This document lays out quick help for these header files:
- myc.h - new string and other utility functions for C
- mydb.h - an Sqlite3 c template and three new functions
- mynet.h - a small Internet library with 4 new functions
NOTE: myc.h also includes most of the common C headers.
compiled myc.h is about 52k
between • charat • center • chomp • compare • concat • contains • contvars • string_cat • string_cpy • string_new • string_del • string_def • string_rsz • string_wrp • decrypt • deletechar • dollar • endswith • encrypt • equals • equalsignore • field • indexof • insert • insert_new • isnum_us • lastcharat • lastindexof • lastsub • lof • lowercase • lpad • ltrim • replace • replace_new • replacechar • rof • rpad • rtrim • startswith • strcon • strrev • strtype • substr • trim • uppercase • urlencode
List - static Array of strings
list_del • list_dir • list_display • list_def • list_find • list_init • list_inject • list_read • list_redef • list_remove • list_io • list_split • list_string • list_update
intstr • intstr_new • lngstr • lngstr_new • dblstr • dblstr_new
isbinary • file_exists • filesize • filecopy • filedelete • filemove • isfile • getbasename • getbasepath • getfullpath • getini • open_for_append • open_for_read • open_for_write • readfile • textlines • writefile
ARRSIZE • cbcopy • cbpaste • colors • date • flogf • timeout • multifree • ERRMSG • isort • dsort • ssort • randini • randnum
zenmsg • zenfile • zenform • zenlist • zentry • zentext • zenotify • zen
mydb_count • mydb_names • mydb_open
webbrowser • webget • webpage • webpost
The standard C string.h library has fifteen or so functions for string manipulation.
This section is a quick reference for the standard string.h library.
copy n chars from ct to s (may overlap)
copy n chars from ct to s (may overlap)
compare n chars of cs with ct
pointer to first c in first n chars of cs
put c into first n chars of s
copies the string s2 into the character array s1. The value of s1 is returned.
copies at most n characters of the string s2 into the character array s1. The value of s1 is returned.
appends the string s2 to the end of character array s1. The first character from s2 overwrites the '\0' of s1. The value of s1 is returned.
appends at most n characters of the string s2 to the end of character array s1. The first character from s2 overwrites the '\0' of s1. The value of s1 is returned.
returns a pointer to the first instance of c in s. Returns a NULL pointer if c is not encountered in the string.
returns a pointer to the last instance of c in s. Returns a NULL pointer if c is not encountered in the string.
returns a pointer to a duplicated string allocating memory in the heap. Use free() to free memory.
compares the string s1 to the string s2. The function returns 0 if they are the same, a number < 0 if s1 < s2, a number > 0 if s1 > s2.
compares up to n characters of the string s1 to the string s2. The function returns 0 if they are the same, a number < 0 ifs1 < s2, a number > 0 if s1 > s2.
returns the length of the longest substring of s1 that begins at the start of s1 and consists only of the characters found in s2. size_t strcspn( char *s1, const char *s2 ) returns the length of the longest substring of s1 that begins at the start of s1 and contains none of the characters found in s2.
determines the length of the string s. Returns the number of characters in the string before the '\0'.
returns a pointer to the first instance in s1 of any character found in s2. Returns a NULL pointer if no characters from s2 are encountered in s1.
returns a pointer to the first instance of string s2 in s1. Returns a NULL pointer if s2 is not encountered in s1.
repeated calls to this function modifies string s1 by breaking it into "tokens"--that is the string is broken into substrings, each terminating with a '\0', where the '\0' replaces any characters contained in string s2. The first call uses the string to be tokenized as s1; subsequent calls use NULL as the first argument. A pointer to the beginning of the current token is returned; NULL is returned if there are no more tokens. consider using list... in myc.h. Warning: this changes the original string!
STRING functions myc.h ^
I've tried not to duplicate the existing string.h functions. The goal here is to extend (and simplify) string manipulation in C.
.
Obtains a substring found between to other substrings. Returns an index to the next position beyond the second delimiting string. Returns -1 on not found or failure.
p = between(subs, page, "<p>", "</p>", 0);
// returns the text between the paragraph tags.Finds and returns the index of a character. On failure returns -1.
char * s = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit";
printf("index of 'm' found at: %li\n", strchr(s, 'm') - s); // using string.h function
// find index of 'm' with charat
printf("index of 'm' found at: %i\n", charat(s, 'm')); // index of 'm' found at: 4Centers a string within a larger string.
The initialized length of "space" must be greater than or equal to "n"
which is the final length of "space" including "str".
Returns the string with record separators removed from the end of the string.
