- junit
- dom4j
InputStream is = null;
try {
ClassLoader cl = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
is = cl.getResourceAsStream(configFile);
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(is);
Element root = doc.getRootElement();
Iterator iter = root.elementIterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Element el = (Element) iter.next();
String id = el.attributeValue(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
String beanClassName = el.attributeValue(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE);
BeanDefinition db = new GenericBeanDefinition(id, beanClassName);
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(id, db);
}
}BeanDefinition bd = this.getBeanDefinition(beanID);
if (bd == null) {
return null;
}
ClassLoader cl = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
String beanClassName = bd.getBeanClassName();
try {
Class<?> clz = cl.loadClass(beanClassName);
return clz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
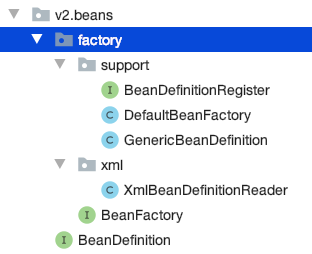
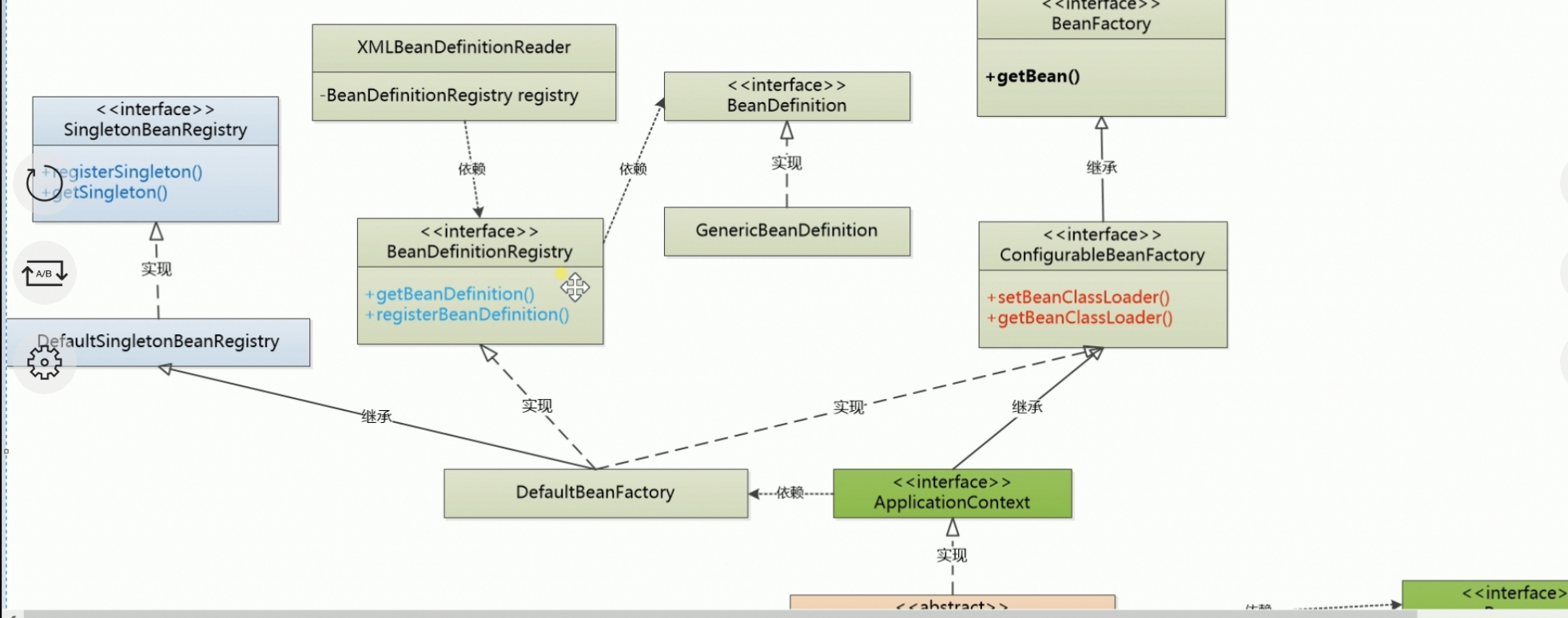
}DefaultBeanFactory 实现了 BeanDefinitionRegister 与 BeanDefinitionRegister
xmlBeanDefinitionReader 负责解析 xml 文件 并将其存入 factory
@Test
public void testGetBean(){
DefaultBeanFactory factory = new DefaultBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
reader.LoadBeanDefinitionReader("petstore-v1.xml");
BeanDefinition definition = factory.getBeanDefinition("petStore");
Assert.assertEquals("de.o0o0o0.service.v1.PetStoreService", definition.getBeanClassName());
PetStoreService service = (PetStoreService) factory.getBean("petStore");
Assert.assertNotNull(service);
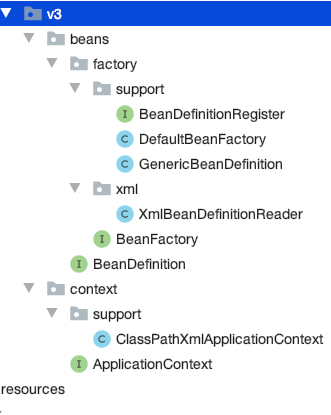
}V3 在 v2 的基础上 增加 context 包 ApplicationContext 继承了 BeanFactory 接口(拥有 getBean 方法)
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 实现了 ApplicationContext 接口
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
private DefaultBeanFactory factory = null;
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configFile) {
factory = new DefaultBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
reader.LoadBeanDefinitionReader(configFile);
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanID) {
