Code for the paper:
Transferable Class-Modelling for Decentralized Source Attribution of GAN-Generated Images
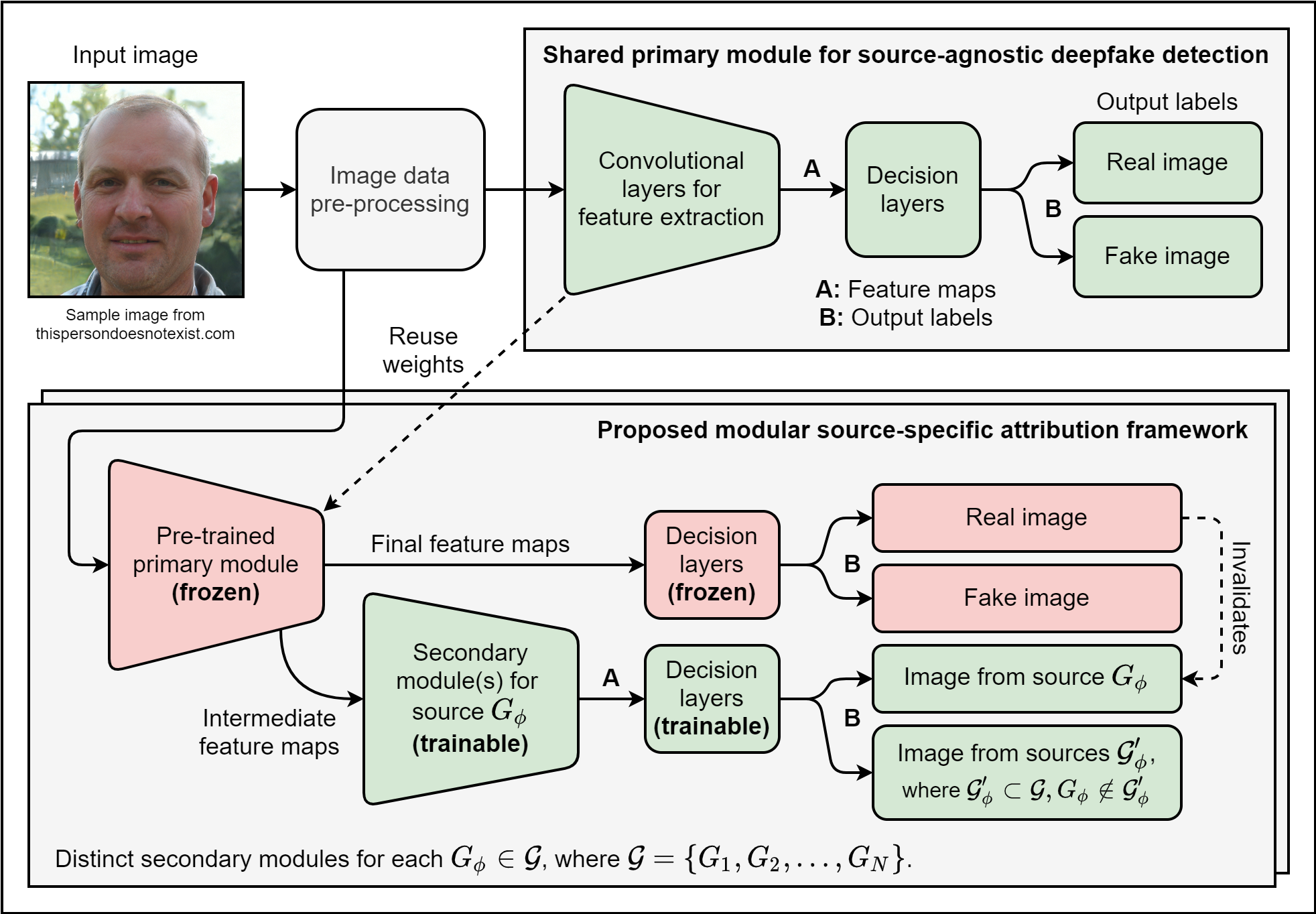
This project proposes a convolutional neural net framework that utilizes transfer learning to efficiently identify "deepfake" images synthesized by generative model sources such as generative adversarial networks (GANs), and attribute them to their specific sources relative to all others.
