leetcode206:反转链表
sisterAn opened this issue · comments
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL进阶:
你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
附leetcode地址:leetcode
方法一:遍历
- 先遍历到尾部
- 在遍历过程中让节点新增属性 pre 使单向链表变成双向链表
- 遍历到尾部时开始指向反转并删除节点的 pre 属性
边界条件:
- 在头部时,节点的 pre 属性为 null
- 到尾部时,节点的 next 属性为 null
function reverseList(head) {
// 链表只有一个元素时
if( head.next === null ) return head;
// 否则
let current = head.next,
preNode = head;
// 链表反向后原来的头就变成尾了
preNode.pre = null; // 相当于 head.pre = null;
while( current.next ){
current.pre = preNode; // 建立反向联系
// 指针后移
preNode = current;
current = current.next;
}
current.pre = preNode; // 建立最后一个元素和倒数第二个元素的联系
// 至此,一个双向链表已经完成了
// 然后就要开始往前遍历了
while( current.pre ){
// 指向反向
current.next = current.pre;
// 使"先指针"和"后指针"都指向当前对象
preNode = current;
// "先指针"前移
current = current.pre;
// 将初始从前向后遍历时新增的属性删掉
delete preNode.pre;
}
// 修正原链表第一个元素的指向
current.next = current.pre;
delete current.pre;
}方法二:递归
- 每次只对一个元素进行操作,如果当前元素的后一项不为空,则递归调用本函数,传入的值为当前元素的后一项
- 在每次递归形成的作用域中使后面的元素指向当前元素,当前元素指向空
边界条件:
- 当传入参数的属性 next 为 null时,说明这个元素是链表的最后一个元素
function reverseList(node) { // 传入链表的头结点
if( node.next === null ) {
/*
* 能走到这里的有只有两种情况:
* 1.链表只有一个元素
* 2.链表不止一个元素同时已经遍历到链表的最后一个元素了
* */
return node;
} else{
const nextNode = reverseList(node.next);
nextNode.next = node;
node.next = null; // 如果不是原链表的第一个元素,则会在上一次递归的作用域中被修改
return node;
}
}测试代码:
function CreateNode(val){
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
function CreateList(...nodes){
this.head = nodes[0];
this.length = nodes.length;
