pico-cs is a proof-of-concept for a model railway command station talking DCC (Digital Command Control) defined by the NMRA DCC working group and using the Raspberry Pi Pico as DCC signal generator.
pico-cs is intended for skilled users with expert levels of model railway electronics and protocol knowledge.
- Its support of programmable IO (PIO) enables implementing the core DCC protocol within a few lines of assembler code
- Due to its dual cores the DCC signal generation and the command interface are implemented using different cores being run in parallel
- Its small form factor and cost effectiveness allows and supports multiple command stations to be used as part of the model railroad layout
- Its great ducumentation
- The Pico W WiFi capabilities to operate the command station remotely via a TCP/IP connection
- And last but not least the fun using it
- Raspberry Pi Pico / Pico W
- A PC, Laptop, Raspberry Pi or any suitable device with an USB interface to flash the firmware and operate the command station via serial over USB and / or WiFi
- A model railway booster
- A model railroad locomotive roller test stand
- A DCC decoder equiped test locomotive
As there is a lot of booster alternatives (motor shield, H-bridge, commercial booster, ...) the selection and connection options to the Pico goes beyond the scope of this document. You might find potential solutions searching the internet.
Voltage levels:
- Pico DCC signal output is on GP2 with 3.3V level
- As most digital booster DCC inputs would not work with 3.3V (please consult booster documentation) one need to choose a safe and reliable solution for level conversion
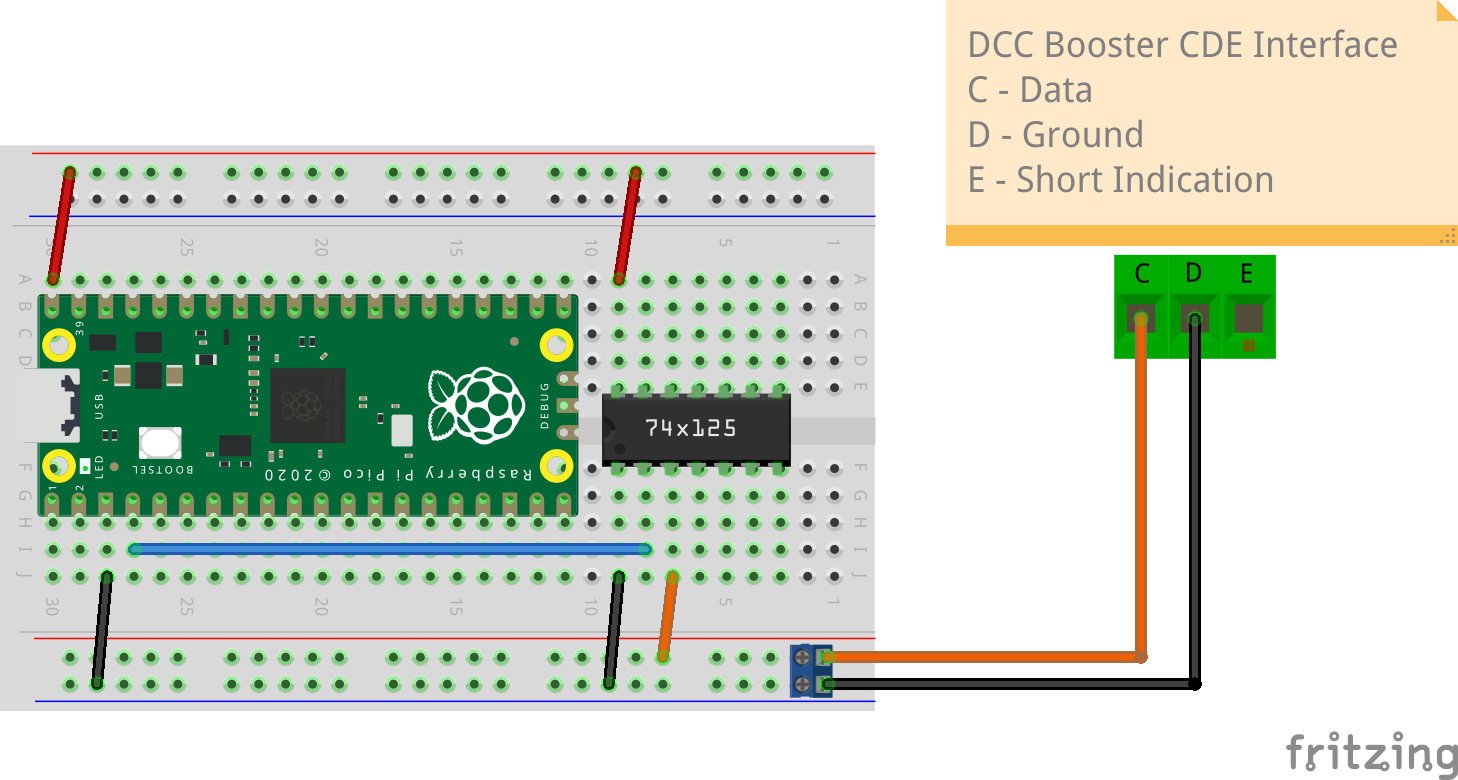
- Example with SN74HCT125N as level shifter (Fritzing circuit diagram)
Please be aware that not all DCC decoders do support all of the DCC commands. The pico-cs command station is using the DCC commands which most standard compliant DCC decoders should be able to understand. Nonetheless some decoders
- do have issues with main track programming
- do behave weird in case functions are used not supported by the decoder or writing CVs in general
Please be cautious and test all loco decoders on a roller test stand before using on track.