Returns true or false given two strings and a conditional operator:
| symbol | macro | macro |
|---|---|---|
| ">" | GT | GreaterThan |
| "<" | LT | LessThan |
| ">=" | GTE | GreaterThanOrEqual |
| "<=" | LTE | LessThanOrEqual |
| "==" | EQ | Equal |
| "!=" | NEQ | NotEqual |
if (compare("Dogs", ">=", "Cats"))
puts("Dogs are at least equal to Cats");
if (compare("Cats", LessThan, "Dogs"))
...
if (compare(somestring, NEQ, someotherstring)) { ...Note: only the "symbols == < > <= >= !=" may be used in variables
Concatenate a variable number of strings.
END must be used for the last argument.
Warning: the destination buffer must initialized large enough to hold all the concatenations.
char s[MAX_L];
strcpy(s, "Ms ");
concat(s, "Mary ", "Elizabeth ", "Smith", END);
puts(s); // Ms Mary Elizabeth SmithReturns a count of the number of substrings found. Returns 0 if none found.
char line[] = "sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore";
printf("%d\n", contains(line, "id")); // 2
printf("%d\n", contains(line, "e")); // 4Returns a count of the number of delimited variables or tokens found in a C string. Returns 0 if none found. Ignores delimiters within double quotes.
Returns a pointer to a new string allocated to size length and initialized with all fill character. Uses the string struct.
typedef struct string {
size_t length; // allocated length
char *value;
} string;Returns a pointer to a new string allocated to its size. Uses the string struct.
string newstring = string_new("Hello World!");
printf("%s - %ld\n", newstring.value, newstring.length);
string_del(newstring);Returns a new string variable re-allocated from an existing string.
string s = string_def(10, '\0');
string_cpy(s, "Hello");
puts(s.value);
s = string_rsz(s, 20);
strcat(s.value, " Universe");
puts(s.value); // Hello Universe
string_del(s);Concatenates data to a predefined "string" string
with boundary checking.
Copies a string into a predefined
"string" string with boundary checking.
Alternative to strncpy.
string s = string_def(32, '\0');
string_cpy(s, "Hello World");
puts(s.value);
string_del(s);Frees memory for a string allocated with string_new or string_wrp.
Reformats lines of text into separate lines of size length. Lines are created on word boundaries. Returns a new string with memory allocated to hold the new block of text (string.)
char lines[] = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,\nconsectetur adipiscing elit,\nsed do . . .";
string wrapped = string_wrp(lines, 30, '\n');
puts(wrapped.value);
printf("allocated: %ld\n", wrapped.length);
string_del(wrapped);
/* OUTPUT:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
consectetur adipiscing elit,
sed do eiusmod tempor
incididunt ut labore et dolore
magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim
veniam, quis nostrud
exercitation ullamco laboris
nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo
consequat.
allocated: 255
*/Decrypts a buffer (from encrypt() function) into another plain text buffer.
Returns the plain text buffer.
Use a plain text key of less than 50 characters.
see encrypt
size_t fsize = filesize(fi); // get size of input file
string s1 = string_def(fsize, '\0'); // create work buffer input
string s2 = string_def(fsize, '\0'); // create work buffer output
if (readfile(s1.value, fi) == -1) {
puts("read input file failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (action == 'e') {
printf("encrypting %s...\n", fi);
encrypt(s2.value, s1.value, key);
} else if (action == 'd') {
printf("decrypting %s...\n", fi);
decrypt(s2.value, s1.value, key);
}
printf("%s size=%ld\n", fi, fsize);
writefile (s2.value, outfile, false);
string_del(s1);
string_del(s2);Removes all target characters from a string.
Set starting index.
Limit deletions or 0 means no limit.
char rec[] = "\"Edgar\", Allan , Poe,, \"American Author\"";
char data[100];
printf("%s\n", deletechar(data, rec, "\"", 12, 2));
// "Edgar", Allan , Poe,, American Author
printf("%s\n", deletechar(data, rec, "\"", 0, 2));
// Edgar, Allan , Poe,, "American Author"
deletechar(data, data, "Aaeiou\"", 0, 0);
puts(data); // Edgr, lln , P,, mrcn thr
deletechar(data, data, "Edgr, ", 0, 0);
puts(data); // llnPmcnthReturns a formatted US currency dollar amount.
- type: 1 = no $ and no separator
- type: 2 = yes $ and no separator
- type: 3 = yes $ and yes separator
The formatted amount is returned right justified in the specified field size.
Warning: make sure the buffer is large enough to hold the formatted
dollar amount with any padding
Uses a substitution cipher similar to the Vigenère cipher.
Encrypts a pre-defined plain text buffer into another buffer.
