The quest is divided into 4 parts:
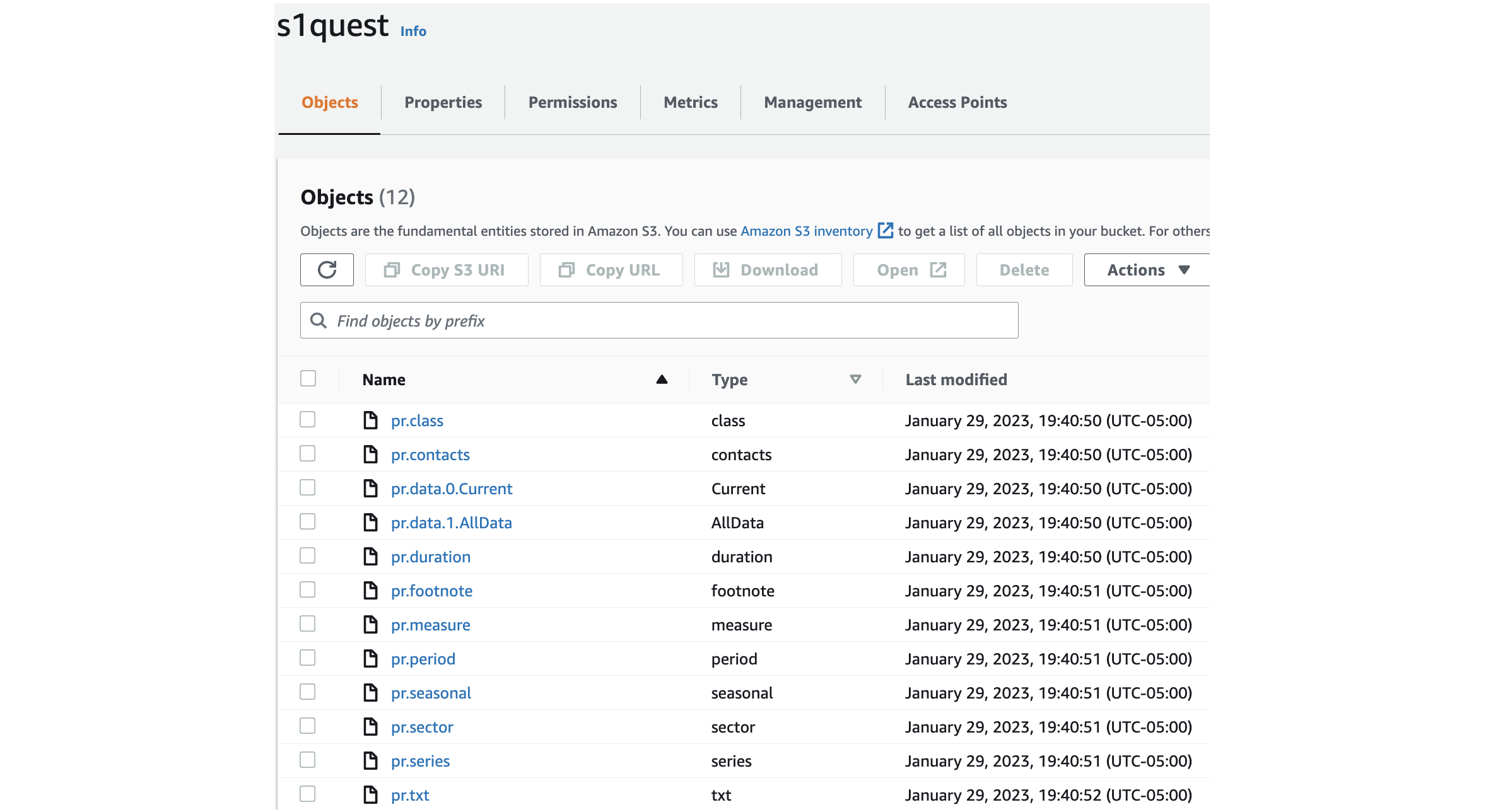
This dataset was uploaded to the S3 Bucket using s3_script.py.
Files can be downloaded from S3 bucket using this page
-
Run locally:
Create an Access key (required to run the script locally) for your IAM User (We have used the root user keys for this step only).