To mitigate some of the function setting issues the pico-cs command station is only refreshing functions which were explicitly used via the protocol.
- Connect the Raspberry Pi Pico to your PC via an USB cable
- Build the pico-cs firmware
- Install firmware (Pico: cs.uf2, Pico W: cs_w.uf2) via BOOTSEL mode (see Raspberry Pi Pico documentation)
- On macOS Ventura copying via drag&drop in Finder was broken but seems to work again with version 13.1 - anyway, copying the file via the command line is always an option:
cp -X cs.uf2 /Volumes/RPI-RP2/
cp -X cs_w.uf2 /Volumes/RPI-RP2/
- Use a terminal emulation tool supporting serial over USB communication like
- the Serial Monotor of the Arduino IDE or
- the Serial Monitor extension of Visual Studio Code
- Set the baud rate to 115200 and <CR> (Carriage Return) as command / message ending character
- The firmware uses the following Raspberry Pi Pico GPIOs:
- GP2: DCC signal output
- GP3: DCC signal output (inverted)
- GP4: DCC signal power
- GP5: DCC signal power (inverted)
For building there is two options available:
- local build: install the toolchain and build on your local machine
- docker build: no toolchain installation but a running docker environment on your local machine is required
To build the firmware the Raspberry Pi Pico C/C++ SDK and toolchain needs to be installed. For details please consult the Raspberry Pi Pico documentation.
As the binary for the Pico W including the WiFi and network capabilities is significant larger and the WiFi SSID and a WiFi password is needed two firmware versions are build:
git clone https://github.com/pico-cs/firmware.git
cd firmware/src
Pico:
mkdir pico_build
cd pico_build
cmake .. -DPICO_BOARD=pico
make
- firmware: cs.uf2
Pico W:
export PICO_CS_WIFI_SSID="MyWifiName"
export PICO_CS_WIFI_PASSWORD="MyPassword"
export PICO_CS_TCP_PORT= 4242
mkdir pico_w_build
cd pico_w_build
cmake .. -DPICO_BOARD=pico_w
make
- if the TCP_PORT environment varible (PICO_CS_TCP_PORT) is not set the default port 4242 is used.
- firmware: cs_w.uf2
With the help of the picotool the firmware binaries can be inspected:
./picotool info -a <path to firmware>/firmware/src/pico_build/cs.uf2
File <path to firmware>/firmware/src/pico_build/cs.uf2:
Program Information
name: cs
version: <firmware version>
web site: https://github.com/pico-cs
description: pico-cs DCC command station
features: Refresh buffer size 128
double reset -> BOOTSEL
UART stdin / stdout
USB stdin / stdout
binary start: <start address>
binary end: <end address>
Fixed Pin Information
0: UART0 TX
1: UART0 RX
2: Main track: DCC signal output
3: Main track: DCC signal output (inverted)
4: Main track: DCC signal power
5: Main track: DCC signal power (inverted)
25: On-board LED
Build Information
sdk version: <sdk version>
pico_board: pico
boot2_name: boot2_w25q080
build date: <build date>
build attributes: Release
./picotool info -a <path to firmware>/firmware/src/pico_w_build/cs_w.uf2
File <path to firmware>/firmware/src/pico_w_build/cs_w.uf2:
Program Information
name: cs_w
version: <firmware version>
web site: https://github.com/pico-cs
description: pico-cs DCC command station
features: WiFi SSID MyWiFiSSID password MyWiFiPassword
TCP port 4242
Refresh buffer size 128
double reset -> BOOTSEL
UART stdin / stdout
USB stdin / stdout
binary start: <start address>
binary end: <end address>
Fixed Pin Information
0: CYW43 LED, UART0 TX
1: UART0 RX
2: Main track: DCC signal output
3: Main track: DCC signal output (inverted)
4: Main track: DCC signal power
5: Main track: DCC signal power (inverted)
Build Information
sdk version: <sdk version>
pico_board: pico_w
boot2_name: boot2_w25q080
build date: <build date>
build attributes: Release
Please see protocol for information about the implemented text protocol.
- Pico firmware implementing DCC commands to control model railway locomotives
- Simple command human readable and debug friendly text protocol
- which can be used directly via serial terminal programs supporting serial over USB
- and easily integrated into any programming language or tool supporting serial over USB communication
- Pico W WiFi support
- Go Client library
- MQTT gateway
Copyright 2021-2023 Stefan Miller and pico-cs contributers. Please see our LICENSE for copyright and license information. Detailed information including third-party components and their licensing/copyright information is available via the REUSE tool.