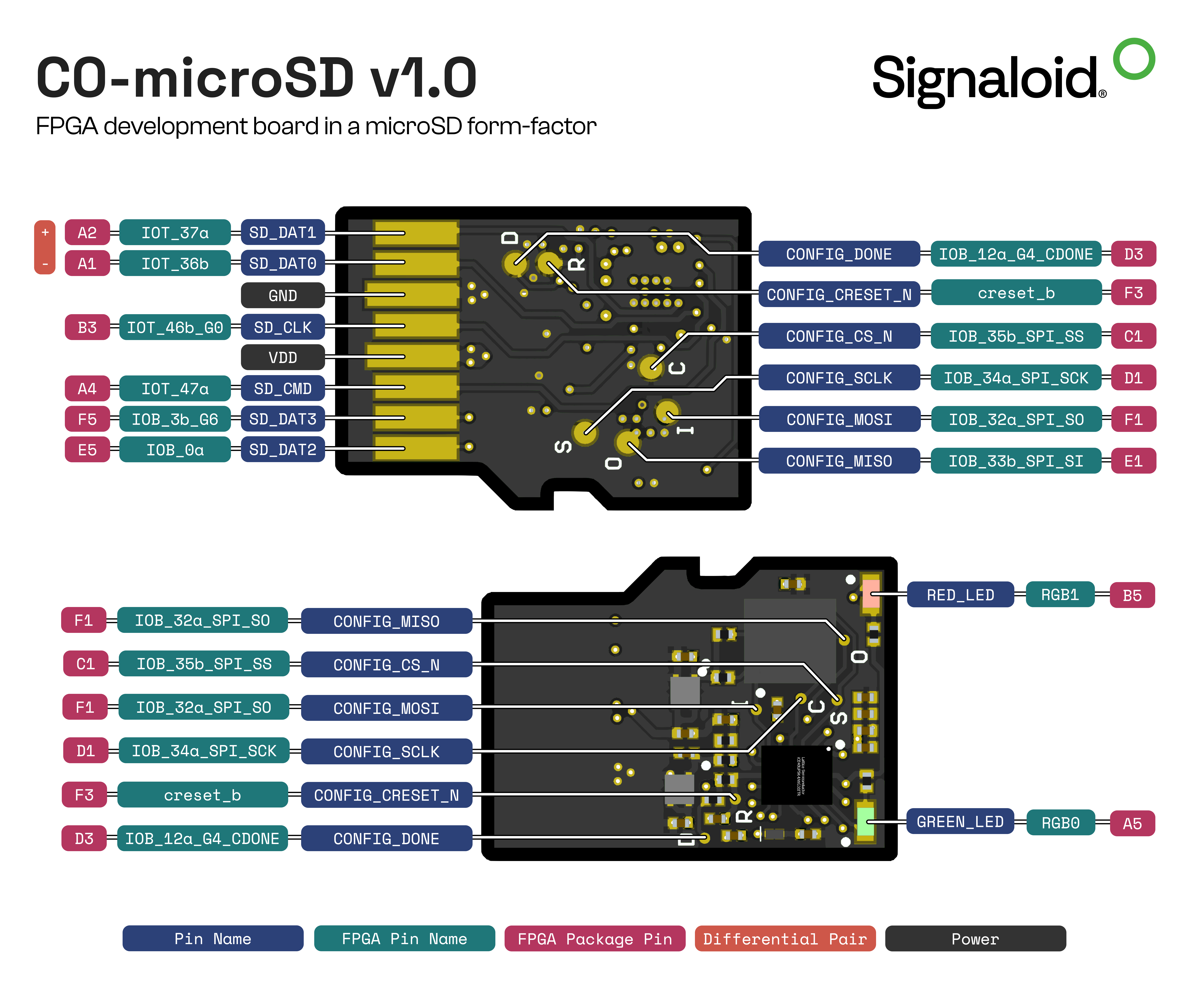
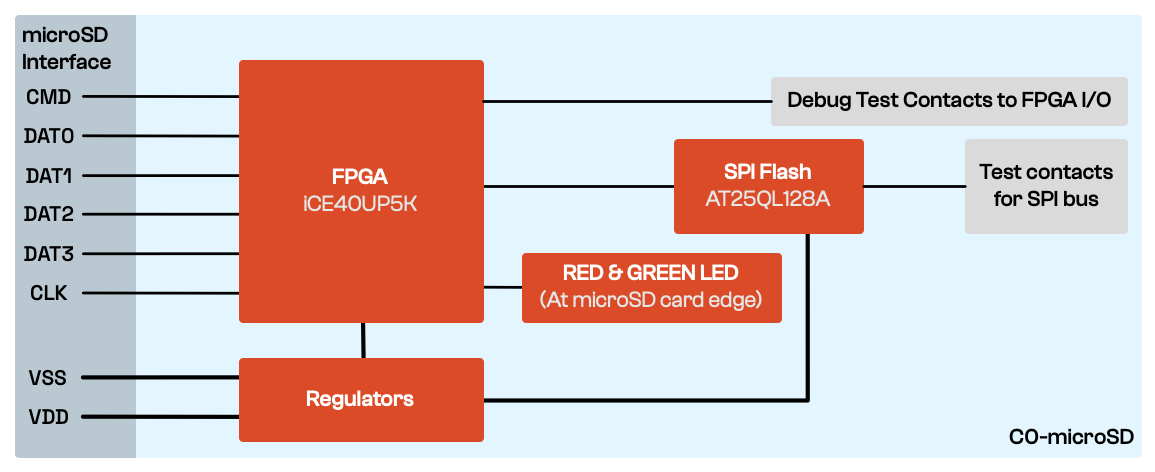
This repository contains Verilog design examples for use with the Signaloid C0-microSD hot-swappable hardware module. A companion repository for the hardware module's bootloader utilities, included as a submodule, contains utilities for interacting with the bootloader.