for( var i = 0; i < nodes.length - 1; i++ ){
if( nodes[i+1] ){
nodes[i].next = nodes[i+1];
}
}
}
function reverseList(head){
// 选择上面所示的任意一个翻转链表的函数
}
const node1 = new CreateNode(1);
const node2 = new CreateNode(2);
const node3 = new CreateNode(3);
const node4 = new CreateNode(4);
const node5 = new CreateNode(5);
const list = new CreateList(node1, node2, node3, node4, node5);
console.log(node1);
reverseList(node1);
console.log(node5);解法一:迭代法
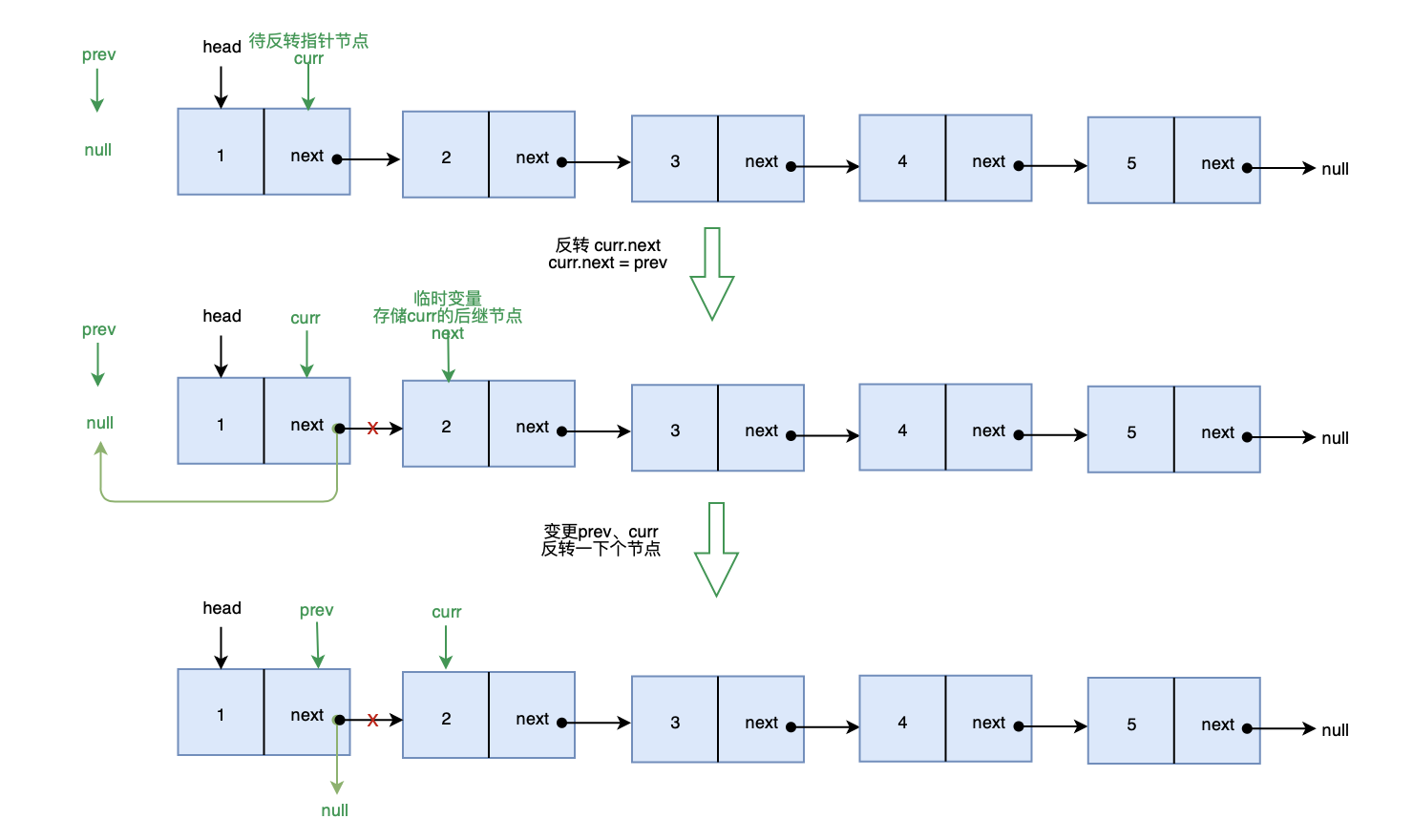
解题思路: 将单链表中的每个节点的后继指针指向它的前驱节点即可
画图实现: 画图帮助理解一下
确定边界条件: 当链表为 null 或链表中仅有一个节点时,不需要反转
代码实现:
var reverseList = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head
var prev = null, curr = head
while(curr) {
// 用于临时存储 curr 后继节点
var next = curr.next
// 反转 curr 的后继指针
curr.next = prev
// 变更prev、curr
// 待反转节点指向下一个节点
prev = curr
curr = next
}
head = prev
return head
};时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
解法二:尾递归法
解题思路: 从头节点开始,递归反转它的每一个节点,直到 null ,思路和解法一类似
代码实现:
var reverseList = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head
head = reverse(null, head)
return head
};
var reverse = function(prev, curr) {
if(!curr) return prev
var next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
return reverse(curr, next)
};时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
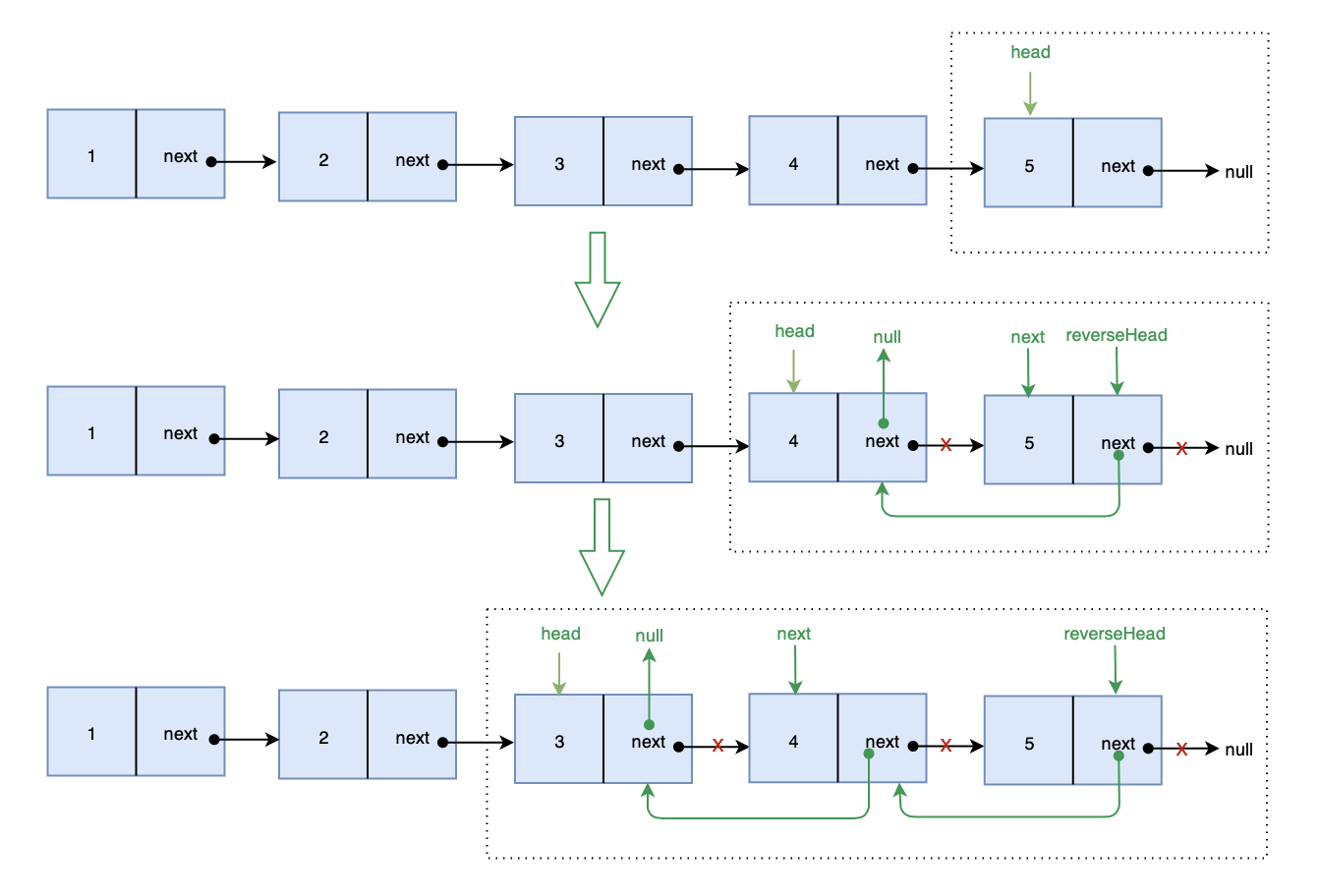
解法三:递归法
解题思路: 不断递归反转当前节点 head 的后继节点 next
画图实现: 画图帮助理解一下
代码实现:
var reverseList = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head
var next = head.next
// 递归反转
var reverseHead = reverseList(next)
