leetcode236:二叉树的最近公共祖先
sisterAn opened this issue · comments
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
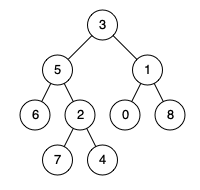
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
示例 1:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出: 3
解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。示例 2:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出: 5
解释: 节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉树中。
附赠leetcode地址:leetcode
解答:递归实现
解题思路:
如果树为空树或 p 、 q 中任一节点为根节点,那么 p 、 q 的最近公共节点为根节点
如果不是,即二叉树不为空树,且 p 、 q 为非根节点,则递归遍历左右子树,获取左右子树的最近公共祖先,
- 如果
p、q节点在左右子树的最近公共祖先都存在,说明p、q节点分布在左右子树的根节点上,此时二叉树的最近公共祖先为root - 若
p、q节点在左子树最近公共祖先为空,那p、q节点位于左子树上,最终二叉树的最近公共祖先为右子树上p、q节点的最近公共祖先 - 若
p、q节点在右子树最近公共祖先为空,同左子树p、q节点的最近公共祖先为空一样的判定逻辑 - 如果
p、q节点在左右子树的最近公共祖先都为空,则返回null
代码实现:
const lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root
const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if(left === null) return right
if(right === null) return left
return root
};复杂度分析:
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
const lowestCommonAncestor=function(root,p,q){
if(root==null || root==p || root==q){
return root
}
const left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
const right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left==null) return right;
if(right==null) return left;
return root;
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q){
return root;
}
let left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
let right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left != null && right != null){
return root;
}
return left != null ? left : right;
};- 从根节点递归往下找,找到一个节点,这个节点满足p和q分别在这个节点的左右子树上就是满足条件的
- 但是如果找到一个节点发现p和q同时在左子树或者右子树上,说明p和q一个是另一个的子节点,也就是说最近公共祖先是p和q自身中的一个,那么只要继续往下找,先找到谁就返回谁
var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q) {
function isInTree(root, node) {
if (root === null) return false;
if (root === node) return true;
return isInTree(root.left, node) || isInTree(root.right, node);
}
let current = root;
while (true) {
if (current === p || current === q) return current;
if (isInTree(current.left, p)) {
if (isInTree(current.right, q)) {
return current;
} else {
current = current.left;
}
} else {
if (isInTree(current.left, q)) {
return current;
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
}
};解答:递归实现
解题思路:
如果树为空树或
p、q中任一节点为根节点,那么p、q的最近公共节点为根节点如果不是,即二叉树不为空树,且
p、q为非根节点,则递归遍历左右子树,获取左右子树的最近公共祖先,
- 如果
p、q节点在左右子树的最近公共祖先都存在,说明p、q节点分布在左右子树的根节点上,此时二叉树的最近公共祖先为root- 若
p、q节点在左子树最近公共祖先为空,那p、q节点位于左子树上,最终二叉树的最近公共祖先为右子树上p、q节点的最近公共祖先- 若
p、q节点在右子树最近公共祖先为空,同左子树p、q节点的最近公共祖先为空一样的判定逻辑- 如果
p、q节点在左右子树的最近公共祖先都为空,则返回null代码实现:
const lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) { if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q) const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q) if(left === null) return right if(right === null) return left return root };复杂度分析:
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
这思路是怎么想到的,有什么可迁移的方法套路嘛