This method was conceived within a series of experiments to determine if reactive deepfake attribution using the GAN fingerprints-based method pioneered by Yu et al. (2019) and Frank et al. (2020) can be successfully performed in a sustainable and decentralized manner that retains external validity despite limited data in an open-world setting.
TensorFlow 2 (Keras API) is used in this implementation.
Official experimental model weights now available in their respective trained_models subfolders.
Refer to README_DATASET.md.
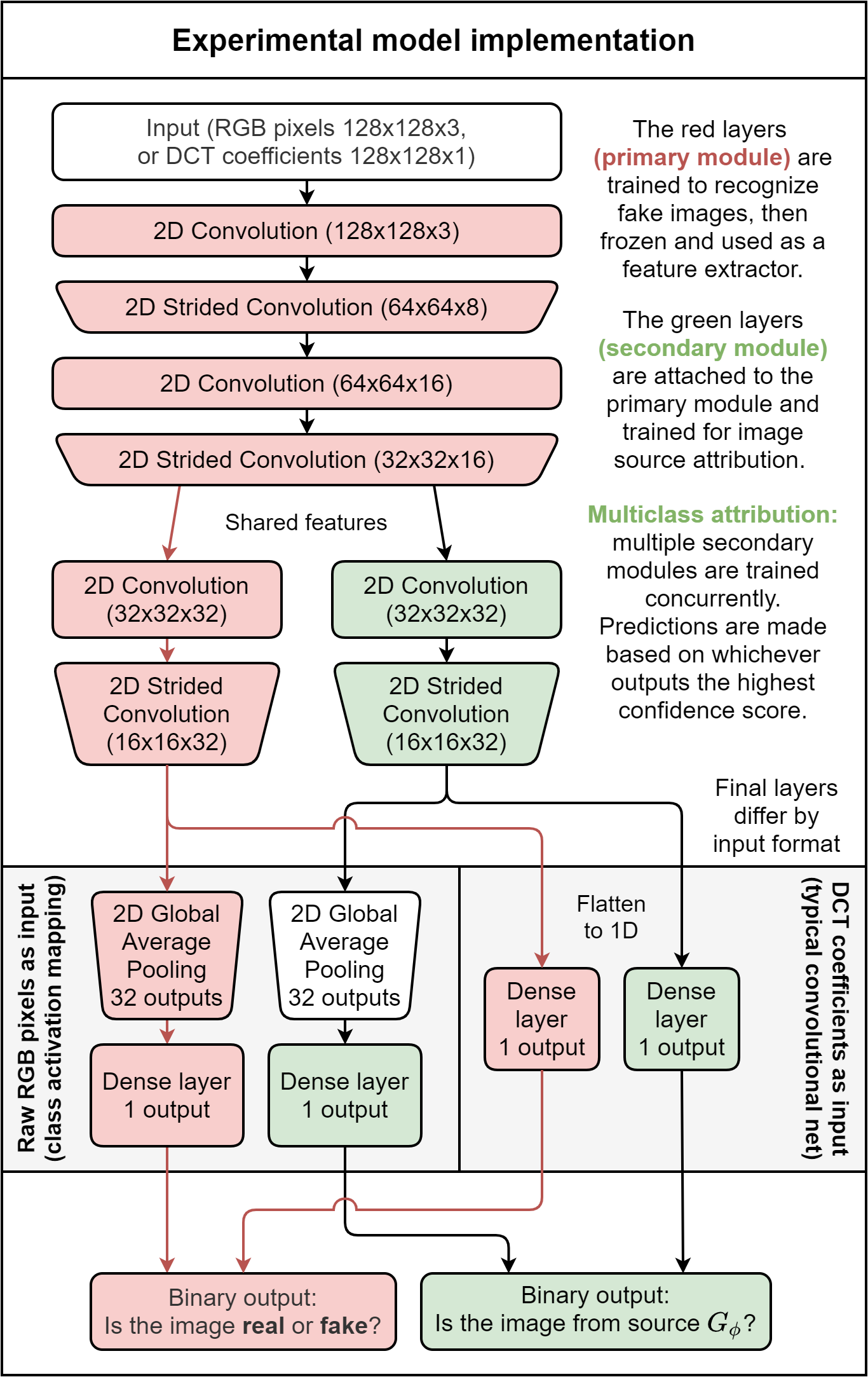
A convolutional neural network based on the gandct-conv model, but with extensive modifications to the architecture informed by the research objective:
- The model topology branches out midway into primary and secondary modules.