Add the following policies to your IAM User:
- AmazonS3FullAccess
- AWSGlueConsoleFullAccess
-
Run on AWS Glue:
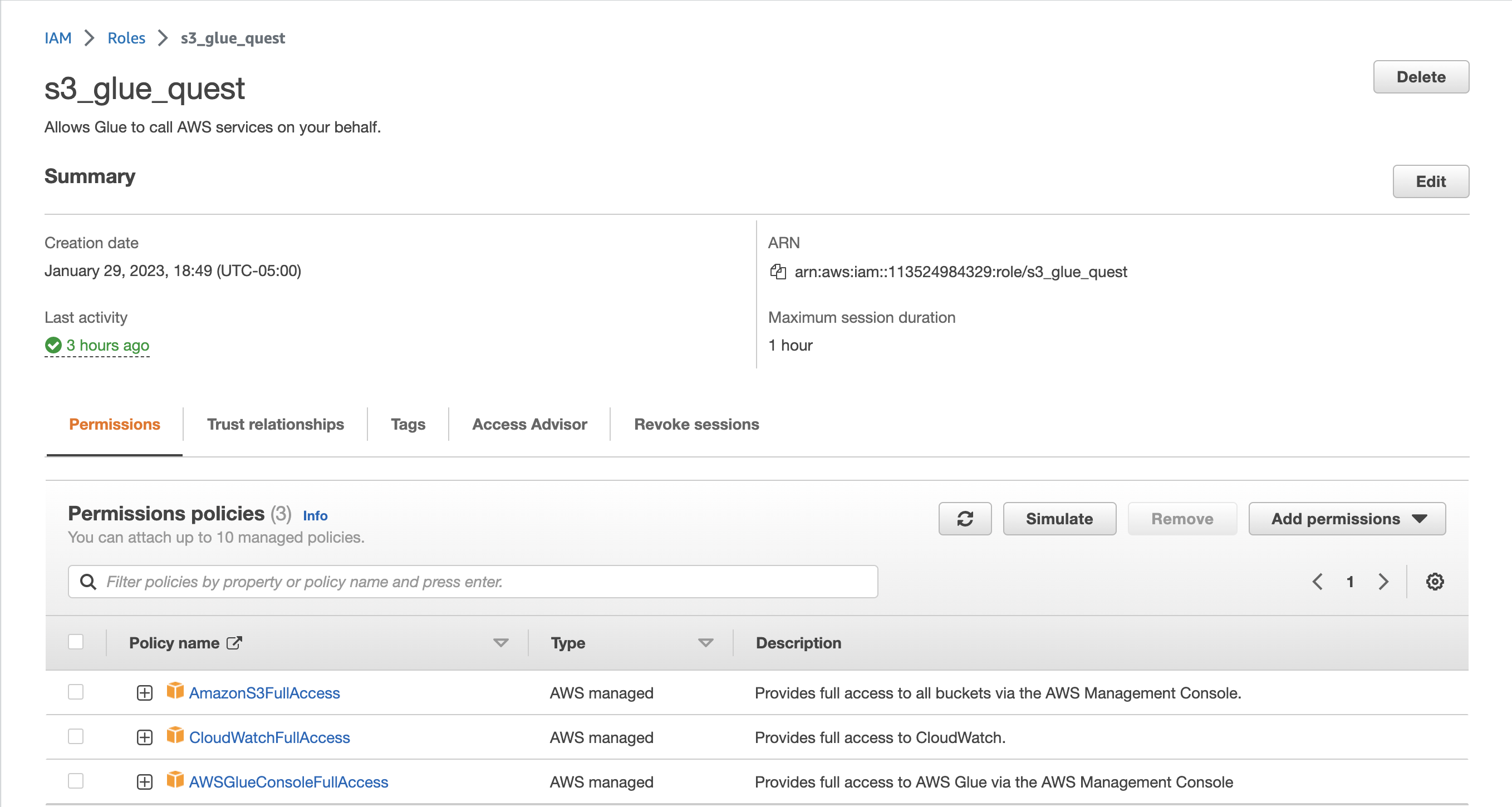
Create a new role
s3_glue_quest:- Add Use case as
Glueand click next. - Add following Permissions policies:
- AmazonS3FullAccess
- CloudWatchFullAccess
- AWSGlueConsoleFullAccess
- Add Use case as
key = "../srd22_accessKeys.csv" if environ.get('LH_FLAG') else None
bucket_name = "s1quest"
res_url = "https://download.bls.gov/pub/time.series/pr/"
s = ManageS3(bucket_name, res_url, key)
s.sync_files()Once we have the script running locally, we can upload it to AWS Glue. And schedule a job.