Returns the encrypted buffer.
Use a plain text key of less than 50 characters.
see decrypt
Returns true if string ends with specified substring, otherwise returns false.
Returns true if strings are equal, otherwise returns false.
Returns true if strings are equal reguardless of any case differences, otherwise returns false.
Returns a substring at column n within a delimited string. When delimiter is a ' ' consecutive spaces act as a single delimiter. When strip is true leading and trailing whitespace is removed. Delimiters are ignored inside of double quotes. Double quotes are NOT REMOVED in the result. See deletechar function to remove quote characters. The original string is preserved. Returns NULL for an invalid column index.
char rec[] = "Author, \"Edgar, Allan, Poe\", American";
char data[100];
void main() {
for (int x=0; x < 3; x++) {
printf("field %d: [%s]\n", x,
field(data, rec, ',', x, true));
}
/* output:
field 0: [Author]
field 1: ["Edgar, Allan, Poe"]
field 2: [American]
*/
for (int x=0; x < 3; x++) {
printf("field %d: [%s]\n", x,
field(data, rec, ' ', x, true));
}
/* output:
field 0: [Author,]
field 1: ["Edgar, Allan, Poe",]
field 2: [American]
*/
}Returns the index of a substring within a string. If not found returns -1.
Inserts a substring into a string at index.
The new string is copied into the first argument and returned.
Warning: the buffer must be large enough to hold the original string and the inserted string.
char text[] = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit";
char buf[120];
insert(buf, text, " amor", 26);
puts(buf); //Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet amor, consectetur adipiscing elit
puts(insert(buf, text, "\n", 28));
// Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
// consectetur adipiscing elit
puts(insert(buf, text, "prepended ", 0));
// prepended Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit
puts(insert(buf, text, " appended.", strlen(text))); //
// Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit appended.Inserts a substring into a string at index. Returns a pointer to the new string allocated in the heap. Note: use the standard c 'free' function to deallocate.
char text[] = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit";
puts(text);
char *buf = insert_new(text, " amor", 26);
puts(buf);
free(buf);
/* OUTPUT
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet amor, consectetur adipiscing elit
*/Returns the last index of some character in a string. If not found returns -1.
Return true if the string argument is numeric (whole or decimal) (US only).
Returns the last index of a substring within a string. If not found returns -1.
Returns a pointer to a substring to the left of some delimiting string. A starting offet may be used or set to 0. Also see rof.
char buf[MAX_L];
char *line = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit";
void main () {
lof(buf, line, "amet, ", 0); // [Lorem ipsum dolor sit ]
printf("[%s]\n", buf);
printf("[%s]\n", rof(buf, line, "amet, ", 0));
// [consectetur adipiscing elit]
}Returns the string in lower case.
Returns the string with trailing whitespace removed.
Returns a string with added left padding. The padding (filler) is another string which is repeated n times. Warning: the resulting buffer must be large enough to hold the original string and the padding.
Replaces substrings within a string. Set starting index and limit replacements or set to 0, no limit. Warning: the resulting buffer must be large enough to hold the original string and the replacements.
char mystr[64] = "The long and winding road.";
char newstr[128];
puts(replace(newstr, mystr, " ", ", ", 8, 1));
// The long, and winding road.
replace(newstr, newstr, "and ", "", 0, 0);
puts(newstr); // The long, winding road.Replaces substrings within a string. Limit replacements or set to 0, no limit. Returns a pointer to the new string allocated in the heap. Note: use the standard c 'free' function to deallocate.
char mystr[32] = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet";
char * newstr = replace_new(mystr,
"dolor",
"labore et dolore magna",
0, // start
0); // how many
printf("[%s] %ld\n", newstr, strlen(newstr));
// [Lorem ipsum labore et dolore magna sit amet] 43
free(newstr);Replaces characters within a string. Limit replacements or set to 0, no limit. Returns count of replacements made.
int c = 0;
char line[] = "abcd abcd abcd";
c = replacechar(line, 'a', 'A', 0);
puts(line); // Abcd Abcd Abcd
c = replacechar(line+5, 'd', '7', 1);
puts(line); // Abcd Abc7 AbcdReturns a calculated new string length for a more accurate memory allocation size when creating an output buffer for replace.
Returns a pointer to a substring to the right of some delimiting string. Set a starting index or set to 0. See lof.
Returns a string with added right padding. The padding (filler) is another string which is repeated n times. Warning: the resulting buffer must be large enough to hold the original string and the padding.
Returns string with trailing whitespace removed.