return factory.getBean(beanID);
}
} @Test
public void testGetBean(){
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("petstore-v1.xml");
PetStoreService storeService = (PetStoreService) ctx.getBean("petStore");
Assert.assertNotNull(storeService);
}至此,使用方法就和原生 spring 差不多了。
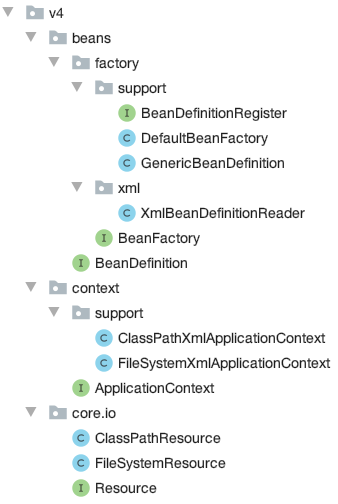
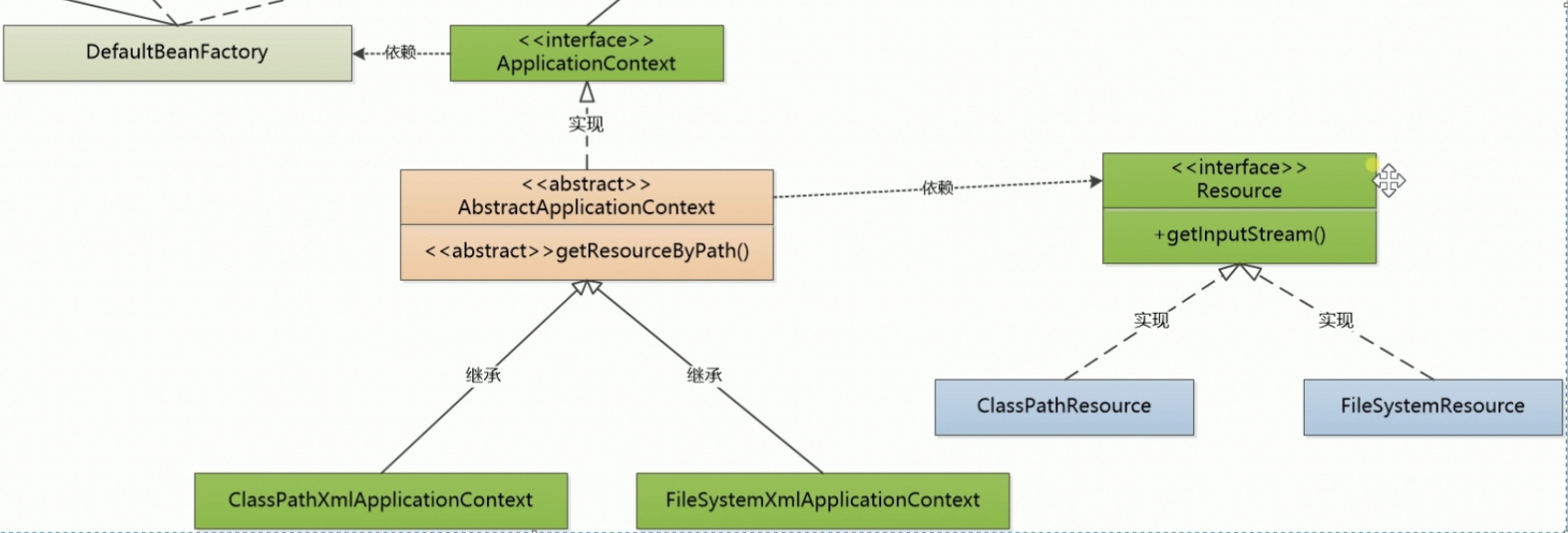
增加了用于读取文件的 Resource 接口 放在 core.io 包下
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader {
private static final String ATTRIBUTE_ID = "id";
private static final String ATTRIBUTE_CLASS = "class";
private BeanDefinitionRegister register;
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegister register) {
this.register = register;
}
public void LoadBeanDefinitionReader(Resource resource){
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
try {
Document doc = reader.read(inputStream);
Element root = doc.getRootElement();
Iterator iterator = root.elementIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Element el = (Element) iterator.next();
String id = el.attributeValue(ATTRIBUTE_ID);
String beanClassName = el.attributeValue(ATTRIBUTE_CLASS);
BeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition(id, beanClassName);
this.register.registerBeanDefinition(id, bd);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("load configFile failed", e);
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader {
private static final String ATTRIBUTE_ID = "id";
private static final String ATTRIBUTE_CLASS = "class";
private BeanDefinitionRegister register;
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegister register) {
this.register = register;
}
public void LoadBeanDefinitionReader(Resource resource){
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
try {
Document doc = reader.read(inputStream);
Element root = doc.getRootElement();
Iterator iterator = root.elementIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Element el = (Element) iterator.next();
String id = el.attributeValue(ATTRIBUTE_ID);
String beanClassName = el.attributeValue(ATTRIBUTE_CLASS);
BeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition(id, beanClassName);
this.register.registerBeanDefinition(id, bd);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("load configFile failed", e);