// 变更指针
next.next = head
head.next = null
return reverseHead
};时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
思路
反转链表,即是如下操作:

准备三个指针:pLeft、pMid和pRight,分别先指向链表的前三个节点,如下

接着,我们只需让pLeft的next指向null,pMid的next指向pLeft,pRight的next指向pMid,并且依次将三个指针同时向前移动,边移动边调整三个指针的next指向,直到pRight为null时,此时pMid为链表的最后一个结点,然后让pMid的next指向pLeft,如下:

而pMid也就是反转后链表的头结点,最终将pMid返回即可。
代码
/*function ListNode(x){
this.val = x;
this.next = null;
}*/
function ReverseList(pHead) {
if (!pHead) {
return null
}
// 如果传入的链表只有一个元素,那就将原链表返回
if (!pHead.next) {
return pHead
}
// 准备三个指针
let pLeft = pHead;
let pMid = pHead.next;
let pRight = pMid.next;
pLeft.next = null
while (pRight) {
pMid.next = pLeft;
// 依次向前移动三个指针
pLeft = pMid
pMid = pRight
pRight = pRight.next
}
pMid.next = pLeft
return pMid
}1 递归甩锅
function reverse_digui(head) {
if(!head) return null
if(!head.next) return head
const new_head = reverse_digui(head.next) // 先让 head.next 进行反转
head.next.next = head // 反转完成后, head.next 是新链表的尾节点, 再连接上 head
head.next = null // head 成为新链表的尾节点
return new_head // 返回新链表的首节点
}2 迭代法 // 当前节点指向上一个节点
const reverse_link3 = (head) => {
let pre_node = null
let curr_node = head
while (curr_node) {
const next_node = curr_node.next // 保存下个节点
curr_node.next = pre_node // 当前节点指向上一个节点
// 指针向后滑动
pre_node = curr_node
curr_node = next_node
}
return pre_node
}
头插法
var reverseList = function (head) {
if (!head) return head;
let p = head.next, L = head, temp;
L.next = null;
while (p) {
temp = p;
p = p.next;
temp.next = L;
L = temp;
}
return L;
};
// nb