Returns true if a string starts with some substring, otherwise returns false.
concatenate strings from an array of strings
programmer is responsible for all bounds checking
strcon(char*, // return buffer
char**, // array of strings
char*, // delimiter
int, // rows in the array
int); // starting row numberExample:
char onestr[4096] = {'\0'}; // for the new SINGLE string
char *people[] = {"Mike", "Mark", "Caren", "Coline", "Katy"};
int sz = ARRSIZE(people);
strcon(onestr, people, "^^", sz, 0);
puts(onestr); // output: Mike^^Mark^^Caren^^Coline^^KatyReturns a string with the character sequence reversed.
Returns a pointer to the last occurrence of some substring within a string. Returns NULL if not found. replaces missing strrstr function
functions to detect the type of a string.
Compliments ctype.h functions for characters:
/*
ALPHA .. PUNCT is an enum in that order.
Returns int:
- 0 = none found
- N = number found
- -1 = all found
*/
char string[] = "Amount: 123.21";
printf(" ALPHA = %d\n", strtype(string, ALPHA));
printf(" ALNUM = %d\n", strtype(string, ALNUM));
printf(" DIGIT = %d\n", strtype(string, DIGIT));
printf(" PUNCT = %d\n", strtype(string, PUNCT));
printf(" PRINT = %d\n", strtype(string, PRINT));
printf(" SPACE = %d\n", strtype(string, SPACE));
printf(" UPPER = %d\n", strtype(string, UPPER));
printf(" LOWER = %d\n", strtype(string, LOWER));
/* output:
ALPHA = 6
ALNUM = 11
DIGIT = 5
PUNCT = 2
PRINT = -1
SPACE = 1
UPPER = 1
LOWER = 5
*/Copies a substring within a string, located by a start position and a length, into a buffer, and returns it. Checks boundaries for overflow.
char s[64] = "Hello Sublime Text";
char data[64];
printf("\n%s\n", substr(data, s, 6, 0)); // Sublime Text
printf("%s\n", substr(data, s, 6, 7)); // Sublime
substr(data, s, 0, 13);
printf("%s\n", data); // Hello SublimeReturns the string with both leading and trailing whitespace removed.
Returns the string in all upper case.
Returns the string with all characters conforming to Uniform Resource Locator syntax rules.
char querystring[] = "?key=value;client=First Middle Last";
char encoded[64] = {'\0'};
urlencode(encoded, querystring);
puts(encoded);
// output: %3fkey%3dvalue%3bclient%3dFirst%20Middle%20LastNumber to string functions myc.h ^
Static and Dynamic memory versions. Thousands separator optional for all.
Copies an integer into a string buffer and returns pointer to it.
Returns a new pointer to a string of an integer. (Dynamic)
Copies a long value into a string buffer and returns pointer to it.
Returns a new pointer to a string of a long value. (Dynamic)
Copies a double value into a string buffer and returns a pointer to it. Requires a value for decimal places. Requires true to include thousands separators.
Returns a new pointer to a string of a double value. Requires a values for decimal places. Requires true to include thousands separators. (Dynamic)
puts(dblstr(snum, 321321321.321 / 3, 2, true)); // automatic memory
// 107,107,107.11
double n_dbl = 123456789.101 / 3;
char *rnum = dblstr_new(n_dbl, 4, false); // dynamic memory
puts(rnum); // 41152263.0337
free(rnum);Creating a List (static array of strings) myc.h ^
These functions operate around a static array of strings that
use a predefined struct.
// struct used for list functions
typedef struct list {
int nbr_rows; // maximum rows (columns, fields)
int len_rows; // maximum length of one row (col, field)
char ** item; // array of strings (fields)
} list;Returns a list structure variable with memory allocated to hold an array of strings.
list a = list_def(20, 65); // 20 itemsAfter creating a new list use this to initialize each element with a string literal. NOTE: Each list item must be initialized.
list my_list = list_def(5, 32);
list_init( my_list,
"first string",
"second string",
"third string",
"fourth string",
"fifth string" );Finds an item in the list and returns its index. Returns -1 if not found.
After creating a new list use this to initialize or change an element with a string literal.
list my_list = list_def(5, 32);
list_update(my_list, "F I R S T STRING", 0);
list_update(my_list, "L A S T STRING", 4);Splits a delimited string into a list (an array of strings.) Returns int of actual number parsed. Length of delimiter must be exactly 1. Define the list prior to using this function.
list a = list_def(20, 65);
int n = list_split(a, line_in, ",");Individual list items can now be accessed like:
a.item[n] // where n is the item (field) numberDelimiters are ignored inside double quotes. Double quotes are NOT REMOVED from the result fields. See deletechar function for removing quote characters. When delimiter is " " (space) consecutive spaces are treated as one delimiter. The input string is destroyed in the process.
