- Design the instagram news feed
- Posts might contain photos and videos
- Design post's and likes and comments functionality
- User publish post
- User likes a post
- User comments a post
- User views the user posts (activity from the user)
- User views the news feed (activity from people the user is following)
- Publishing post should be fast
- 135 million active users
- 500 million publications per day or 15 billion publications per month
- Each post delevered to 10 followers in average.
- 5 billion total posts delivered per day
- 150 billion posts delivered month
- 250 billion read requests per month
- Viewing the news feed should be fast
- Instagram is more read heavy than write heavy
- Optimize for fast reads of posts
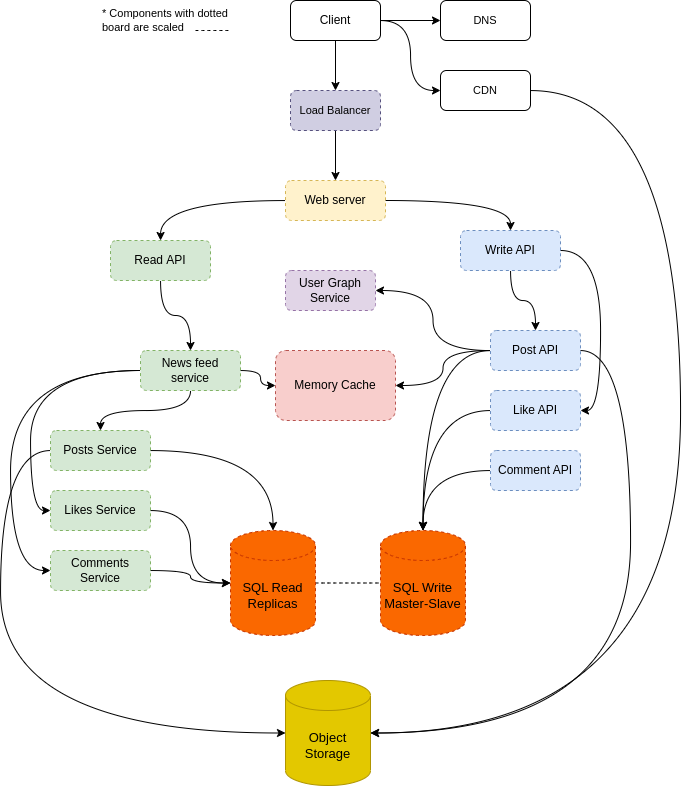
The post might be stored in relational database. When user create post it must be delivered to the all of his followers. The query to the relational db for that will be something like:
select posts.*, users.* from posts
join users on posts.author_id = users.id
join followers on followers.followee_id = users.id
where followers.follower_id = current_userwhich will be extremely slow on big data tables.
The alternative might be to store the news feed posts ids for each user in Memory Cache.
Post publication flow:
- User creates a post.
- The request is forwarded to the Web Server by Load Balancer
- The request is forwarded from the Web Server to Write API
- The request is forwarded from the Write API to Post API
- Post API stores post in relational database.
- Post API asks User Graph Service for followers of post's author.
- Post API add post_id to each follower in Memory Cache
- Post API stores post media to Object Storage
- User likes a post.
- The request is forwarded to the Web Server by Load Balancer
- The request is forwarded from the Web Server to Write API
- The request is forwarded from the Write API to Like API
- Like API stores like in relational database
- User creates a comment.
- The request is forwarded to the Web Server by Load Balancer
- The request is forwarded from the Web Server to Write API
- The request is forwarded from the Write API to Comment API
- Comment API stores comment in relational database
- User views another user posts.
- The request is forwarded to the Web Server by Load Balancer
- The request is forwarded from the Web Server to Read API
- The request is forwarded from the Read API to New Feed Service
- The request is forwarded from the Read API to New Feed Service
- New Feed Service takes all posts with likes and comments of concrete user from relational database via Posts Service, Likes Service and Comments Service. O(n)
- The media of the posts might be delivered from CDN.
- User views a news feed.
- The request is forwarded to the Web Server by Load Balancer
- The request is forwarded from the Web Server to Read API
- The request is forwarded from the Read API to New Feed Service
- New Feed Service takes news feed posts ids of current user from Memory Cache. O(1)
- New Feed Service takes these posts with likes and comments from relational database via Posts Service, Likes Service and Comments Service. O(n)
- The media of the posts might be delivered from CDN.