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}public class FileSystemResource implements Resource {
private final String path;
private final File file;
public FileSystemResource(String path) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must be not null");
this.path = path;
this.file = new File(path);
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws FileNotFoundException {
return new FileInputStream(file);
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "file [" + this.file.getAbsolutePath() + "]";
}
}public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
private DefaultBeanFactory factory;
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configFile) {
factory = new DefaultBeanFactory();
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(configFile);
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
reader.LoadBeanDefinitionReader(resource);
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanID) {
return factory.getBean(beanID);
}
} @Test
public void testClassPathResource() {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("petstore-v1.xml");
PetStoreService storeService = (PetStoreService) ctx.getBean("petStore");
Assert.assertNotNull(storeService);
}
@Test
public void testFileSystemResource() {
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("/Users/d.glua/IdeaProjects/liteSpring/src/test/resources/petstore-v1.xml");
PetStoreService storeService = (PetStoreService) ctx.getBean("petStore");
Assert.assertNotNull(storeService);
}V4 中两个 applicationContext 的实现有大块的重复代码,可以用模版方法抽象出一个新类 AbstractApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
private DefaultBeanFactory factory;
public AbstractApplicationContext(String path) {
factory = new DefaultBeanFactory();
Resource resource = this.getResourceByPath(path);
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
reader.LoadBeanDefinitionReader(resource);
}
abstract Resource getResourceByPath(String path);
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanID) {
return factory.getBean(beanID);
}
}public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String path) {
super(path);
}
@Override
Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathResource(path);
}
}如此,让整个代码无比清爽
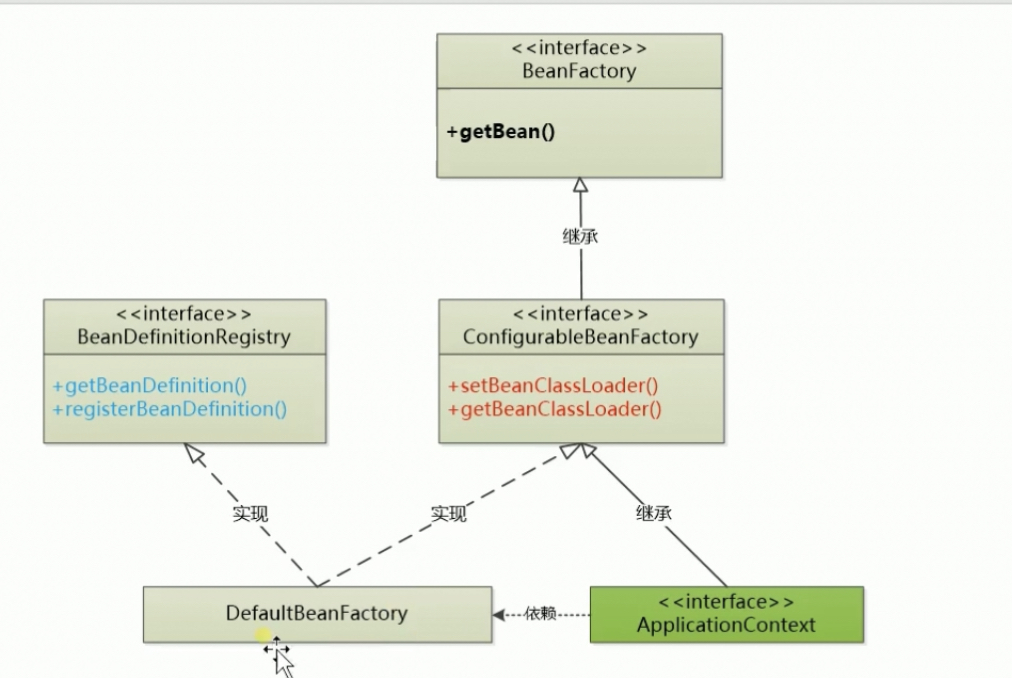
前几个版本中 classLoader 都是由 ClassUtils 中写死的 ClassLoader 这样并不好
Spring 添加了一个 ConfigurableBeanFactory 接口使 factory 拥有可配置性
public class DefaultBeanFactory implements ConfigurableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegister {
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
public BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanID) {
return this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanID);
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String id, BeanDefinition bd) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(id, bd);
}
public Object getBean(String beanID) {
BeanDefinition bd = this.getBeanDefinition(beanID);
if (bd == null) {
throw new BeanCreationException("Bean Definition Does Not Exist");
}
ClassLoader cl = this.getBeanCLassLoader();
String beanClassName = bd.getBeanClassName();
try {
Class<?> clz = cl.loadClass(beanClassName);
return clz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeanCreationException("Create Bean For Class '" + beanClassName + "' failed");
}
}
@Override
public void seatBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = beanClassLoader;
}
@Override
public ClassLoader getBeanCLassLoader() {
return this.beanClassLoader != null ? this.beanClassLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
}public interface ApplicationContext extends ConfigurableBeanFactory {
}public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
private DefaultBeanFactory factory;
private ClassLoader BeanClassLoader;
public AbstractApplicationContext(String path) {
factory = new DefaultBeanFactory();
factory.setBeanClassLoader(this.getBeanCLassLoader());
Resource resource = this.getResourceByPath(path);
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
reader.LoadBeanDefinitionReader(resource);
}
abstract Resource getResourceByPath(String path);
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanID) {
return factory.getBean(beanID);
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
this.BeanClassLoader = beanClassLoader;
}
@Override
public ClassLoader getBeanCLassLoader() {