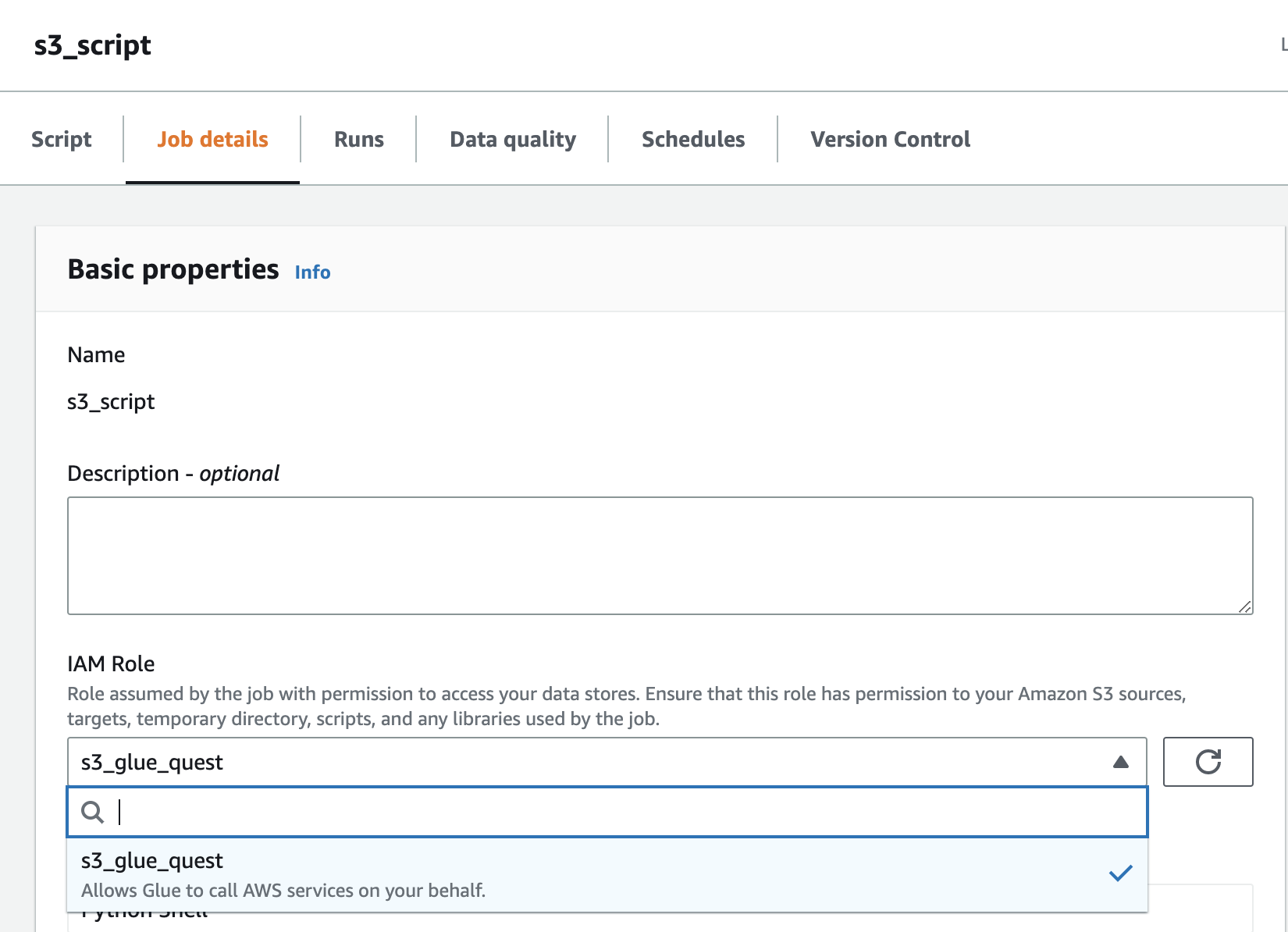
In Glue Studio, select Python Shell script editor and select Upload and edit an existing script and click Create.
Attach your IAM Role to your job.