- The primary module are trained for deepfake detection only, learning features meant to distinguish all synthetically generated images (regardless of source) from real images.
- The secondary modules build upon intermediate features extracted from pretrained primary module layers, exploiting them to identify whether the features correspond to the intrinsic fingerprints embedded within the outputs of a particular image source.
- Each module has their own output predictions, but the primary module is customarily prioritized in the inevitable event of self-contradictory predictions.
- The model is designed to approach image source attribution as a binary classification problem akin to class-modelling, in which an image can be attributed to either a certain source generator or its complement set of all other source generators.
- Ideally, the binary attribution approach should also recognize images created by a novel, unknown generator (which may or may not be an unconditional GAN) as belonging in the complement set. Current findings imply that this may not be possible when relying entirely on intrinsic fingerprints.
- The conventional multiclass attribution approach used by other studies can be approximated using multilabel outputs from independently trained secondary modules, though expect performance worse than baseline as mutual exclusivity of outputs is not assumed.
- Strided convolution is used instead of average pooling to retain fine-scale information.
- Batch normalization is applied in all layers but the first. This is inspired by the PatchGAN discriminator architecture.
- For pixel input variants of the model, the class activation mapping structure using global average pooling (GAP) is implemented towards the output layer.
- This assumes the functionality of post-pooling in reducing spatial dimensionality.
- This allows the model to innately produce heatmaps that localize image regions contributing significantly to the model's prediction for interpretability purposes.
- This suppresses the prioritization of any specific image region in identifying GAN fingerprints.
- For DCT input variants, Grad-CAM is applied instead.
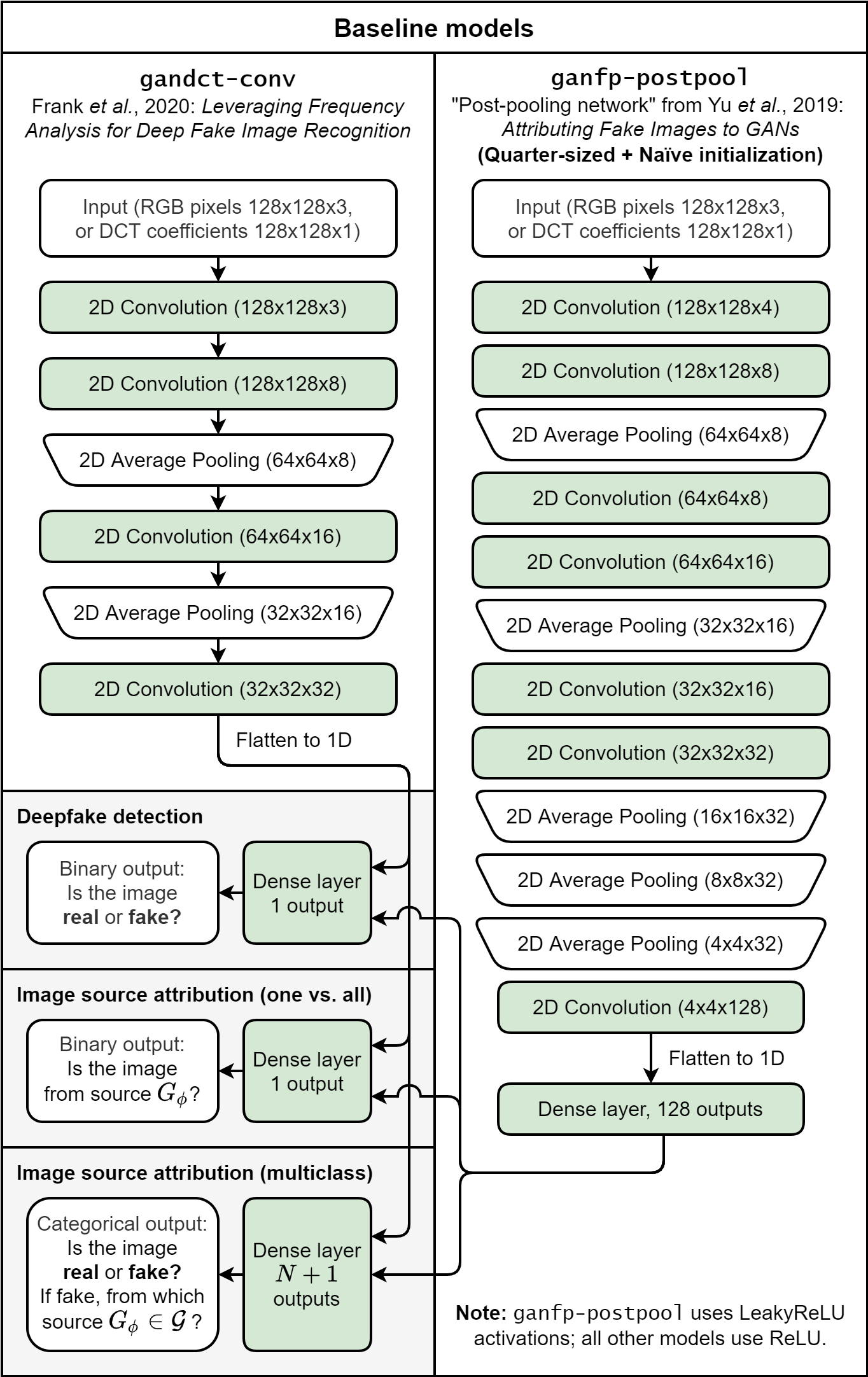
- gandct-conv (
gdaconv) : The simple convolutional network used by Frank et al. (2020) for their experiments on GAN-generated deepfake detection and source image attribution using 2D Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) spectral analysis. - ganfp-postpool (
postpool) : A post-pooling variant of the convolutional network used by Yu et al. (2019) for their GAN Fingerprints experiments. This version starts consecutive average pooling from 32x32 resolution, uses naïve weight initialization, and contains 1/4 of the number of neurons and convolutional kernels per layer to satisfy hardware constraints.
This procedure outputs the following:
trained_models: (Re-)trained classifier modellogs: Training logs for TensorBoardcheckpoints: Keras checkpoint backup weights
For training a classifier model from scratch on the GANFP dataset:
python classifier.py det \
-c [model_class] --seed 2021 \
train \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_train \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_val \
--model_id [model_id] --instance_id [instance_id] \
--epochs 100 --image_size 128 --learning_rate 0.001 \
--num_sources 4 --num_real_sources 1 \
--batch_size 256 --train_size 20000 --val_size 4000 \
--early_stopping [early_stopping]
- Replace
[model_class]withdefaultfor the proposed model, orgdaconvorpostpoolfor baseline benchmark classifier topologies.- It is recommended to use seed
1000instead of2021forpostpoolmodels.
- It is recommended to use seed
- Add argument
-for--dctif training on DCT inputs.- Change the specified dataset directories accordingly as well.
- Add argument
-afortf.config.gpu_options.allow_growth=True. - Change
cleanwhen working with augmented versions of the dataset. - Change
[model_id]to whatever identifier you wish to call your trained model by. - Change
[instance_id]to whatever identifier you wish to call this particular trained instance of the model. Default:[instance_id]=[model_id]. - Set
[early_stopping]to the number of epochs permitted to continue training if validation set loss fails to decrease under early stopping regularization. Default is 5. - Equivalent for the FacesHQ+ dataset (default model only):
python classifier.py det \ -c default --seed 2021 \ train \ dataset/faceshq+/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_train \ dataset/faceshq+/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_val \ --model_id [model_id] --instance_id [instance_id] \ --epochs 100 --image_size 256 --learning_rate 0.001 \ --num_sources 3 --num_real_sources 2 \ --batch_size 128 --train_size 7000 --val_size 1000 \ --early_stopping 10
For retraining an already trained model instance on an augmented GANFP dataset:
python classifier.py det \
-c [model_class] --seed 2021 \
train \
dataset/ganfp/multi/pixel/multi_raw_colour_normalized_train \
dataset/ganfp/multi/pixel/multi_raw_colour_normalized_val \
--model trained_models/[model_id]/[instance_id].h5 \
--model_id [model_id] --instance_id [instance_id] \
--epochs 100 --image_size 128 --learning_rate 0.001 \
--num_sources 4 --num_real_sources 1 \
--batch_size 256 --train_size 20000 --val_size 4000 \
--early_stopping [early_stopping]
- Equivalent for the FacesHQ+ dataset:
python classifier.py det \ -c default --seed 2021 \ train \ dataset/faceshq+/multi/pixel/multi_raw_colour_normalized_train \ dataset/faceshq+/multi/pixel/multi_raw_colour_normalized_val \ --model trained_models/[model_id]/[instance_id].h5 \ --model_id [model_id] --instance_id [instance_id] \ --epochs 100 --image_size 256 --learning_rate 0.001 \ --num_sources 3 --num_real_sources 2 \ --batch_size 128 --train_size 7000 --val_size 1000 \ --early_stopping 10
For training the baseline models from scratch on the GANFP dataset:
python classifier.py att \
-c [model_class] --seed 2021 \
train \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_train \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_val \
--model_id [model_id] --instance_id [instance_id] \
--epochs 100 --image_size 128 --learning_rate 0.0001 \
--num_sources 4 --num_real_sources 1 \
--batch_size 256 --train_size 20000 --val_size 4000 \
--arch_level --source [source] --early_stopping [early_stopping]
For training the proposed model from scratch on the GANFP dataset (requires pre-trained deepfake detection model):
python classifier.py att \
-c default --seed 2021 \
train \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_train \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_val \
--det_model trained_models/[model_id]/[instance_id].h5 \
--model_id [model_id] --instance_id [instance_id] \
--epochs 100 --image_size 128 --learning_rate 0.0001 \
--num_sources 4 --num_real_sources 1 \
--batch_size 256 --train_size 20000 --val_size 4000 \
--arch_level --source [source] --early_stopping [early_stopping]
- Replace
[source]with whatever source of interest you want this instance to model:- GANFP:
sngan_celeba, progan_celeba, mmdgan_celeba, cramergan_celeba - FacesHQ+:
stylegan_tpdne, stylegan_100k, stylegan2_tpdne
- GANFP:
- Omit
--arch_levelfor FacesHQ+ if you want your model to distinguish betweenstylegan_tpdneandstylegan_100k. - (Required) Load primary module from existing model via
--det_model. - For retraining on augmented datasets, reload existing model via
--model.
Firstly, load the source_ids.csv files (included) in the main directory of each dataset, e.g. dataset/ganfp/source_ids.csv.
python classifier.py att \
-c [model_class] --seed 2021 \
train \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_train \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_val \
--model_id [model_id] --instance_id [instance_id] \
--epochs 100 --image_size 128 --learning_rate 0.0001 \
--num_sources 4 --num_real_sources 1 \
--batch_size 256 --train_size 20000 --val_size 4000 \
--multiclass --early_stopping [early_stopping] \
--source_list dataset/ganfp/source_ids.csv
- Do not use
--sourceor--arch_level.
This procedure outputs the following in test_results:
- Classifier model predictions on the provided test set (both raw and categorized)
- Ground truth labels supplied by test set
- Confusion matrices with classification performance metrics
For testing a trained classifier model on a clean GANFP dataset:
python classifier.py det \
-c [model_class] --seed 2021 \
test \
trained_models/[model_id]/[instance_id].h5 \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_test \
--image_size 128 --num_sources 4 --num_real_sources 1 \
--batch_size 256 --test_size 6000
- Replace
[model_class]withdefaultfor the proposed model, orgdaconvorpostpoolfor baseline benchmark classifier topologies. - Provide the paths to the trained model and test set respectively.
- (FacesHQ+ dataset) To evaluate the model on out-of-distribution data, replace the test set path with
dataset/faceshq+/clean/pixel/clean_..._test_only, set--num_sourcesand--num_real_sourcesto1and0respectively, and set--image_sizeand--test_sizeto FacesHQ+ appropriate values. Note that the test report graphics will look odd due to the imbalanced dataset.