Frees memory allocated by list_def function.
list a = list_def(20, 32);
// process ...
list_del(a);Prints out indexes and values to the console.
Inserts a new list item at an existing index. Values are shifted down to allow for the new value thus changing the indexs of the shifted items. The last item in the list is dropped off. The dimensions of the list are not changed.
see list_remove
Reads a text file's lines into a list and returns the new list. Ending line separator is removed. To remove all leading and trailing whitespace set strip to true. Note: uses textlines to calculate the new list's allocated size.
list flst = list_read("test.txt", false);
list_display(flst);
list_del(flst);Returns a RE-DEFined list with new dimensions. Retains items from lst1 and deallocates lst1.
void main (int argc, char *argv[]) {
int x = 0;
list lst = list_def(5, 32);
list_init(lst, "Entry zero",
"Entry ONE",
"2 2 2 2 2",
"Three Two One Zero",
"ffoouurr");
list_display(lst);
puts("\nadding two more rows ...\n");
lst = list_redef(lst, 7, 32);
list_update(lst, "added 1 after redef", 5);
list_update(lst, "added 2 after redef", 6);
list_display(lst);
list_del(lst);
}
/* OUTPUT
000 - [Entry zero]
001 - [Entry ONE]
002 - [2 2 2 2 2]
003 - [Three Two One Zero]
004 - [ffoouurr]
adding two more rows ...
000 - [Entry zero]
001 - [Entry ONE]
002 - [2 2 2 2 2]
003 - [Three Two One Zero]
004 - [ffoouurr]
005 - [added 1 after redef]
006 - [added 2 after redef]
*/Removes a list item at an index.
Values are shifted up to fill the space. thus changing the indexes of the shifted items. The last item in the list becomes empty "\0". The dimensions of the list are not changed.
see list_inject
Reads list items from and Saves to a text file. modes:
- "r" read
- "w" write
Returns a list struct filled with file and/or directory names for path. If sort is "true" then the names will be sorted in ascending order. dtype must be set to: dir = 0 files and directories dir = 1 just files dir = 2 just directories Note: list_dir makes use of the list struct.
list d = list_dir("/home/user/", 1, true);
list_display(d);
list_del(d);Returns a field delimited string of list items.
Alphanumeric fields are enclosed in double quotes when quote is true.
Also zero length trailing rows are bypassed in the return string.
FILE & PATH functions myc.h ^
Return true if filename is a binary file
otherwise, return false.
Return true if filename exists otherwise, returns false.
Returns the byte size of a file.
if(file_exists(f2)) {
if(zenmsg("Exists", "Overwrite Destination file?", "question") == ZENMSG_YES)
filemove(f1, f2);
} else {
filemove(f1, f2);
}Return 1 if name is a file. Returns 0 if name is a directory. Returns -1 if name is undetermined.
Returns the basename of a file with or without the file extension.
Returns only the fullpath of a file without the file name itself. see getfullpath
Returns the fullpath of a file. see getbasepath
Returns the value of a key name found in an ini file.
Returns a FILE handle to fname or NULL if unsuccessful.
Returns a FILE handle to fname or NULL if unsuccessful.
Returns a FILE handle to fname or NULL if unsuccessful.
Loads buffer with the contents of filename or returns -1 if unsuccessful.
Returns count[0] number of lines and count[1] length of longest line in a text file.
Writes buffer to the contents of filename or returns -1 if unsuccessful. Appends to file if append is true.
Utility & Miscellaneous (myc.h) ^
Macro expands to: (sizeof(x) / sizeof((x)[0])) to return an array length (number of elements.)
Copies from text to the X system clipboard
Return code of 0 means successful.
NOTE: "xclip" must be installed on the Linux system.
Pastes into text from the X system clipboard
returns text.
NOTE: "xclip" must be installed on the Linux system.
clr_fg.color colors forground
clr_bg.color colors background
colors
dft (default)
black
dark_red
dark_green
dark_yellow
dark_blue
dark_magenta
dark_cyan
light_gray
dark_gray
red
green
yellow
blue
magenta
cyan
white printf("%s%s\n", clr_fg.cyan, "This will be cyan...");Sorts an array of n integer values.
Sorts an array of n strings. if case is "true" the sort will be case-insensitive.
char *strings[] = { "Zorro",
"Alex",
"Celine",
"Bill",
"Forest",
"Dexter",
"decimal man"};
. . .
ssort(strings, ARRSIZE(strings), false);
printout(ARRSIZE(strings));
ssort(strings, ARRSIZE(strings), true);
printout(ARRSIZE(strings));
/*
OUTPUT:
Alex
Bill
Celine
Dexter
Forest
Zorro
decimal man
Alex
Bill
Celine
decimal man
Dexter
Forest
Zorro
*/Sorts an array of n doubles.