return this.BeanClassLoader != null ? this.BeanClassLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
}public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String path) {
super(path);
}
@Override
Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathResource(path, this.getBeanCLassLoader());
}
}public interface BeanDefinition {
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = "singleton";
String SCOPE_DEFAULT = "";
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = "prototype";
String getBeanClassName();
boolean isSingleton();
boolean isPrototype();
void setScope(String scope);
String getScope();
}public class GenericBeanDefinition implements BeanDefinition {
private String id;
private String beanClassName;
private boolean singleton = true;
private boolean prototype = false;
private String scope = SCOPE_DEFAULT;
public GenericBeanDefinition(String id, String beanClassName) {
this.id = id;
this.beanClassName = beanClassName;
}
public String getBeanClassName() {
return this.beanClassName;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return this.singleton;
}
@Override
public boolean isPrototype() {
return this.prototype;
}
@Override
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
this.singleton = scope.equals(SCOPE_SINGLETON) || scope.equals(SCOPE_DEFAULT); // 空也要判断
this.prototype = scope.equals(SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);
}
@Override
public String getScope() {
return this.scope;
}
}if(el.attribute(ATTRIBUTE_SCOPE) != null){
String scope = el.attributeValue(ATTRIBUTE_SCOPE);
bd.setScope(scope);
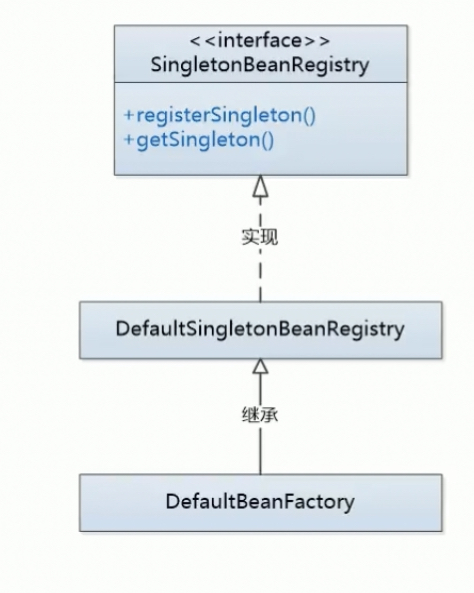
}通过 SingletonBeanRegister 让 DefaultBeanFactory 有 实现 singleton 的能力
public interface SingletonBeanRegister {
void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject);
Object getSingleton(String beanName);
}public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegister implements SingletonBeanRegister {
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "'beanName' must be not null");
Object oldObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (oldObject != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not register object [" + singletonObject + "] under" +
