This is a summary of the Advanced Session taught on March 29, as part of the accelaration program at Codaisseur. The learning goals of the day are:
- Understand basic concepts OO Design
- Understand basic concepts of good Unit Testing
- Get some experience with Unit Testing
- Practice Pair Programming

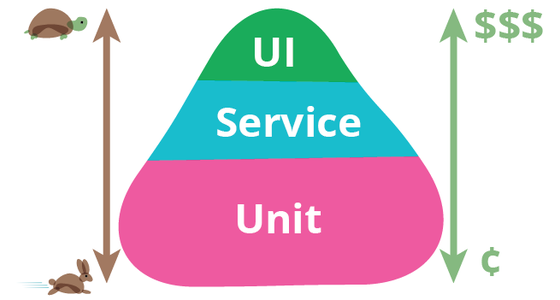
2) End to end tests (The whole system from one end to another end)
3) Integration tests (Realy calls the db, test multiple components)
4) Components tests (Testing multiple units)
5) Unit tests (Smallest test possible)
The higher you get, the slower your tests are
- Testing the smallest testable part of a system (Could be method, a class, a module, etc.) in isolation.
- It is about verifying expectations - does this do what I expect it does?
- Unit testing helps not only to reduce bugs, but also reduce bug-fix-time.
- You have a test runner (such as Jest, Enzyme, JRuby) which has a
- Test framework (with some helper methods such as
expect) - The test runner runs your test class (test code) which verifies your production code.
- Reproduce it with a (new) unit tests(s). (The test should fail)
- Fix your production code.
- Run all your tests. All should pass.
- (Code should compile/build)
- Run all Unit Tests
- If all tests pass: Commit. Else, fix code to make test pass.
- Boundaries (min, max, exactly)
- Error-conditions
- Happy Path
- Dependencies
- ( Properties (such as get/set) - topic of debate)
- You set up an environment (Arrange)
- You perform a certain action (Action)
- You verify your expectation (Assert)
Use only one Assert per test!
Fakes are tools to write (UNIT) tests, to manage dependencies, to not let good design interfere with your testability.
- Always returns a constant
when object.doSomething(anyArgument) then
return "Foo"
- Returns default (or predefined) output
when object.doSomething("Foo" ) then
return "Bar"
- Verify interactions
when object.doSomething("Barz") then
return "Has been clicked"
- Anything (function, model, class, etc.) should only have one reason to change.
- Closely connected to the idea of separation of concerns.
-
Dependency injection is an implementation of this principle
-
Low level modules should depend on high level modules, not the other way round.
-
Abstractions should not depend upon details, details should depend upon abstractions.
-
Definition of bad design: Rigidity (hard to change), Fragility (other stuff breaks if change something), Immobility (Can it be reused or is it hard to disentangle from another application)
-
You are looking for one way dependencies:
A service namespace might depend on a model and parsers, the parsers on a model, but the model shouldn't also depend on the service or parsers!
-
Regression: you introduce something new and code you wrote before fails
Given are two structures:
- Presentation Layer
- Logic layer
- Data Access layer
and:
- Service Interface Layer
- Logic Layer
- Data Access Layer
They are both connected vertically in terms of dependencies.
Imagine the first would be a mail module and the second an auth module, you could also connect them horizontally - the Micro Services SetUp.
- Dynamically typed - types are checked in run time.
- Duck typing: if it quacks like a duck and it looks like duck it probably is duck, but we are not going to check.
- Statically typed - types are checked in compiler time.
This Repository is created by Mimi Magusin. Her personal profile can be found here, her Codaisseur Profile can be found here.