Returns a date string in a strftime format. (see man strftime for the format codes.)
puts(date("%B %F %r")); // February 2022-02-05 10:29:17 AMA variation on fprintf to be used for logging and debugging. flogf only accepts the following formats:
| symbol | type |
|---|---|
| f | float / double |
| d | integer decimal |
| s | string |
| l | long |
| $ | double %.2f |
int x = 123;
long y = 1231231234;
double amount = 98765.345;
flogf(stdout, "%s %d \n", "Value of x:", x);
flogf(stdout, "long value:%l\n", y); // %l is long for flogf
flogf(stderr, "log: %s line: %d -- amount: %$\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, amount);
flogf(stdout, "%s Begin App!\n", date("%F %r"));
FILE * log_file = open_for_append("logfile.txt");
flogf(log_file, "%s Begin App!\n", date("%F %r"));
fclose(log_file);
/////////// OUTPUT ////////////
// Value of x: 123
// long value:1231231234
// log: flogf.c line: 62 -- amount: 98765.35
// 2022-03-29 02:12:24 PM Begin App!
//timeout sets up a SIGALRM to call function after sec seconds.
void timeout_hand() {
// user timout handler function
// code actions to occur
// at end of timeout
}
. . .
timeout(6, timeout_hand); // call "timout_hand" every 6 seconds
. . .Free multiple (num) heap pointers. Also sets to NULL.
char *w1 = malloc(1000);
char *w2 = malloc(2000);
multifree(2, w1, w2);Macro to display an error event errmsg works with the ERRMSG macro use ERRMSG with three arguments: 1> the return code to be checked 2> true or false to terminate the program 3> an additional error or debug message (string)
if (realpath("../nope", fpath) == NULL) {
ERRMSG(errno, true, "realpath returned NULL");
} else {
puts(fpath);
}
/* OUTPUT
ERRMSG near line: 40, errno: 2 No such file or directory
realpath returned NULL
Program Exited
*/Use -1 in 1st argument for non-stock error message.
Seeds random number generator. Use once before using one or more calls to randnum function.
Returns a randum number between and inclusive of some min and max values.
Gtk Dialogs ^
website Zenity is required for these functions.
apt install zenityMessage dialog of four varieties: info, question, error, warning.
if (zenmsg("Hey!", "Asking you a question ...", "question")) {
zenmsg("title", "you answered NO", "info"); // returned 256
} else {
zenmsg("TITLE ..", "you answered YES", "info"); // returned 0
}File dialogs for open or save. savemode open = false, save = true Existence of file to be saved is not checked. Selected file fullpath stored into first argument.
char data[256];
zenfile(data, "/usr/local/bin", false); // open file dialog
puts(data);Design and show a form to collect information. Form widgets include: entry, calendar, list, and combo A delimited string of responses is stored into first argument.
char data[256];
char form_layout[] =
"--title='New Member' "
"--text='Enter your information' "
"--separator=',' "
"--add-entry='Your full name' "
"--add-password='Password' "
"--add-entry='Your Email' "
"--add-combo='Fav ice cream' "
"--combo-values='strawberry|cherry|vanilla|chocolate' "
"--add-calendar='Birthday' "
"--add-list='Fav Color' "
"--list-values='black|blue|red|orange|green|yellow' ";
zenform(data, form_layout);
puts(data); // Delimited items from the form responseDesign and show a list with columns. column data is space delimited.
char list_layout[] =
"--title='New Friends' "
"--text='Enter your information' "
"--print-column='1' " // or 'ALL'
"--multiple " // optional multiple row selection
"--separator=',' " // optional delimited results
"--column='Name' " // column 1
"--column='Age' " // column 2
"--column='Fav Color' " // column 3
"Jack 70 orange " // space delimited data ...
"Joel 60 blue "
"Jill 65 yellow "
"Jane 66 purple "
"James 50 'dark red' ";
zenlist(data, list_layout);
puts(data); // what was selectedDialog with a single entry field.
char data[256];
zentry(data, "zentry exam.", "Enter something witty!", "");
puts(data); // what was enteredDialog to display/edit simple text file. false = read only.
zentext(data, "Notes (edit)", "testinfo.txt", true);
// edited content is now in 'data'
// write back the the file
FILE * f = open_for_write("testinfo.txt");
fprintf(f, "%s", data);
fclose(f);Dialog to obtain username and password or just password (false)
zenpass(data, "user / passwd", true);Displays a system notification. true to include an "info" icon.
