Every logic to initiate EC2 instance is implemented using boto3 API. This means that you will need Python virtual environment to follow this demo.
python3 --version # Python 3.9.6
python3 -m venv venv
pip install -r requirements.txt
source venv/bin/activate
Then, execute following command to create every resource to initiate EC2 instance. Note that your own administrator profile (or IAM user profile with appropriate roles) has to be prepared prior to this demo(ex. admin.kim). For more details on the codes executed on this command, refer to this link.
python main.py create admin.kim
To fetch launch command of public URL of instance that has been just created, execute following command with your own profile name(like admin.kim). This works because initial state of the instance will be 'running'.
python main.py instance describe admin.kim
To [stop the instance to prevent unnecessary cost charge|restart the stopped instance], type in following command with your own profile name.
python main.py instance [stop|start] admin.kim
To delete every resource created during this demo, execute following command. As always, admin.kim stands for your own profile name.
python main.py delete admin.kim
After instance being launched, whole tutorial starts from making sure that JDK is installed in the instance.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y openjdk-8-jdk
java -version # check if JDK is installed successfully
This demo will use 7.2.0 version of ELK services. Thus, downloading version specific deb binary file would be simplest installation solution. That being said, type in following commands:
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.2.0-amd64.deb
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-7.2.0.deb
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-7.2.0-amd64.deb
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-7.2.0-amd64.deb
Next, install each service from installed deb packages
sudo dpkg -i elasticsearch-7.2.0-amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i logstash-7.2.0.deb
sudo dpkg -i kibana-7.2.0-amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i filebeat-7.2.0-amd64.deb
To check if Elasticsearch is properly installed, start the service and check out its status using following commands:
sudo service elasticsearch start
sudo service elasticsearch status
You should see something like this:
elasticsearch.service - Elasticsearch
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-10-19 14:08:47 UTC; 1s ago
Docs: http://www.elastic.co
Main PID: 6023 (java)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 4686)
Memory: 921.7M
...
Or, send GET request to 127.0.0.1:9200 to recive response from launched Elasticsearch.
curl -XGET 127.0.0.1:9200
If you received 'Connection refused' response, wait for a few seconds more. Normal response would look like this:
{
"name" : "ip-172-40-11-66",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "ebXhz34wS0KG-aLXgrntOw",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.2.0",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "deb",
"build_hash" : "508c38a",
"build_date" : "2019-06-20T15:54:18.811730Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.0.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Before starting Kibana, you should get Elasticsearch running on your instance. After that, official document says that some modification on configuration file is needed since you will be wanting to remotely connect to Kibana from your local machine.
- Enter
sudo vi /etc/kibana/kibana.ymlcommand - Enter
/server.host:to move cursor to the line that defines connectable remote host. Uncomment this line. - Change
"localhost"to"0.0.0.0"to let Kibana allow connections from any remote users
According to other page of the official guide, launch command differs according to the Linux initialization program. To check this out, type in following command:
ps -p 1 # print process with PID=1
If it says, for example, that corresponding program is systemd, launch command becomes:
sudo systemctl start kibana.service
Wait for a few seconds and send request from a browser in your local machine like this. If 'Kibana server is not ready yet' message comes up, wait extra seconds. After that, you will see beautiful, neat UI of Kibana.
https://<your-own-public-IPv4-address-of-the-instance>:5601
# ex. https://ec2-3-36-85-138.ap-northeast-2.compute.amazonaws.com:5601
Few additional notes:
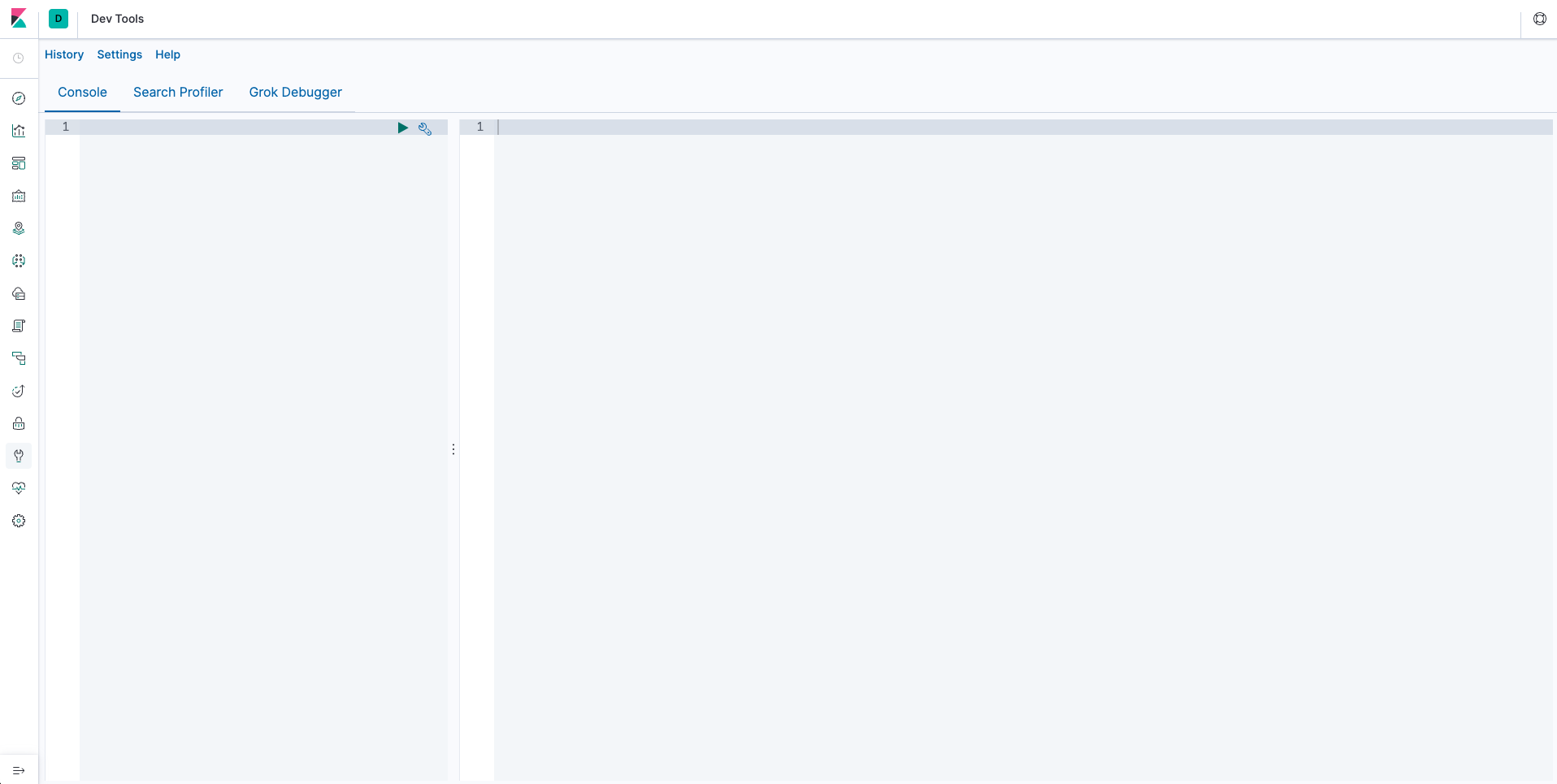
- Note the location of icon for
Dev Toolspage, since most of the works will be done in that page in this demo. - Like Kibana, Elasticsearch is only binded to localhost by default. You can change this behavior by following guide in this page, but this would not be necessary in this demo since most CRUD operation on Elasticsearch will be done through
Dev Toolspage.
Since type is being removed from from Elasticsearch 7 as explained in this page, analogy between RDBMS and Elasticsearch became simpler by index per document type principle.
| RDBMS | Elasticsearch |
|---|---|
| Table | Index |
| Row | Document |
| Column | Feature |
| Schema | Mapping |
Get into Dev Tools page to see this blank console where you will be typing commands presented in this demo.
GET _cat/health?v
PUT users
If users index is created successfully, result of following command
GET _cat/indices?v
should look like this:
health status index uuid
yellow open users c1R3jf0YQSuKGZcNYkbvAg
green open .kibana_task_manager sQlT2F4jRfi5z3Ai94TS0Q
green open .kibana_1 LO9tWZ2ZQtexUcPe0YRFhw
This command will create document whose _id is 1.
POST users/_doc/1
{
"name": "Admin Kim",
"hobby": "Elasticsearch",
"age": 26
}
This command will fetch information of document whose _id is 1.
GET users/_doc/1
If document was created successfully, result should look like this:
{
"_index" : "users",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "Admin Kim",
"hobby" : "Elasticsearch",
"age" : 26
}
}
This command updates existing value of a document whose _id is 1
POST users/_update/1/
{
"doc": {
"name": "Admin Park"
}
}
After executing this command, result of GET request on the same document should look like this. Note that value of _version increased from 1 to 2.
{
"_index" : "users",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 2,
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "Admin Park",
"hobby" : "Elasticsearch",
"age" : 26
}
}
You would like to define how you would like to update as a function. In this case, you can use Javascript syntax within script source as below.
POST users/_update/1/
{
"script": {
"source": "if(ctx._source.age < 100) {ctx._source.age++}"
}
}
Result of same GET request on this user should look like this. As expected, since age of the user did not exceed 100, its age got incremented from 26 to 27.
{
"_index" : "users",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 3,
"_seq_no" : 2,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "Admin Park",
"hobby" : "Elasticsearch",
"age" : 27
}
}
DELETE users/_doc/1
If document is deleted, value of found field in result of GET request should be false.
{
"_index" : "users",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"found" : false
}
Bulk API lets user to execute multiple create(or indexing), update, delete operations can be done in single API call. Command to create multiple documents should look like this. Note that bulk request should always end with blank line change character.
POST users/_bulk
{"index": {"_id": "1"}}
{"name" : "Admin Kim", "hobby" : "Elasticsearch", "age" : 26}
{"index": {"_id": "2"}}
{"name" : "Admin Park", "hobby" : "Kibana", "age" : 28}
{"index": {"_id": "3"}}
{"name" : "Admin Lee", "hobby" : "Logstash", "age" : 24}
{"index": {"_id": "4"}}
{"name" : "Admin Song", "hobby" : "Filebeat", "age" : 30}
Different operations can be mixed into single bulk API request as below.
POST users/_bulk
{"update": {"_id": "1"}}
{"doc": {"age": 27}}
{"delete": {"_id": "3"}}
{"delete": {"_id": "2"}}
It is time to insert real data and make some queries on it. This repository provides code to download iris dataset from source in preprocess.py.
Since Python3 and git are pre-installed in Ubuntu 20.04, just clone the current repository into the instance to have codes to download the dataset.
sudo apt install -y python3-pip
sudo apt install -y python3-venv
git clone https://github.com/sunsikim/aws-elk-demo.git
cd aws-elk-demo
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
Execute logics implemented in preprocess.py by using following command
python main.py preprocess
Then, create iris index and insert preprocessed data using POST request with bulk API.
curl -XPUT 127.0.0.1:9200/iris?pretty
curl -XPOST 127.0.0.1:9200/iris/_bulk?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-binary @data/iris_data.json
curl -XGET 127.0.0.1:9200/iris/_doc/0?pretty # check if data is inserted properly