" bean name '" + beanName + "': there is already object [" + oldObject + "]");
}
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
}
@Override
public Object getSingleton(String beanName) {
return this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
}
}public class DefaultBeanFactory extends DefaultSingletonBeanRegister
implements ConfigurableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegister {
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
public BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanID) {
return this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanID);
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String id, BeanDefinition bd) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(id, bd);
}
public Object getBean(String beanID) {
BeanDefinition bd = this.getBeanDefinition(beanID);
if (bd == null) {
return null;
}
if (bd.isSingleton()) {
Object bean = this.getSingleton(beanID);
if (bean == null) {
bean = createBean(bd);
this.registerSingleton(beanID, bean);
}
return bean;
}
return createBean(bd);
}
private Object createBean(BeanDefinition bd) {
ClassLoader cl = this.getBeanCLassLoader();
String beanClassName = bd.getBeanClassName();
try {
Class<?> clz = cl.loadClass(beanClassName);
return clz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeanCreationException("Create Bean For Class '" + beanClassName + "' failed");
}
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = beanClassLoader;
}
@Override
public ClassLoader getBeanCLassLoader() {
return this.beanClassLoader != null ? this.beanClassLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
}新加依赖
- log4j
- commons-logging
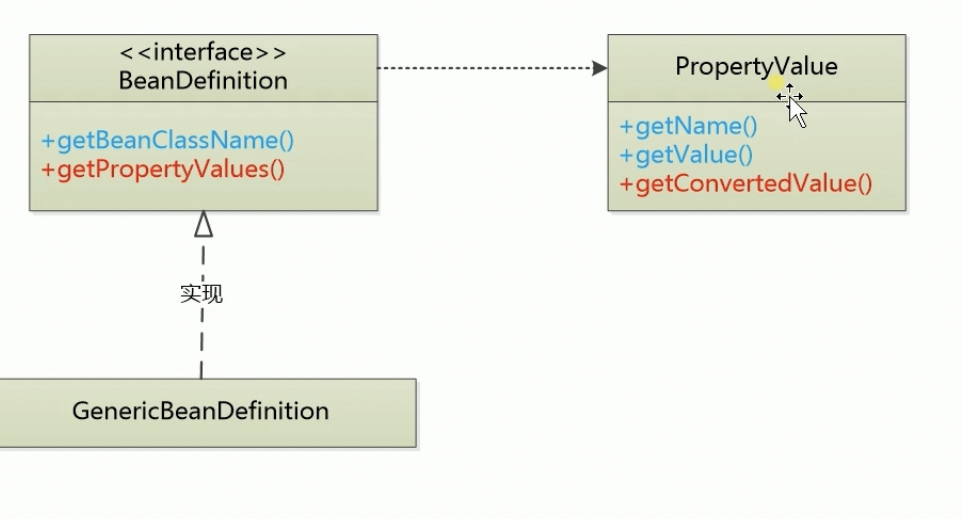
添加一个额外的类叫 PropertyValue 保存 需要注入的 property 信息
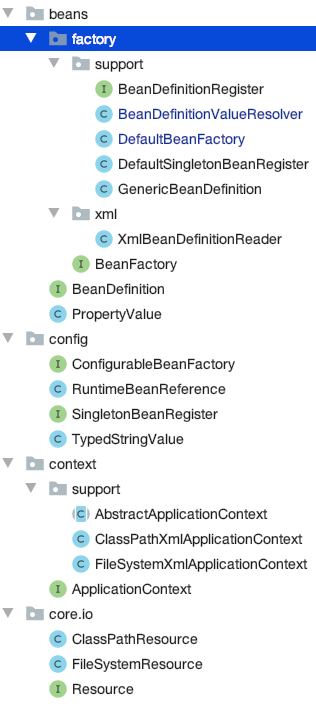
整体类图
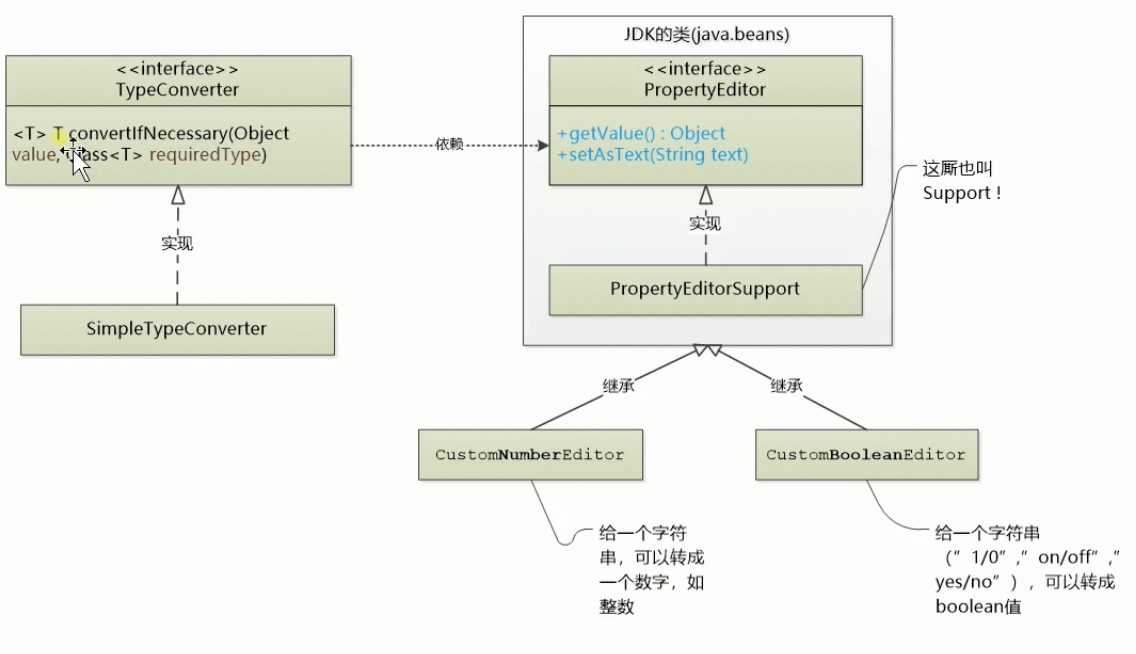
类型转换
-
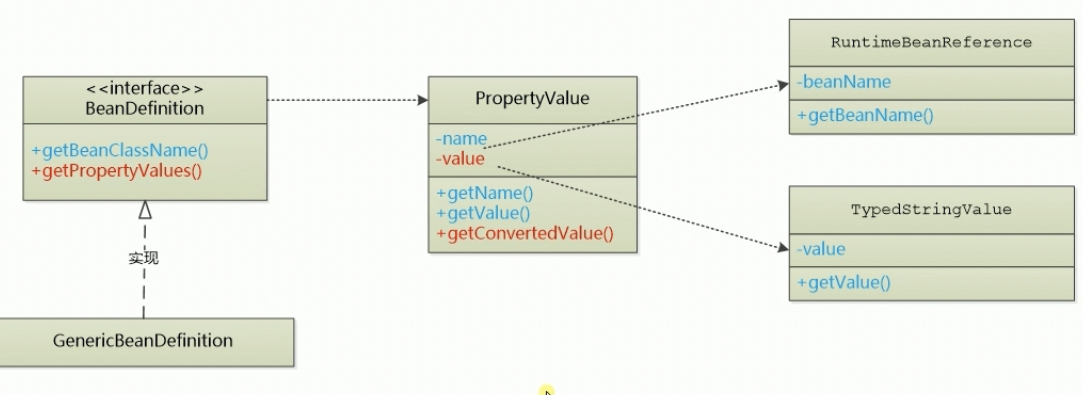