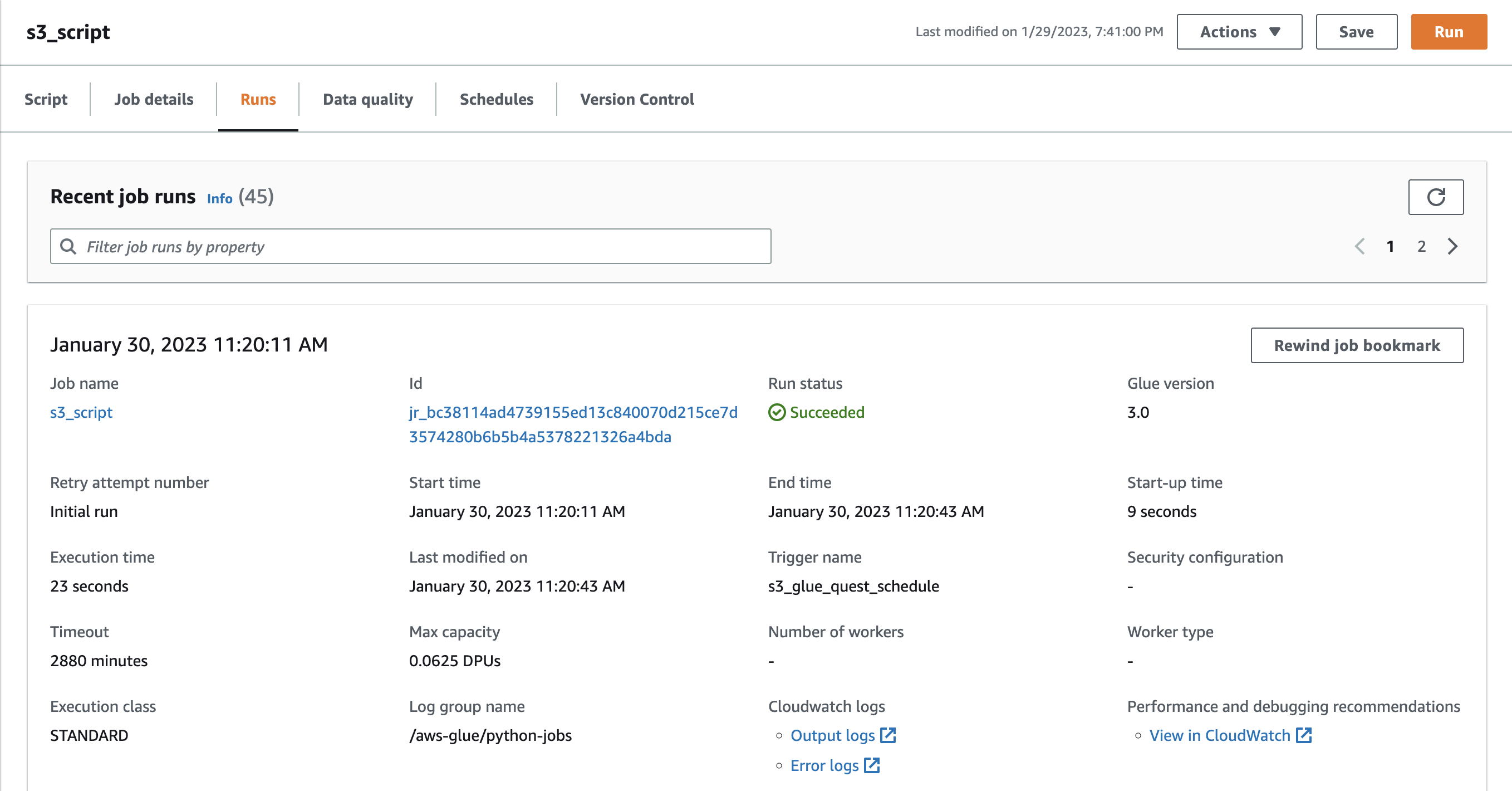
Test run the job by clicking Run.
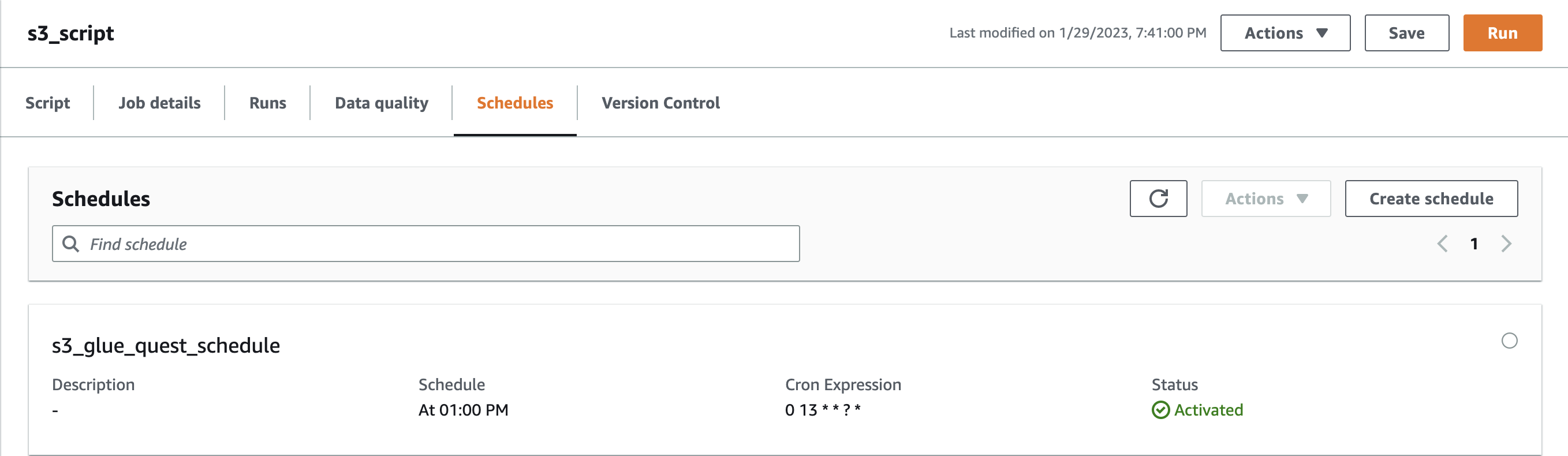
Go to Schedules Tab and click Create Schedule, type in name and select the frequency. This will keep the S3 bucket in sync with the dataset.
