Spring Boot Application
A Spring Boot app with Java 18.
Spring Boot Setup
Using Initializr
-
Generate the boilerplate:
- Spring Initializr
- Basic Java-Maven project with Java 18 (
Spring Webdependency is required)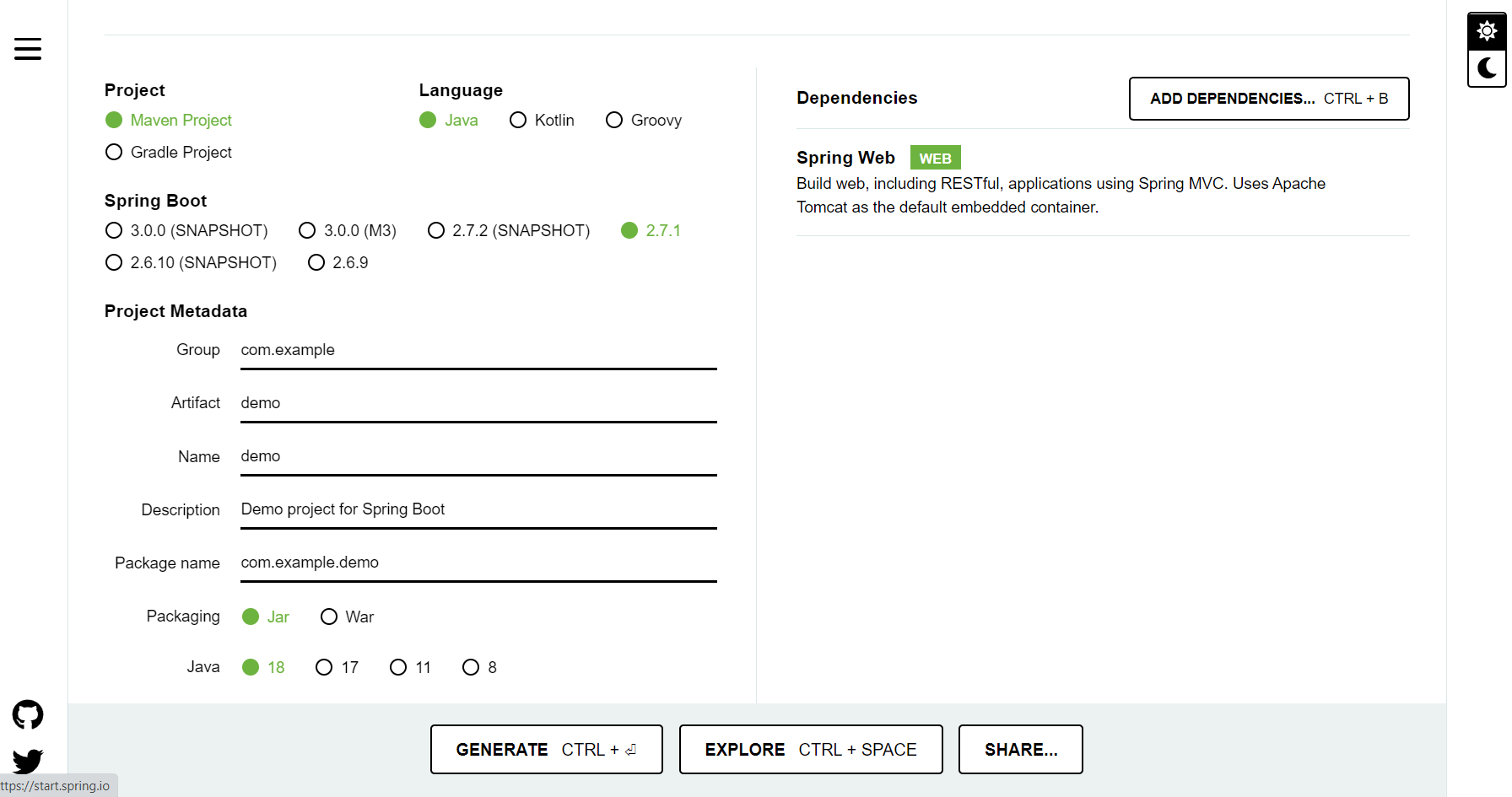
-
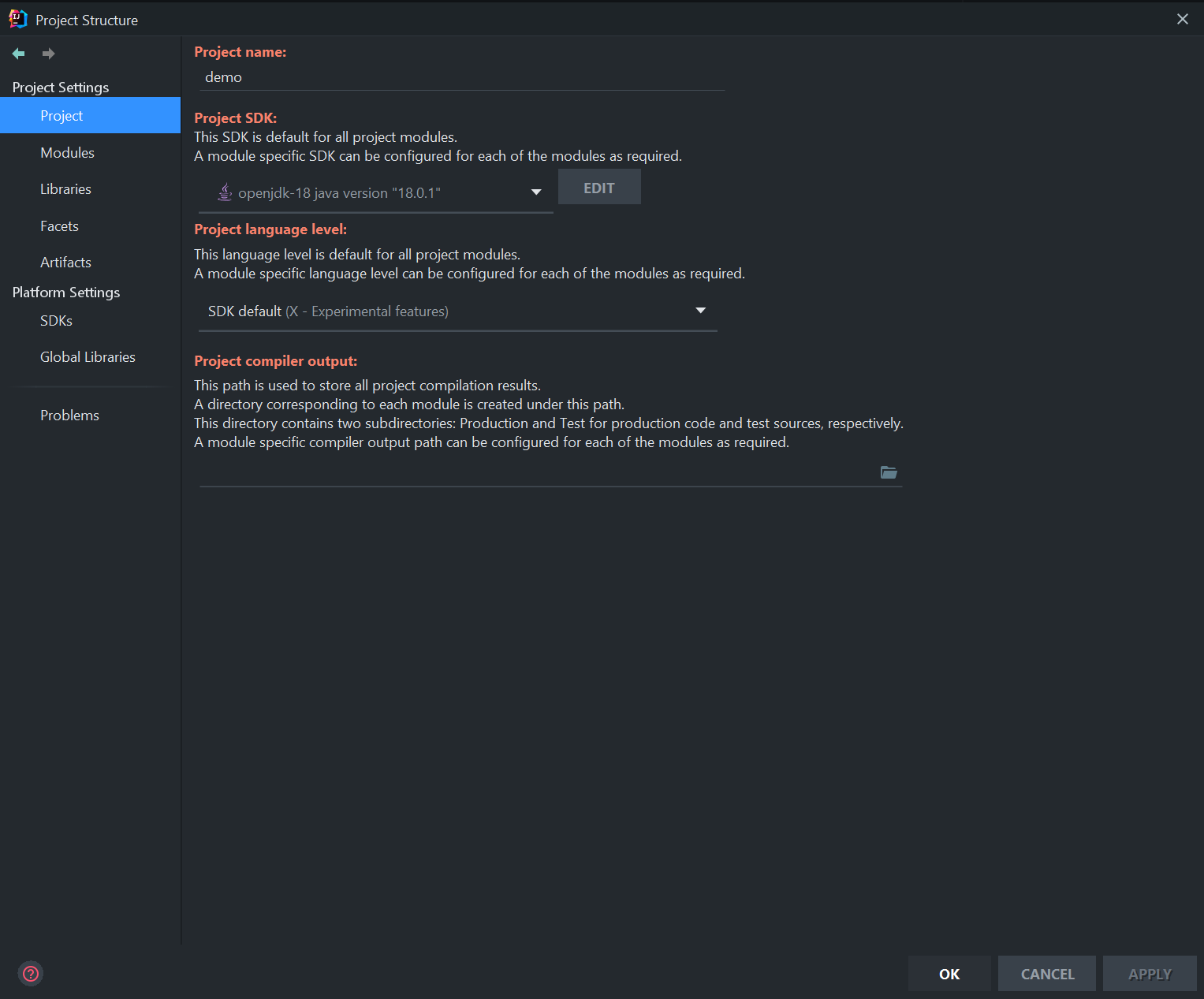
Start a new project with the generated file and set
Project SDK(e.g. 18 - if it is the latest Java version, you will need to download the JDK-18, and set all the project with it and the SDK with X-Experimental):NOTE: You can download the latest JDK version from Oracle and set the environment variable with the new Java path, e.g.