PropertyValue主要有name、value属性, 前者储存被注入的属性的名称,后者储存被注入的类的类型(RuntimeBeanReference或者TypedStringValue)public class PropertyValue { private final String name; private final Object value; private boolean converted = false; private Object convertedValue; public PropertyValue(String name, Object value) { this.name = name; this.value = value; } public String getName() { return name; } public Object getValue() { return value; } public synchronized boolean isConverted() { return this.converted; } public synchronized Object getConvertedValue() { return convertedValue; } public synchronized void setConvertedValue(Object convertedValue) { this.converted = true; this.convertedValue = convertedValue; } }
-
RuntimeBeanReference、TypedStringValue各有一个value属性,储存需要注入的属性的类名或值(ref与value)public class RuntimeBeanReference { private final String beanName; public RuntimeBeanReference(String beanName) { this.beanName = beanName; } public String getBeanName() { return this.beanName; } }
-
BeanDefinitionValueResolver持有一个Factory根据PropertyValue储存的value属性 从factory取得类。public class BeanDefinitionValueResolver { private final DefaultBeanFactory factory; public BeanDefinitionValueResolver(DefaultBeanFactory factory) { this.factory = factory; } public Object resolveValueIfNecessary(Object value) { if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanReference) { String refName = ((RuntimeBeanReference) value).getBeanName(); return factory.getBean(refName); } else if (value instanceof TypedStringValue) { return ((TypedStringValue) value).getValue(); } // TODO throw new RuntimeException("the value " + value + " has not implemented"); } }
BeanDefinition 添加一个 PropertyValue map 用于储存 bean 的 set 注入参数
// 解析
private void parsePropertyElement(Element element, BeanDefinition definition) {
Iterator iterator = element.elementIterator(ELEMENT_PROPERTY);
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Element ele = (Element) iterator.next();
String propertyName = ele.attributeValue(ATTRIBUTE_NAME);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(propertyName)) {
logger.fatal("Tag 'properties' must have a 'name' attribute");
return;
}
Object val = parsePropertyValue(ele, definition, propertyName);
PropertyValue pv = new PropertyValue(propertyName, val);
definition.getPropertyValues().add(pv);
}
}
private Object parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition definition, String propertyName) {
String elementName = (propertyName != null) ?
"<property> element for property '" + propertyName + "'" :
"<constructor-arg> element";
