This repository contains pytorch implementation for the models from the paper Utterance-level Dialogue Understanding: An Empirical Study
The models are all trained in an end-to-end fashion. The utterances, labels, loss masks, and speaker specific information are thus read directly from tab separated text files. All data files follow the common format:
Utterances: Each line contains tab separated dialogue id and the utterances of the dialogue.
train_1 How do you like the pizza here? Perfect. It really hits the spot.
train_2 Do you have any trains into Cambridge today? There are many trains, when would you like to depart? I would like to leave from Kings Lynn after 9:30.
Lables: Each line contains tab separated dialogue id and the encoded emotion/intent/act/strategy labels of the dialogue.
train_1 0 1
train_2 2 0 2
Loss masks: Each line contains tab separated dialogue id and the loss mask information of the utterances of the dialogue. For contextual models, the whole sequence of utterance is passed as input, but utterances having loss mask of 0 are not considered for the calculation of loss and the calcualtion of classification metrics. This is required for tasks where we want to use the full contextual information as input, but don't want to classify a subset of utterances in the output. For example, in MultiWOZ intent classification, we pass the full dialogue sequence as input but don't classify the utterances coming from the system side.
train_1 1 1
train_2 1 0 1
Speakers: Each line contains tab separated dialogue id and the speakers of the dialogue.
train_1 0 1
train_2 0 1 0
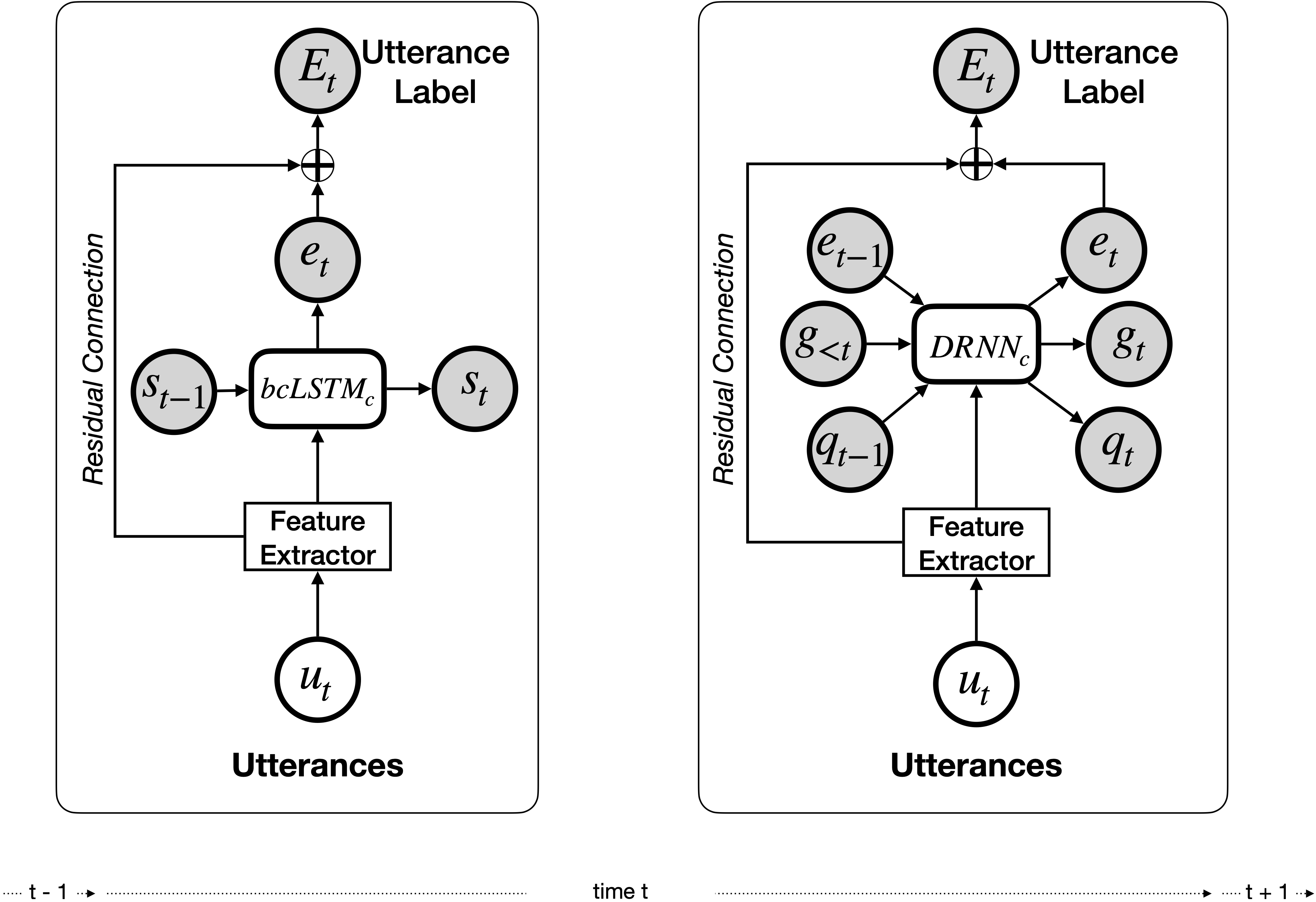
We provide implementations for end-to-end without context classifier, bcLSTM and DialogueRNN models. For bcLSTM and DialogueRNN we also provide training argument which lets you specify whether to use residual connections or not. Navigate to roberta-end-to-end or glove-end-to-end directories to use RoBERTa or GloVe based feature extractors for the models.
To train and evaluate the without context classifier model and the bcLSTM/DialogueRNN model with full context and residual connections:
python train.py --dataset [iemocap|dailydialog|multiwoz|persuasion] --classify [emotion|act|intent|er|ee] --cls-model [logreg|lstm|dialogrnn] --residual
The --cls-model logreg corresponds to the without context classifier.
To train and and evaluate bcLSTM model in w/o inter setting i.e. only with context from the same speaker:
python train_intra_speaker.py --dataset [iemocap|dailydialog|multiwoz|persuasion] --classify [emotion|act|intent|er|ee] --residual
To train and and evaluate bcLSTM model in w/o intra setting i.e. only with context from the other speaker:
python train_inter_speaker.py --dataset [iemocap|dailydialog|multiwoz|persuasion] --classify [emotion|act|intent|er|ee] --residual
If you are running GloVe-based end-to-end models, please run the scripts multiple times and average the test scores of those runs.
Utterance-level Dialogue Understanding: An Empirical Study. Deepanway Ghosal, Navonil Majumder, Rada Mihalcea, Soujanya Poria. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.13902 (2020).