"Time Break" program:
char mesg[256] = {'\0'}; // your message from argv[1]
int sec = 0; // wait time set from argv[2]
void main (int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc < 3)
ERRMSG(-1, true, "Missing Arguments: message seconds");
sec = atoi(argv[2]);
strcpy(mesg, argv[1]);
while(true) {
if (file_exists("timebrk.stop")) {
filedelete("timebrk.stop");
zenotify("Stopping timebrk", true);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} else {
zenotify("Starting TimeBrk", true);
}
sleep(sec);
zenmsg("Time Brk", argv[1], "warning");
} // while infinite loop
}This is a generic function for zenity dialogs. Put all of the zenity code except "zenity" in the second argument.
/*
The "zen" function is completely 'free form'.
It just supplies the 'zenity ' command and you
supply the rest in a string. It purpose is to
allow for other zenity dialogs or variations
not covered by the other "myc.h zenity" functions.
https://help.gnome.org/users/zenity/stable/index.html.en#dialogs
*/
// color picker dialog
zen(data, "--color-selection --show-palette");
puts(data);
// scale dialog
zen(data, "--scale --text='How many jelly-beans are in the jar?' --value=100");
puts(data);
// password entry dialog
zen(data, "--password --username");
puts(data);
// calendar dialog
concat(src, "--calendar ",
"--text='Click on a date to select it.' ",
"--date-format='%F' ", // strftime formats
"end");
zen(data, src);
puts(data);Sample Program using myc.h ^
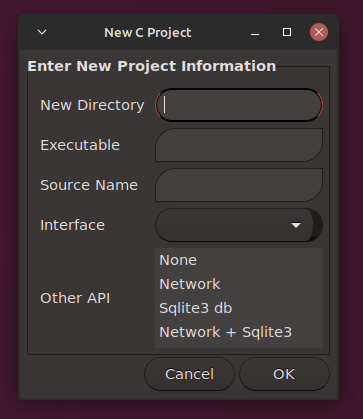
Here is a simple program that sets up a C project. It uses some of the zenity functions as well as several myc functions. Notice in particular how the list_ functions and enums help with the output from the zenform to make the process clean and easy.
/* cproj.c
This is a simple demo of what a C program
looks like when using some of the myc.h
features. It uses some of the zenity functions
as well as several myc functions. Notice in particular
how the list\_ functions and enums help with the output
from the zenform to make the process clean and easy.
*/#include <myc.h>
void main (int argc, char *argv[]) {
char specs[1024] = {'\0'}; // will be used for multiple purposes
char path[1024] = {'\0'};
char initial[256] = {'\0'};
enum names {DIR, EXC, SRC, MODE, API}; // five fields
char form_layout[] =
"--title='New C Project' "
"--text='Enter New Project Information' "
"--separator=',' "
"--add-entry='New Directory' "
"--add-entry='Executable' "
"--add-entry='Source Name' "
"--add-combo='Interface' "
"--combo-values='Gtk-3|Console' "
"--add-list='Other API' "
"--list-values='None|Network|Sqlite3 db|Network + Sqlite3' ";
zenform(specs, form_layout);
list form = list_def(5, 64);
list_split(form, specs, ",");
if (equals(form.item[EXC], "") ||
equals(form.item[SRC], "") ||
equals(form.item[MODE], "") ||
equals(form.item[API], "")) {
zenmsg("Aborting", "Canceled or One or more fields left blank.", "error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Obtain default path to projects
readfile(initial, "initial_directory"); // one line file with main proj path
zenfile(path, trim(initial), false, true);
// HAVE ALL INPUTS
// Make directory and copy over starter source file
strcpy(specs, path);
concat(specs, "/", form.item[DIR], END);
mkdir(specs, 0755);
concat(specs, "/", form.item[SRC], END);
filecopy("./src.c", specs);
/*
Create complile script (cmpc)
The helper scripts (cmp_con, cmp_gtk)
should be placed in the system path.
This generated script (cmpc) will provide
the correct parameters to one of these two
scripts.