boolean hasRefAttribute = ele.attribute(ATTRIBUTE_REF) != null;
boolean hasValueAttribute = ele.attribute(ATTRIBUTE_VALUE) != null;
// 引用类型
if (hasRefAttribute) {
String refName = ele.attributeValue(ATTRIBUTE_REF);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
logger.error(elementName + " contains empty 'ref' attribute");
}
return new RuntimeBeanReference(refName);
// 字符类型
} else if (hasValueAttribute) {
TypedStringValue value;
value = new TypedStringValue(ele.attributeValue(ATTRIBUTE_VALUE));
return value;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException(elementName + "must specify a ref or value");
}
}读取 BeanDefinition 的 PropertyValueMap 列表,调用 BeanDefinitionValueResolver 方法获取类的实体,然后用 JavaBean 的方法完成注入。
private Object createBean(BeanDefinition bd) {
// 构建实例
Object bean = instantiateBean(bd);
// 设置属性
populateBean(bd, bean);
return bean;
}
private void populateBean(BeanDefinition bd, Object bean) {
List<PropertyValue> values = bd.getPropertyValues();
if (values == null || values.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
BeanDefinitionValueResolver resolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this);
try {
for (PropertyValue value : values) {
String propertyName = value.getName();
Object originalValue = value.getValue();
Object resolverValue = resolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(originalValue);
// 调用bean 的set 方法注入参数
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean.getClass());
PropertyDescriptor[] pds = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDescriptor descriptor : pds) {
if (descriptor.getName().equals(propertyName)) {
descriptor.getWriteMethod().invoke(bean, resolverValue);
break;
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeanCreationException("failed to obtain BeanInfo from class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]");
}
}
private Object instantiateBean(BeanDefinition bd) {
ClassLoader cl = this.getBeanCLassLoader();
String beanClassName = bd.getBeanClassName();
try {
Class<?> clz = cl.loadClass(beanClassName);
return clz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeanCreationException("Create Bean For Class '" + beanClassName + "' failed");
}
}