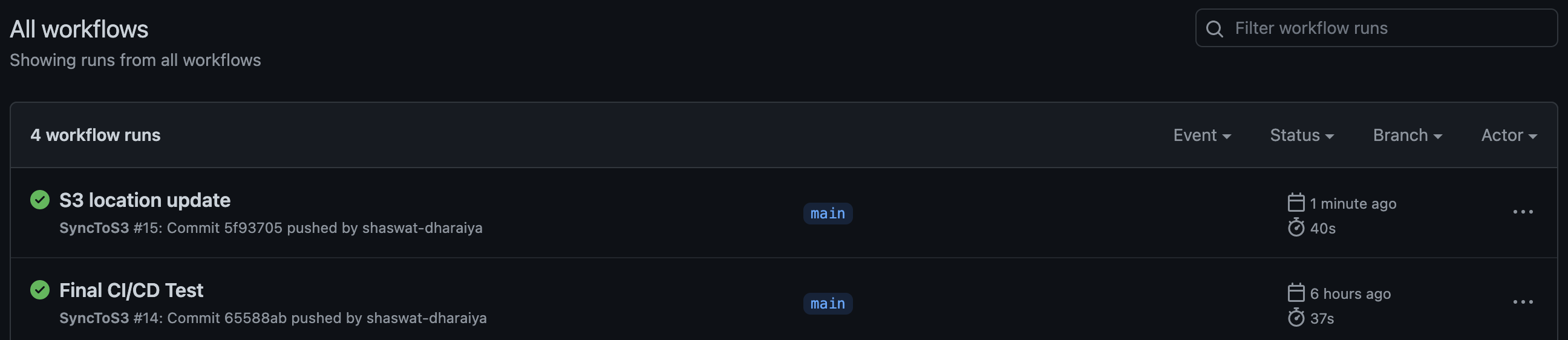
The python script in Glue comes from s3_script.py file in an S3 bucket. Our aim is to automatically update that file upon git push done on the script.
We ceate a SyncS3 github actions defined in syncS3.yml to achieve this.
It will use AWS Credentials and copy the contents of the s3_script folder to script folder in the S3:
Upon a git push it runs the SyncS3 job.
Using the s3_script.py's new_s3_add_files() method, data from the api is uploaded to the S3 Bucket on AWS.
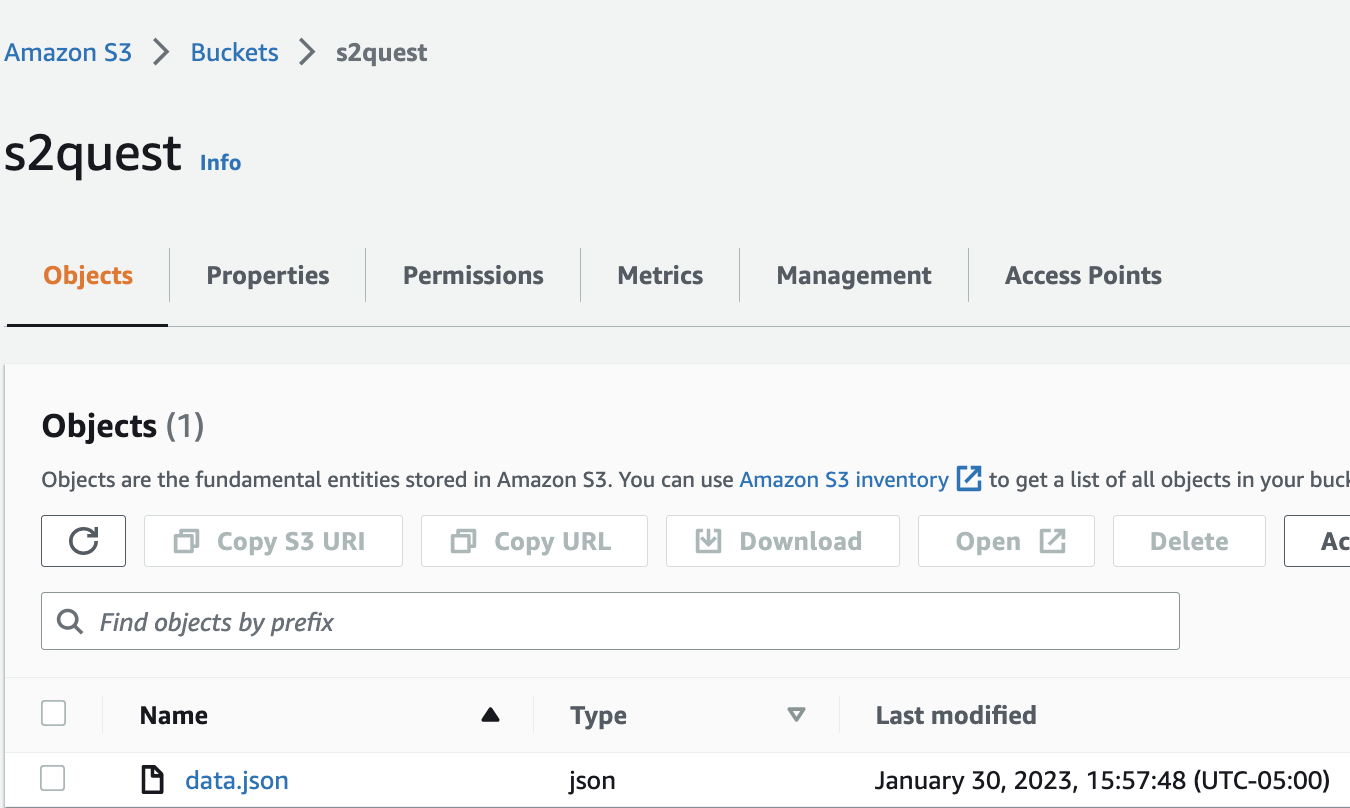
new_bucket = "s2quest"
api = "https://datausa.io/api/data?drilldowns=Nation&measures=Population"
file_key = "data.json"
s.new_s3_add_files(new_bucket, api, file_key)Implementation and output of this part is available in s2quest.ipynb.
This part is divided into 3 Steps:
- Step 3.0 - Data Collection - Data from API & S3 (pr.data.0.Current)
- Step 3.1 - Mean & Standard Deviation
- Mean = 317437383.0
- Standard Deviation = 4257090.0
- Step 3.2 - Grouping
- Step 3.3 - Filtering
For this we use Terraform & Github Actions to achieve Automation of Data Pipeline + CI/CD.
Upon executing the script: scripts/setup.sh following steps execute one after the other.
One change made, is use of AWS Lambda instead of AWS Glue as the former is what's asked and latter is more of an overkill in our case.
- Using the script: scripts/root_setup.sh and root user credentials of srd22, a new IAM user gets created through Terraform.
- The user's access token is storerd to a private bucket.
- Policies attached to that user can be seen in TF_code/user/create_user.tf.
- The User starts infastuctue setup using scripts/setup.sh
- creates 2 new buckets
s1quest(public access) - 1 for the dataset ands2quest- 1 for the API using TF_code/buckets/create_buckets.tf s2quest, The bucket with the API data will also contain code for the lambda functions (uploaded later on).
- creates 2 new buckets
-
The code for lambda function - -
classes/ManageS3.py,lambda/s3_script.py&lambda/s2quest.py- gets zipped up and is uploaded tos2questbucket aslambda_files.zip.
-
Infrastructure setup
-
Access the pre-existing user role:
automate_terraformusingrearc-user's acccess key. -
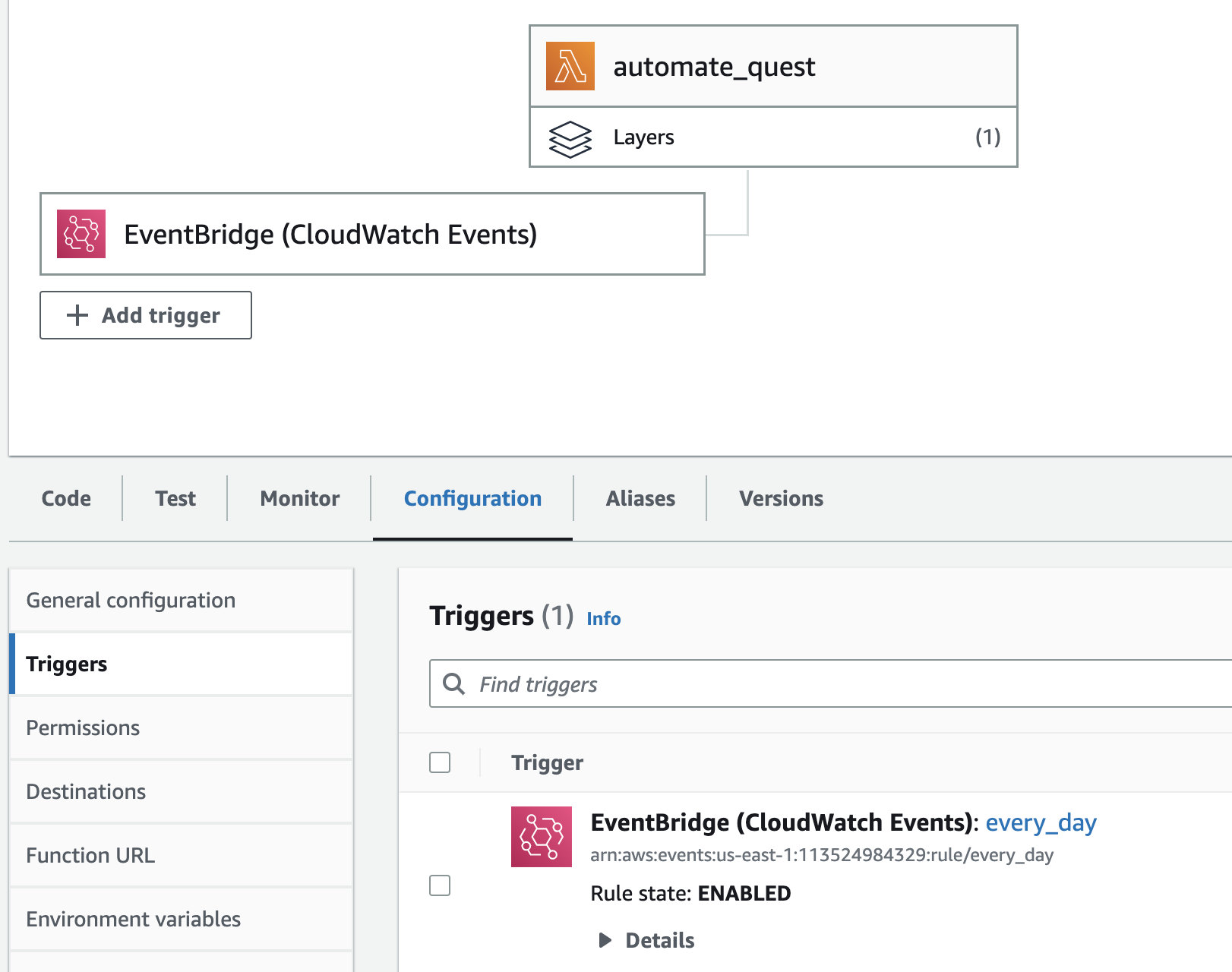
Create a lamabda function:
automate_questthat implement 1st two steps. -
Configure an
aws_cloudwatch_event_rulethat triggers the lambda function once every day. -
Files uploaded to s1quest can be downloaded from S3 bucket using this page or this page
-
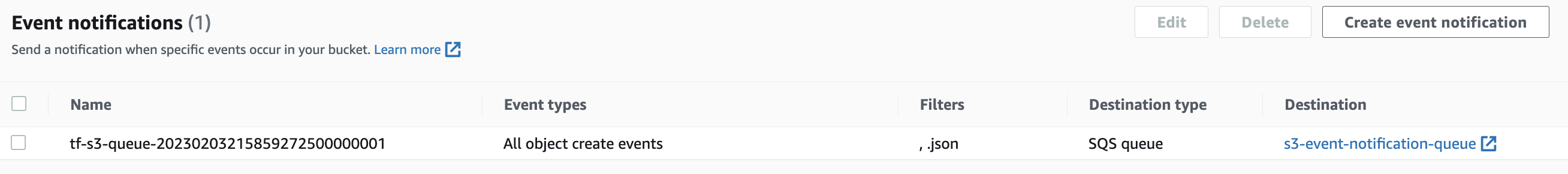