*/
if ( equals(form.item[MODE], "Console") ) {
strcpy(specs, "cmp_con ");
} else {
strcpy(specs, "cmp_gtk ");
}
concat(specs, 4, form.item[EXC], " ", form.item[SRC], " ");
if ( equals(form.item[API], "Network"))
strcat(specs, "\"-l curl\"");
else if ( equals(form.item[API], "Sqlite3"))
strcat(specs, "\"-l sqlite3\"");
else if ( equals(form.item[API], "Network + Sqlite3"))
strcat(specs, "\"-l sqlite3 -l curl\"");
strcat(specs, " \n"); // add a linefeed
// WRITE "cmpc" FILE
concat(path, "/", form.item[DIR], "/cmpc", END);
writefile(specs, path, false);
// SET EXECUTE PERM ON cmpc
sprintf(specs, "chmod 755 %s", path);
system(specs);
zenotify("cproj completed", true);
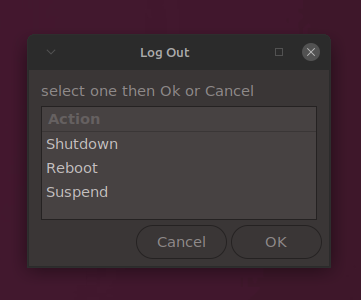
}#include <myc.h>
void main () {
char data[256] = {'\0'};
char list_layout[] =
"--title='Log Out' "
"--text='select one then Ok or Cancel' "
"--separator=' ' "
"--column='Action' "
"Shutdown "
"Reboot "
"Suspend ";
zenlist(data, list_layout);
puts(data); // what was selected
if(equals(data, "Shutdown")) {
system("shutdown now");
}
else if(equals(data, "Reboot")) {
system("reboot");
}
else if(equals(data, "Suspend")) {
system("systemctl suspend");
}
else {
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
}DATABASE Sqlite3 mydb.h ^
Opens an Sqlite3 database using file name is dbname. Checks for existing database file. Exits with error if open fails. db is the database connection pointer. To open another database the open one must be closed first with sqlite3_close(db);
Returns a count(*) result. Uses a where clause. Use empty quotes in where clause to count all rows.
mydb_open("guns.db");
printf("total rows = %i\n\n", mydb_count("guns", ""));
printf("total rows = %i\n\n", mydb_count("guns", "where sex = 'Female'"));Loads an array of strings (mydb_col) containing the text of the column names. Returns the count of columns.
mydb_open("guns.db");
rc = mydb_names("guns"); // table name is 'guns'
printf("number of columns = [%d]\n", rc);
for (int x=0; x < rc; x++) {
printf("%s\n", mydb_col[x]);
}The following function template must be used to process the row/col values after using the sqlite3_exec function. Have one or many.
/*
user function to handle result set
note: may need many different callback functions and/or
use the qid parameter to direct action in one callback
*/
static int resultset(void *qid, int argc, char **argv, char **col) {
int i;
// (const char*)qid; // can use for process control or heading
// one row: process each column in order of sql statement
for(i = 0; i<argc; i++) {
printf("%s = %s\n", col[i], argv[i] ? argv[i] : "NULL");
}
return 0;
}/***
Example using mydb.h functions and above template ...
***/
int rc = 0;
mydb_open("guns.db"); // the database pointer is now 'db'
//char * sql = "select distinct education from guns";
rc = sqlite3_exec(db,
"select distinct education from guns",
resultset,
"ITEM>>>>", // or whatever
0); // or &err_msg
printf("rc from exec was [%d]\n\n", rc); // 1==ERROR, 0==SUCCESS
printf("total rows = %i\n\n", mydb_count("guns", "")); // -1==FAIL
rc = mydb_names("guns"); // -1==FAIL | loads **mydb_col
printf("number of columns = [%d]\n", rc);
for (int x=0; x < rc; x++) {
printf("%s\n", mydb_col[x]);
}
sqlite3_close(db);NET/WEB functions mynet.h ^
Returns the web page code text from url into mybuffer. sz is buffer size of mybuffer.
char *pagebuf;
pagebuf = calloc(10000, sizeof(char*));
if (!webpage(pagebuf, 10000, "https://example.com")) {
printf("exiting because of webpage failure\n");
exit(1);
} else {
printf("webpage success!\n%s\n", pagebuf);
}
Perform a GET request with key-value querystring.
concat(dat, "https://somewhere.net/test/fromgetcurl.php",
"?data=",
urlencode(wrk, "1st-key is data"),
"&var=",
urlencode(wr2, "2nd-key is 'var'..."),
"End");
if (!webget(dat)) {
printf("exiting because of webget failure\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else {
printf("webget success!\n");
}Perform a POST request to url with payload vp_data.
char url[] = "https://somewhere.net/test/frompostcurl.php";
// prepare querystring
concat(dat, "data=",
urlencode(wr1, "content & ampersand!"),
"&var=",
urlencode(wr2, "second variable content!!!!"),
END);
// post to server
if (!webpost(url, dat)) {
printf("exiting because of webpost failure\n");
exit(1);
} else {
printf("webpost success!\n");
}Opens the website at url in the current system default browser.
if (!webbrowser("https://tekvow.net")) {
printf("exiting because of webbrowser mynet.h failure\n");
exit(1);
} else {
printf("webbrowser success!\n");
}end of document