The Signaloid C0-microSD has two main use cases: You can either (1) use it as a hot-pluggable co-processor module (it implements a subset of Signaloid's C0 processor), or you can (2) use it as a hot-pluggable FPGA module. The Signaloid C0-microSD contains a bootloader that exposes the hardware module's functionality as a SD mass storage device, making it easy to configure new applications in either of the two use cases by performing I/O to the module when it is plugged into a host system.
The Signaloid C0-microSD comes with a built-in version of Signaloid’s C0 RISC-V processor, which you can use to run your applications. In this mode of operation, host computers can use the SD protocol to exchange data with applications running on the Signaloid C0-microSD, either by creating custom applications that run on the host platform and which access the SD storage device, or using Unix tools such as dd. Applications running on the Signaloid’s C0 processor in the Signaloid C0-microSD, can take advantage of a subset of Signaloid’s uncertainty-tracking technology to quantify how uncertainties in data affect their outputs.
When using the Signaloid C0-microSD as a hot-pluggable FPGA module, you can plug it into your computer, load new FPGA bitstreams, and then either plug it into a breadboard using a microSD breakout board, or integrate it into a legacy (or custom) PCB that has an unused microSD slot.
The Signaloid C0-microSD detects whether it has been plugged in a SD host, and if so, presents itself as an unformatted block storage device. You can then write your custom bitstream to a specific offset (using tools such as dd) and its built-in bootloader will setup your bitstream so that it is the design that is configured into the FPGA after the system is power cycled. If the Signaloid C0-microSD is powered up but does not detect an SD host, it loads the last custom bitstream written to it in this way.
The correct way to clone this repository is:
git clone --recursive git@github.com:signaloid/C0-microSD-hardware.git
To update all submodules
git pull --recurse-submodules
git submodule update --remote --recursive
If you forgot to clone with --recursive, and end up with empty submodule directories, you can remedy this with
git submodule update --init --recursive
This project requires the following open-source CAD tools:
For pre-compiled binaries of the open-source CAD toolchain, see https://github.com/YosysHQ/oss-cad-suite-build. You can also find two pre-compiled example bitstreams in the bin/ directory of this repository.
You can find example designs along with instructions on how to synthesize and load them to your device in the examples/ directory of this repository.
- ICE40UP5K FPGA
- 5280 logic cells
- 128 Kbit (16 KB) dual-port Block RAM
- 1 Mbit (128 KB) single-port RAM
- One PLL, two SPI, and two I2C hard IPs
- Two internal oscillators (10 kHz and 48 MHz)
- 8 DSPs (16x16 multiply + 32-bit accumulate)
- Hard IP PWM (for the on-board LEDs)
- AT25QL128A SPI Flash
- 128 Mbit (16 MB) non-volatile memory
- 50 MHz typical operating frequency
- 133 MHz maximum operating frequency (fast read)
- Low power dissipation
- Programmable I/O pins
- Two on-board leds (one red and one green), for status indication
- Six programmable I/O pins (from the microSD interface)
- Five additional programmable pins on test pads
- Built-in Signaloid C0 RISC-V processor
- Built-in bootloader, allowing you to load new FPGA bitstreams or RISC-V applications via the SD interface