
⚡ $ helm list NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION rds-chart-1648053478 default 1 2022-03-23 23:38:11.397906502 +0700 +07 deployed rds-chart-v0.0.17 v0.0.17 ⚡ $ helm uninstall rds-chart-1648053478 release "rds-chart-1648053478" uninstalled -
Finally delete the IRSA for ACK RDS
⚡ $ cdk destroy AckControllerSA --profile vc-mfa Are you sure you want to delete: AckControllerSA (y/n)? y AckControllerSA: destroying... ✅ AckControllerSA: destroyed
🚀 Conclusion
- Using ACK to create AWS resources is a big plus for those ones love managing AWS resources through k8s manifests within the EKS cluster
- We can combine cdk8s to crea
References:
