Day 08 – Piscine Java
Spring
Takeaways: Today you will learn about enterprise-level Java development and the basics of the Spring framework
Contents
- Chapter I
1.1. Preamble - Chapter II
2.1. General Rules - Chapter III
3.1. Exercise 00 – Spring Context - Chapter IV
4.1. Exercise 01 – JdbcTemplate - Chapter V
5.1. Exercise 02 – AnnotationConfig
Chapter I
Preamble
Spring Framework is an integral part of the most Java-based corporate systems. This framework makes it much easier to configure applications and relate components to each other. Due to this, a developer can fully focus on business logic implementation.
Spring operation principle is fully based on DI/IoC patterns which you should learn about before using this technology.
The central concept in Spring framework is a bean (component) that represents an object inside an ApplicationContext container. The container also creates links between beans.
There are several ways to configure beans:
- Using an xml.file.
- Using a Java configuration (configuring with annotations).
- Combined configuration.
XML configuration allows to change application's behavior without a reassembly. In turn, Java configuration makes code more developer-friendly.
Chapter II
General Rules
-
Use this page as the only reference. Do not listen to any rumors and speculations about how to prepare your solution.
-
Now there is only one Java version for you, 1.8. Make sure that compiler and interpreter of this version are installed on your machine.
-
You can use IDE to write and debug the source code.
-
The code is read more often than written. Read carefully the document where code formatting rules are given. When performing each task, make sure you follow the generally accepted Oracle standards.
-
Comments are not allowed in the source code of your solution. They make it difficult to read the code.
-
Pay attention to the permissions of your files and directories.
-
To be assessed, your solution must be in your GIT repository.
-
Your solutions will be evaluated by your piscine mates.
-
You should not leave in your "src" directory any other file than those explicitly specified by the exercise instructions. It is recommended that you modify your .gitignore to avoid accidents.
-
When you need to get precise output in your programs, it is forbidden to display a precalculated output instead of performing the exercise correctly.
-
Have a question? Ask your neighbor on the right. Otherwise, try with your neighbor on the left.
-
Your reference manual: mates / Internet / Google. And one more thing. There's an answer to any question you may have on Stackoverflow. Learn how to ask questions correctly.
-
Read the examples carefully. They may require things that are not otherwise specified in the subject.
-
Use System.out for output.
-
And may the Force be with you!
-
Never leave that till tomorrow which you can do today ;)
Chapter III
Exercise 00 – Spring Context
| Exercise 00: Spring Context | |
|---|---|
| Turn-in directory | ex00 |
| Files to turn-in | Spring-folder |
Let's implement a loosely-coupled system comprised of a set of components (beans) and compliant with IoC/DI principles.
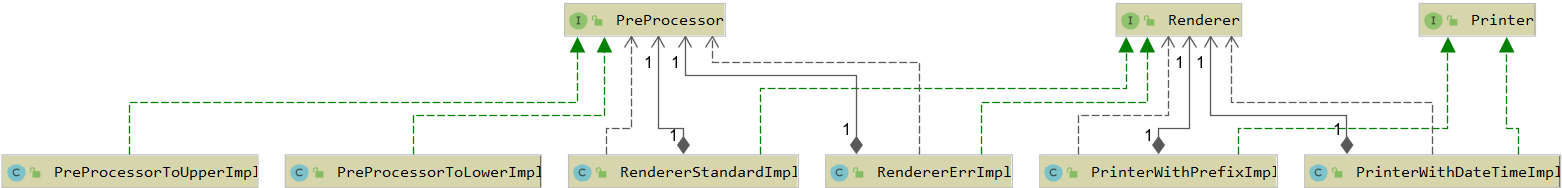
Let's assume there is Printer interface designed to display a specific message.
This class has two implementations: PrinterWithDateTimeImpl and PrinterWithPrefixImpl. The first class outputs messages by specifying output date/time using LocalDateTime, while the second class can be used to set a text prefix for a message.
In turn, both Printer implementations have a dependency on Renderer interface that sends messages onto the console. Renderer also has two implementations: RendererStandardImpl (outputs a message via standard System.out) and RendererErrImpl (outputs messages via System.err).
Renderer also has a dependency on PreProcessor interface that pre-processes messages. Implementation of PreProcessorToUpperImpl translates all letters into upper case, while implementation of PreProcessorToLower translates all letters into lower case.
UML diagram of classes is shown below:
An example of code using these classes in a standard way:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PreProcessor preProcessor = new PreProcessorToUpperImpl();
Renderer renderer = new RendererErrImpl(preProcessor);
PrinterWithPrefixImpl printer = new PrinterWithPrefixImpl(renderer);
printer.setPrefix("Prefix");
printer.print("Hello!");
}
}Running this code will deliver the following result:
PREFIX HELLO!
You need to describe context.xml file for Spring, where all settings for each component and links between them will be specified.
Using these components with Spring looks as follows:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("context.xml");
Printer printer = context.getBean(“printerWithPrefix”, Printer.class);
printer.print("Hello!");
}
}Chapter IV
Exercise 01 – JdbcTemplate
| Exercise 01: JdbcTemplate | |
|---|---|
| Turn-in directory | ex01 |
| Files to turn-in | Service-folder |
JdbcTemplate and its extension NamedParameterJdbcTemplate are convenient mechanisms for working with databases. These classes allow to eliminate writing template code for query execution and processing, as well as the need to intercept exceptions under check.
In addition, they provide a convenient RowMapper concept for ResultSet processing and converting resulting tables into objects.
Now, you need to implement the User model with the following fields:
- Identifier
You also need to implement CrudRepository<T> interface with the following methods:
Optional<T>findById(Long id)List<T>findAll()- void save(T entity)
- void update(T entity)
- void delete(Long id)
UsersRepository interface declared as UsersRepository extends CrudRepository shall contain the following method:
Optional<T>findByEmail(String email)
In addition, two implementations of UsersRepository are required:
UsersRepositoryJdbcImpl (uses standard Statements meachanisms) and UsersRepositoryJdbcTemplateImpl (is based on JdbcTemaplte/NamedParameterJdbcTemaple). Both classes shall accept DataSource object as a constructor argument.
In context.xml file, beans shall be declared for both repository types with different identifiers, as well as two beans of DataSource type: DriverManagerDataSource and HikariDataSource.
In addition, data for connecting to DB shall be specified in db.properties file and included in context.xml using ${db.url} placeholders.
Example of db.properties:
db.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/database
db.user=postgres
db.password=qwerty007
db.driver.name=org.postgresql.Driver
In Main class, operation of findAll method shall be demonstrated using both repositories:
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("context.xml");
UsersRepository usersRepository = context.getBean("usersRepositoryJdbc", UsersRepository.class);
System.out.println(usersRepository.findAll());
usersRepository = context.getBean("usersRepositoryJdbcTemplate", UsersRepository.class);
System.out.println(usersRepository.findAll());
Project structure:
- Service
- src
- main
- java
- school21.spring.service
- models
- User
- repositories
- CrudRepository
- UsersRepository
- UsersRepositoryJdbcImpl
- UsersRepositoryJdbcTemplateImpl
- application
- Main
- models
- school21.spring.service
- resources
- db.properties
- context.xml
- java
- main
- pom.xml
- src
Chapter V
Exercise 02 – AnnotationConfig
| Exercise 02: AnnotationConfig | |
|---|---|
| Turn-in directory | ex02 |
| Files to turn-in | Service-folder |
Now, you need to configure Spring-application configuration mechanisms using annotations. To do so, use the configuration class marked as @Configuration. Inside this class, you need to describe beans for connecting to DataSource DB using @Bean annotation. As in the previous task, connection data shall be located inside db.properties file. You also need to make sure context.xml is not present.
Also implement UsersService/UsersServiceImpl interface/class pair with a dependency on UsersRepository declared in it. Insertion of correct repository bean shall be implemented using @Autowired annotation (similarly, you need to bind DataSource inside repositories). Collisions in automatic binding shall be resolved with @Qualifier annotation.
Beans for UsersService and UsersRepository shall be defined using @Component annotation.
In UsersServiceImpl, implement String signUp(String email)method that registers a new user and saves its details in DB. This method returns a temporary password assigned to the user by the system (this information should also be saved in the database).
To check if your service works correctly, implement an integration test for UsersServiceImp using an in-memory database (H2 or HSQLDB). The context configuration for test environment (DataSource for in-memory database) shall be described in a separate TestApplicatoinConfig class. This test shall check if a temporary password has been returned in signUp method.
Project structure:
- Service
- src
- main
- java
- school21.spring.service
- config
- ApplicationConfig
- models
- User
- repositories
- CrudRepository
- UsersRepository
- UsersRepositoryJdbcImpl
- UsersRepositoryJdbcTemplateImpl
- services
- UsersService
- UsersServiceImpl
- application
- Main
- config
- school21.spring.service
- resources
- db.properties
- java
- test
- java
- school21.spring.service
- config
- TestApplicationConfig
- services
- UsersServiceImplTest
- config
- school21.spring.service
- java
- main
- pom.xml
- src