#Bootstrap
This workshop is important because:
Bootstrap is a library of CSS classes that helps make any old site look nice with very little effort. It comes with a grid system that makes layout out content on a variety of screen sizes much easier to deal with.
After this workshop, developers will be able to:
- Implement class-based CSS
- Require Bootstrap into your project
- Use and build a grid system
- Design HTML pages with the aid of Bootstrap & mockups
Before this workshop, developers should already be able to:
- Write custom HTML & CSS
- Include external stylesheets
##Intro to Bootstrap
- Bootstrap is a front-end framework created by a small team of developers at Twitter and maintained by a much larger community of contributors.
- The framework consists of one main CSS file, an optional theme CSS file, and a main JS file.
- Parts of Bootstrap require jQuery to work.
- And it has excellent documentation!
Bootstrap is extremely popular and knowledge of at least one CSS framework is a very valuable skill to have.
Bootstrap comes with a ton of features, including:
- Responsive Grid System
- CSS library for quick and easy styling
- UI components - HTML + CSS
- buttons
- forms
- etc.
Optional
- Javascript widgets to make your page interactive (e.g. a nav bar)
- Icons
- & more!
##Notable Sites Using Bootstrap
##What is Class-based CSS?
Discussion, challenge, then demonstration
Create modular classes that encapsulate a certain behavior and name them semantically.
How would you style CSS for these elements?
.shout— uppercase the text inside the element.shadow— add a drop-text to text inside the element.invert— flip an element upside-down
Example solution
.shout {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
.shadow {
text-shadow: 1px 1px 2px black;
}
.invert {
transform: rotate(180deg);
}##Including Bootstrap with HTML
Demonstration, then challenge
- To use Bootstrap, we need to include Bootstrap's CSS and Javascript libraries (+ or - an optional Bootstrap-Theme CSS file).
- We also need to include jQuery, as Bootstrap's JS plug-ins depend on it.
- There are a few different ways to accomplish this, listed below. In this class, we'll keep it simple and stick with the CDN.
- CDN (Content Delivery Network - someone else hosts the library/framework and you access it via a URL): http://getbootstrap.com/getting-started/#download-cdn. Where do we include these in our HTML file?
- Download the actual CSS and JS files and link to them on your local computer - better for offline/local development.
Sample code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Bootstrap</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<!-- Bootstrap CDN -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<!-- uncomment for optional javascript
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.1.0.min.js" integrity="sha256-cCueBR6CsyA4/9szpPfrX3s49M9vUU5BgtiJj06wt/s=" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
-->
</head>
<body>
<!--html here-->
</body>
</html>##What is Responsive Design?
Discussion
"Responsive web design (RWD) is an approach to web design aimed at crafting sites to provide an optimal viewing and interaction experience— easy reading and navigation with a minimum of resizing, panning, and scrolling—across a wide range of devices (from desktop computer monitors to laptops to cellphones).
A site designed with RWD adapts the layout to the viewing environment by using fluid, proportion-based grids, flexible images, etc..."
Source: Wikipedia
##Responsive Grid System (aka Columns of Craziness)
Discussion —> Demonstration —> Challenge
- Columns are written in the following format as a class attribute:
col-(breakpoint)-(offset) - For example:
col-sm-4 - Columns are often wrapped into an element with a class of
roworcontainer.
####Start with a container
To ensure all your Bootstrap styles behave properly, always put your content inside an element with a class "container" (usually <div class="container">). This will center your content and leave a small margin on the sides of the page. If you would like to use the full width of the screen (no margin) use class="container-fluid"
####Page layout using the Grid System
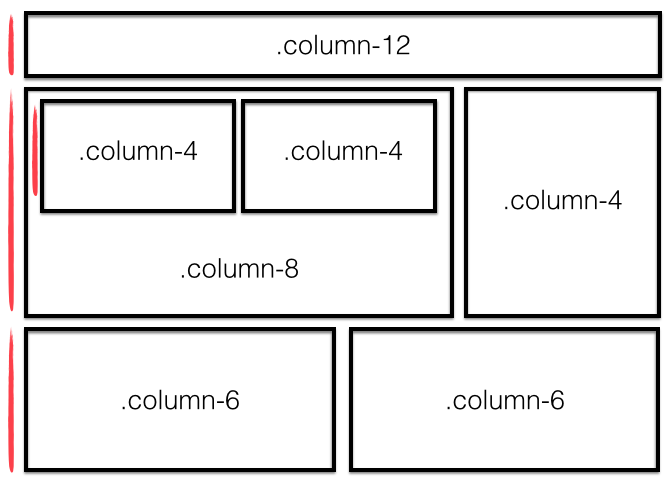
Bootstrap's grid system is based on the idea that a page layout for any given screen size is represented with 12 fluid columns. Columns are always horizontally contained in rows, which in turn are contained inside of the previously mentioned container (container > row > column). But why 12?
12 is divisible by 2, 3, 4, and 6 (meaning we can have columns that are: half-width, third-width, quarter-width, and sixth-width aka 50%, ~33.3%, 25%, and ~16.7%):
12/2 = 6
12/3 = 4
12/4 = 3
12/6 = 2
12/12 = 1
6 + 6 = 12
4 + 4 + 4 = 12
3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 12
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12
1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 12
We can also create the typical two column layout (main content area + sidebar):
8 + 4 = 12
9 + 3 = 12
-
To use the gridsystem we must first have a row:
<div class="row"> ... </div>
-
Then select what screen size we'll want it to display on:
col-xs< 768px (e.g. smartphones)col-sm≥ 992px (e.g. tablets)col-md≥ 1200px (e.g. laptops, desktops)col-lg≥ 1200px (e.g. large desktops, smart TVs)
-
Pick a fraction of
12that will determine how much of the row it will take up. -
You then use the above choices to determine the exact class you will add to an element in the row (bootstrap has them all built in).