For testing a trained DCT input classifier model on a JPEG compression-augmented GANFP dataset:
python classifier.py det \
-c [model_class] --dct --seed 2021 \
test \
trained_models/[model_id]/[instance_id].h5 \
dataset/ganfp/jpeg/dct/jpeg_dct_log_scaled_normalized_test \
--image_size 128 --num_sources 4 --num_real_sources 1 \
--batch_size 256 --test_size 6000
For testing a trained classifier model on the GANFP dataset:
python classifier.py att \
-c [model_class] --seed 2021 \
test \
trained_models/[model_id]/[instance_id].h5 \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_test \
--image_size 128 --num_sources 4 --num_real_sources 1 \
--batch_size 256 --test_size 6000 --arch_level --source [source]
- Replace
[source]with the source of interest that your selected model instance is trained to identify:- GANFP:
sngan_celeba, progan_celeba, mmdgan_celeba, cramergan_celeba - FacesHQ+:
stylegan_tpdne, stylegan_100k, stylegan2_tpdne
- GANFP:
- Omit
--arch_levelfor FacesHQ+ if your model is trained to distinguish betweenstylegan_tpdneandstylegan_100k.
Firstly, load the source_ids.csv files (included) in the main directory of each dataset, e.g. dataset/ganfp/source_ids.csv.
python classifier.py att \
-c [model_class] --seed 2021 \
test \
trained_models/[model_id]/[instance_id].h5 \
dataset/ganfp/clean/pixel/clean_raw_colour_normalized_test \
--image_size 128 --num_sources 4 --num_real_sources 1 \
--batch_size 256 --test_size 6000 --multiclass \
--source_list dataset/ganfp/source_ids.csv
- Do not use
--sourceor--arch_level.
For calling already-trained classifier models for immediate inference on any given raw image(s), producing outputs in the form of class activation heatmaps and classification confidence scores.
- Refer to Runtime examples section in README_DATASET.md for summarized data preparation.
- For deepfake detection, run the following:
python run_classifier.py det \ trained_models/[model_id]/[instance_id].h5 \ dataset/test-[dataset_id]/clean \ run_outputs/[dataset_id] \ --batch_size [batch_size] --image_size [image_size]- Replace
[model_id]and[instance_id]accordingly based on the trained model. - Replace
[dataset_id]with eitherganfp,faceshq+, or any other dataset ID. - Set
[batch_size]to an integer evenly divisible with the total summarized dataset size. - Set
[image_size]to the spatial resolution of square images in the selected dataset. Default is256for FacesHQ+. - Include flag
--dctor-fif working with DCT input instances. Do not forget to provide--normstatsor-nfor image preprocessing (see README_DATASET.md). - Include flag
--nolabelsor-xto exclude classification confidence scores from the outputs. - Include flag
--sourcetagsor-tif using the FacesHQ+ dataset, where image IDs are not prefixed with the source generator ID by default.
- Replace
- For image source attribution, run the following:
python run_classifier.py att \ trained_models/[model_id]/[instance_id].h5 \ dataset/test-[dataset_id]/clean \ run_outputs/[dataset_id] \ --batch_size [batch_size] --image_size [image_size] \ --source [source]- Replace
[source]with the source of interest that your selected model instance is trained to identify (for output formatting only). - Multiclass attribution is currently unsupported.
- Replace
- Inference results are saved as images in
run_outputs/[dataset_id]in individually timestamped folders for each run.
- Most of the codebase is originally derived from the GAN DCT Analysis repository, albeit adapted to accommodate the new scenarios proposed by this paper. Many thanks to the authors for laying the groundwork to accelerate synthetic media forensics research in TensorFlow 2.
- Thanks to the authors behind the GAN Fingerprints repository for providing the pretrained GANs used to generate data for (probably) every work on deepfake attribution since 2019.
- Thanks to Durall et al. (2019) for creating the compact and balanced Faces-HQ dataset during a time when complete representative datasets of 2nd generation GAN images were few and far between. Their dataset is extended with StyleGAN2 images in this project to form FacesHQ+.
- Thanks to DTrimarchi10 for the make_confusion_matrix function to accelerate compilation and analysis of experimental results.
- Thanks to David-Lor for the ThisPersonDoesNotExist API, which is required to facilitate automated acquisition of StyleGAN2 image samples from TPDNE.
- Hardware for experimentation provided by Monash University Malaysia.