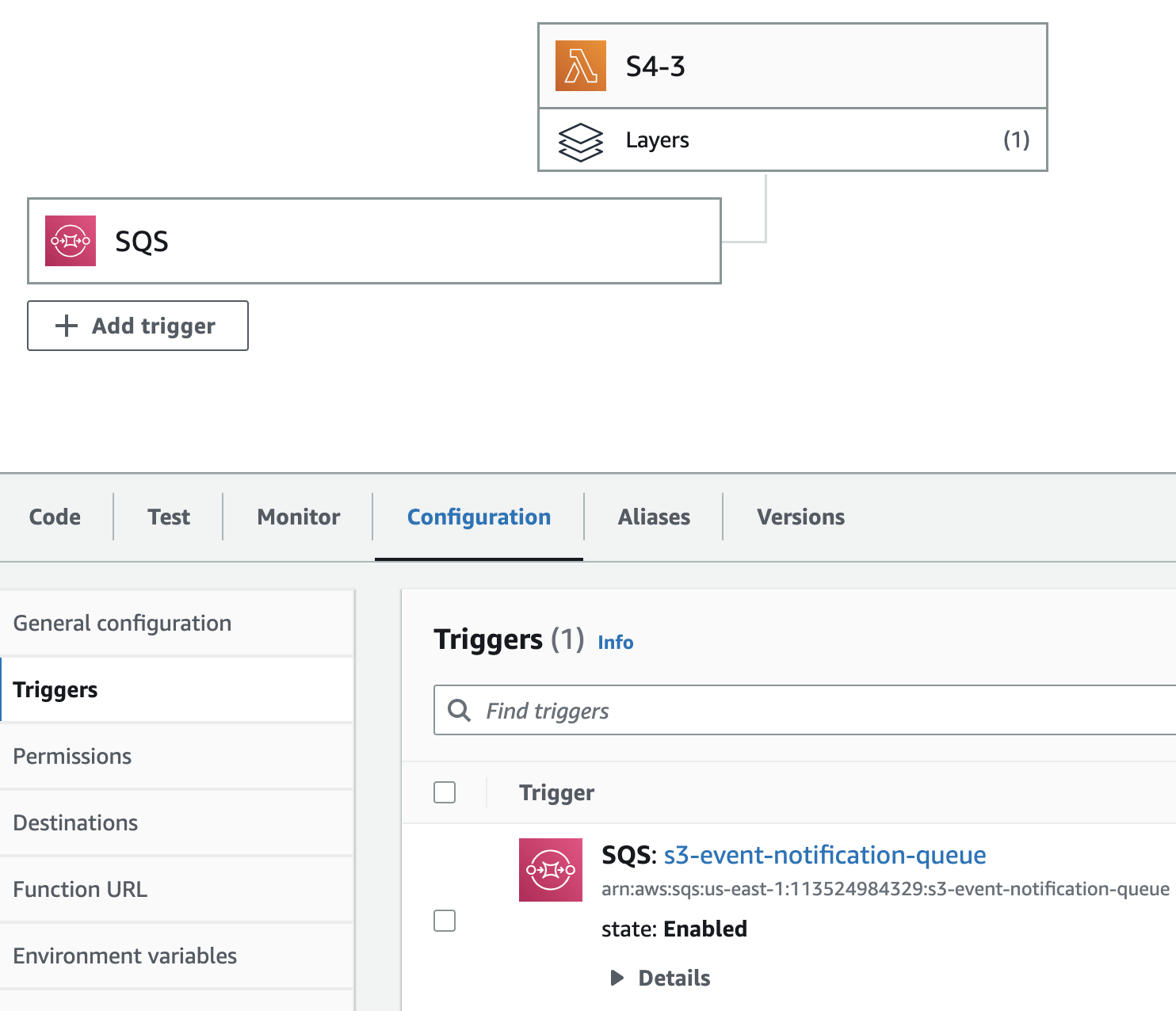
Access the
s2questbucket and attach anSQSqueue such that when thedata.jsonfile from the API gets uploaded to the bucket, it triggers an entry into the queue.
-
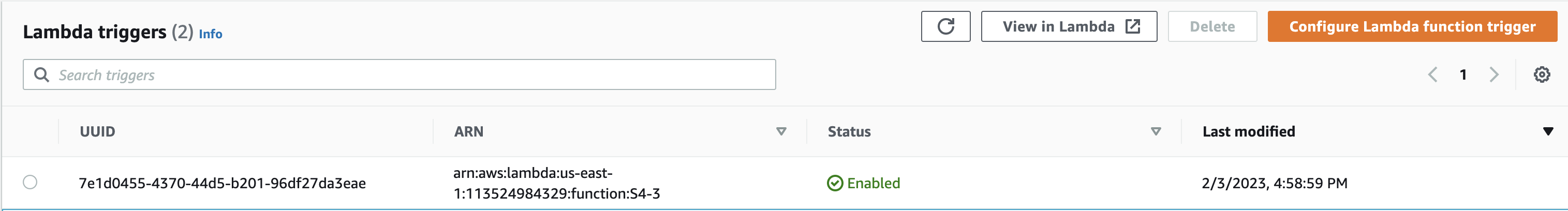
- Attach a lambda function:
S4-3to the SQS queue that gets triggerd when an entry is made to the queue.
- The outputs of both the lambda functions get logged into
CloudWatch.
A GitHub Action: "LambdaSync" in the file .github/workflows/lambdaS3.yml syncs the S3 bucket: s2quest as well as in both the lambda functions upon a git push to the python scripts in the main branch.
The IAM user get's the scripts/destroy.sh script that will delete the entire infrastructure.
On the other hand Root User has the scripts/root_destroy.sh script that will delete the entire infrastructure.