Learning Consul Connect and applying it.
Run the following commands in separate terminals:
- Install prerequisites:
make setup - Start consul, downstream service, upstream service:
make start- Logs are stored in the folder.
- Test the service mesh:
make test-service-mesh
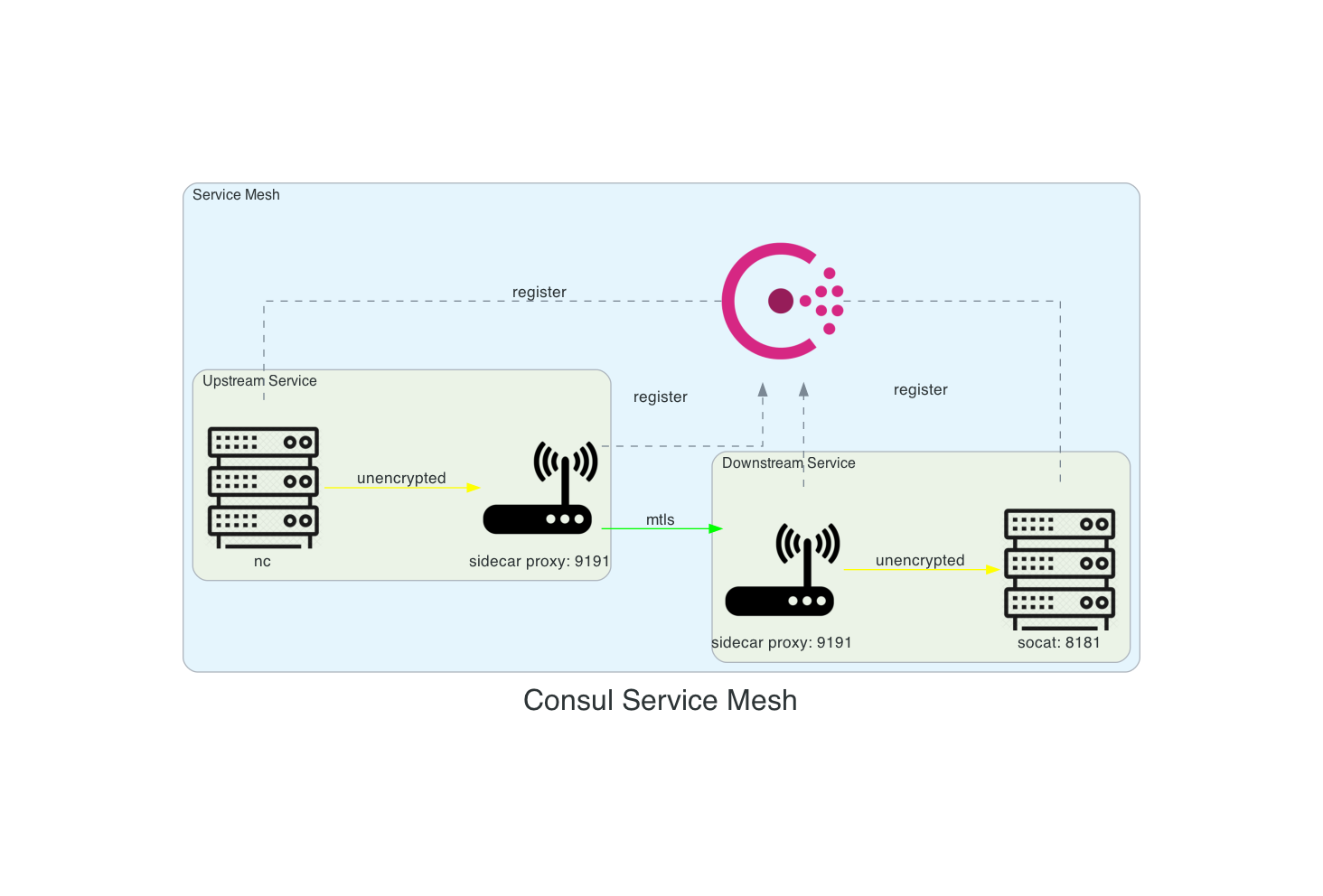
Register sidecar process for the service in upstream.hcl:
service {
# ...
connect {
sidecar_service {}
}
# ...
}This empty configuration notifies Consul to register a sidecar proxy for this process on a dynamically allocated port. It also creates reasonable defaults that Consul will use to configure the proxy once you start it via the CLI.
Consul does not automatically start the proxy process for you. This is because Consul Connect service mesh allows you to chose the proxy you'd like to use.