For example the class: col-lg-3 will take up 3/12 of the space at 1200px. Feel free to add more classes to the same element to change how it will behave at other screen sizes. Let's checkout some more examples...
Here's an example of a two-column layout that spans the width of the page. Notice that the widths of the two columns add up to 12. The column content of any row must always be ≤12.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6">
<p>I'm a medium-sized column</p>
</div>
<div class="col-md-6">
<p>Me too! We have SO much in common</p>
</div>
</div>What will this code do?
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-12 col-md-6">
<p>I take up the entire space when the screen is small, but share it when there's more room.</p>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-12 col-md-6">
<p>Samesies...</p>
</div>
</div>###Challenge: Grid it
Using the bootstrap grid, make a grid that is 3 Columns on Tablet (sm), Laptop (md), and Desktop (lg), 1 Column on Mobile(xs).
Sample code
<div class="row">
<h3 class='text-center'>3 Columns on Tablet, Laptop, and Desktop, 1 Column on Mobile</h3>
<div class="col-sm-4 col-xs-12">Yao</div>
<div class="col-sm-4 col-xs-12">Hey</div>
<div class="col-sm-4 col-xs-12">Ola</div>
</div>For other examples, check out the Bootstrap docs
##Offsets & Nesting
- The way that Bootstrap works is to dynamically reduce column size according to the window size.
- To be mobile (and tablet!) friendly, the columns will break into a stack layout after a minimum width is detected.
- The breakpoints you can select in your columns control at which point this happens.
- Check out their documentation here to see what these breakpoints are in terms of size.
- Let's test it!
You can also offset and nest your columns. When you offset a column, you add a column of whitespace and push the column to the right. Example:
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3 col-md-offset-3">
<p>This column occupies 1/4 of the page width and is moved to the right
by 1/4 of the page width</p>
</div>
</div>Here is an example of nesting columns (putting one row inside another)
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6">
Level 1: Column takes 1/2 the width of the page
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
Level 2: This column takes 1/3 the width of its parent column
</div>
<div class="col-md-8">
Level 2: This column takes 2/3 the width of its parent column
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>##Typography For a complete list: Bootstrap Typography classes
To align text, use these classes.
<p class="text-left">Left aligned text.</p>
<p class="text-center">Center aligned text.</p>
<p class="text-right">Right aligned text.</p>
<p class="text-justify">Justified text.</p>
<p class="text-nowrap">No wrap text.</p>More useful typography classes...
<p class="lead">This text will stand out in a paragraph</p>
<small>This line of text is meant to be treated as fine print.</small>
<p class="text-lowercase">Lowercased text.</p>
<p class="text-uppercase">Uppercased text.</p>
<p class="text-capitalize">Capitalized text.</p>####Icons
Bootstrap comes with a set of icons that can be included in your page using the <i></i> tag. Check out these icons here
####Buttons
Bootstrap provides a wide selection of button sizes and colors. Button classes can be applied not just to <button> elements, but also <a> and <input> elements
Sometimes you need to provide multiple classes to an element in order for Bootstrap to style it. The button classes are an example of this:
<!-- Standard button -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-default">Default</button>
<!-- Provides extra visual weight and identifies the primary action in a set of buttons -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Primary</button>
<!-- Contextual button for informational alert messages -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-info">Info</button>
<!-- Indicates caution should be taken with this action -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-warning">Warning</button>... and so on. See the docs for a comprehensive list of options. Note you can add a third class denoting size to any of the above: .btn-lg, .btn-sm, .btn-xs
###Images
Bootstrap helps you format images using class="img-rounded" (rounds the corners), class="img-circle" (makes the image a circle) and class="img-thumbnail" (adds a border). You can also add a class="img-responsive" to your image to make it scale well when the screen size changes (this sets its max-width to 100% of its parent element and the height to auto for maintaining aspect)
###Forms
Bootstrap is also very helpful when you need to style your forms. All textual <input>, <textarea>, and <select> elements with class="form-control" are set to width: 100% by default. Wrap labels and their associated controls (inputs) in class="form-group" for optimum spacing.
###Javascript plug-ins Bootstrap allows you to incorporate interactive behavior into your page with Javascript plug-ins. While you would ultimately have to write some JS in order for these components to provide actual functionality within the application, you don't have to write JS if you're simply mocking up a UI.
Some examples:
###Challenge: Choose your own adventure
Pick some aspect of Bootstrap that interests you. Spend 5-10 minutes learning how it works and be prepared to share it with the rest of the class.
##Closing Thoughts
Bootstrap demonstrates good practices in terms of exemplifying class-based CSS and introducing the concept of a grid-system. It is useful for most projects where style is somewhat important but not the central to the product.
##Additional Resources
- Foundation - another CSS-library, similar to Bootstrap
- Skeleton - a lovely, minimal, unopinionated CSS library
- Materialize - front-end framework based on "material design"
- Block Element Modifier methodology
- Hipster Ipsum - Dummy placeholder "hipster" text