Consul comes with a L4 proxy for testing purposes, and first-class support for Envoy, which you should use for production deployments and layer 7 traffic management. The Consul L4 proxy doesn't have the L7 capabilities necessary for the observability and traffic shaping features available in Consul versions 1.5 and higher.
Use to start the Consul included L4 proxy sidecar:
make upstream-sidecar
NOTE: The -sidecar-for argument takes a Consul service ID, not a service name.
Register downstream service using downstream.hcl. It specifies downstream dependency on socat, and the port that the proxy will listen on.
The definition includes an downstream block. Downstreams are ports on the local host that will be proxied to the destination service. The downstream block's local_bind_port value is the port your service will communicate with to reach the service you depend on.
It registers a sidecar proxy for the service web that will listen on port 9191 to establish mTLS connections to socat.
This will not start the sidecar, but only informs consul about its existence. Use:
make downstream-sidecarto start the sidecar proxy.
If we were running a real web service it would talk to its proxy on a loopback address. The proxy would encrypt its traffic and send it over the network to the sidecar proxy for the socat service.
Socat's proxy would decrypt the traffic and send it locally to socat on a loopback address at port 8181.
Because there is no web service running, you will pretend to be the web service by talking to its proxy on the port that we specified (9191).
In production, _services should only accept loopback connections**. Any traffic in and out of the machine should travel through the proxies and therefore would always be encrypted.
Intentions allow you to segment your network much like traditional firewalls, but they rely on the services' logical names rather than the IP addresses of each individual service instance.
In the development mode by default all is allowed.
NOTE 2020-12-28: Changing intentions will not affect existing connections! -> Will be addressed in a future version of consul.
Consul provides first class support for Envoy. The only modification to be done is to start the sidecar proxy using Envoy instead of the integrate Consul proxy.
Run the following commands in separate terminals:
- Starting the envoy sidecar:
make service-sidecare-socar-envoy - Starting the envoy sidecar:
make service-sidecare-web-envoy - Testing the connection:
make test-service-mesh
Use mesh gateways to enable inter-datacenter service communication.
Mesh gateways, which connect services in different datacenters, take advantage of Server Name Indication (SNI) – a TLS extension – to inspect the destination of a connection and route to a remote datacenter without decrypting the payload.
Use Envoy as the sidecar proxies and mesh gateways.
You should set enable_central_service_config = true
on your Consul clients
which will allow them to
centrally configure the sidecar and mesh gateway proxies.
Need two wide area network (WAN) joined Consul datacenters with access control list (ACL) replication enabled.
Enable Consul service mesh in both datacenters.
Need to deploy your mesh gateways on nodes that can reach each other over the network.
Need to make sure that both Envoy and Consul are installed on the mesh gateway nodes.
You won't necessarily want to run any services on these nodes other than Consul and Envoy.
You will need to generate a token for each mesh gateway that gives it read access to the entire catalog.
When configuring your mesh gateways, you will need to set the advertise address for the service to be reachable both locally and remotely.
Configure sidecar proxies to use the mesh gateways. Create a proxy-defaults centralized configuration file for all the sidecar proxies in both datacenters.
In one datacenter register a back end service and add a sidecar proxy registration. If you have ACLs enabled, you first need to create a token for the service.
Starting with version 1.5, Consul is able to configure Envoy proxies to collect L7 metrics including HTTP status codes and request latency, along with many others, and export those to monitoring tools like Prometheus.
ACL system ( and hence Intentions ) are by default Allow All.
Connection between proxies is encrypted and authorized. Local connection to and from the proxy are unencrypted - this represents the loopback connection. Traffic in and out of the machine is always encrypted.
The Consul Connect service mesh security model requires trusting loopback connections when you use proxies. To further secure loopback connections you can use tools like network namespacing.
Only supports tcp. No support for tls. Hence perfect tool to test the tls functionality of the Consul Service Mesh.
- HashiCorp Learn: Connect Services with Consul Service Mesh
- HashiCorp Learn: Understand Consul Service Mesh
- HashiCorp Learn: Consul Connect Service Mesh in Production
- HashiCorp Learn: Secure Service Communication with Consul Service Mesh and Envoy
- HashiCorp Learn: Connect Services Across Datacenters with Mesh Gateways
The upstream services are the ones that consume the downstream service.
- sidecar: upstream represents the upstream service - it receives requests and response to them.
- sidecar: downstream simulates a dependent downstream service using
nc. - which send request to the upstream service.