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-18.0.1.1\bin(remember to delete any existing Java path).$ java --version -
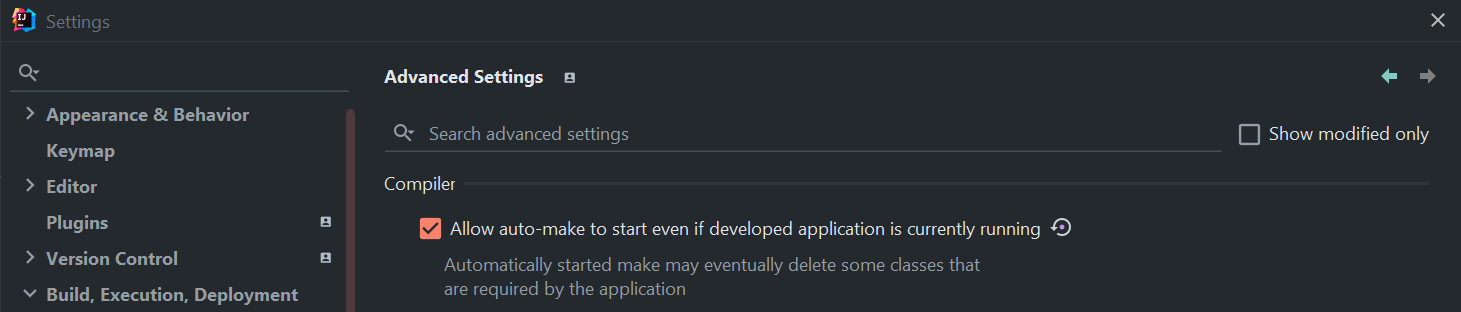
Set your IntelliJ to reload on save:
From Scratch
Spring Boot reference
Getting Started
-
Install any missing local dependency like Maven. You can download the
Binary zip archiveand unzip it in yourProgram Files, and finally add a new environment variable underPath, e.g.C:\Program Files\apache-maven-3.8.6\bin.$ mvn -v -
At this point, you should have only the
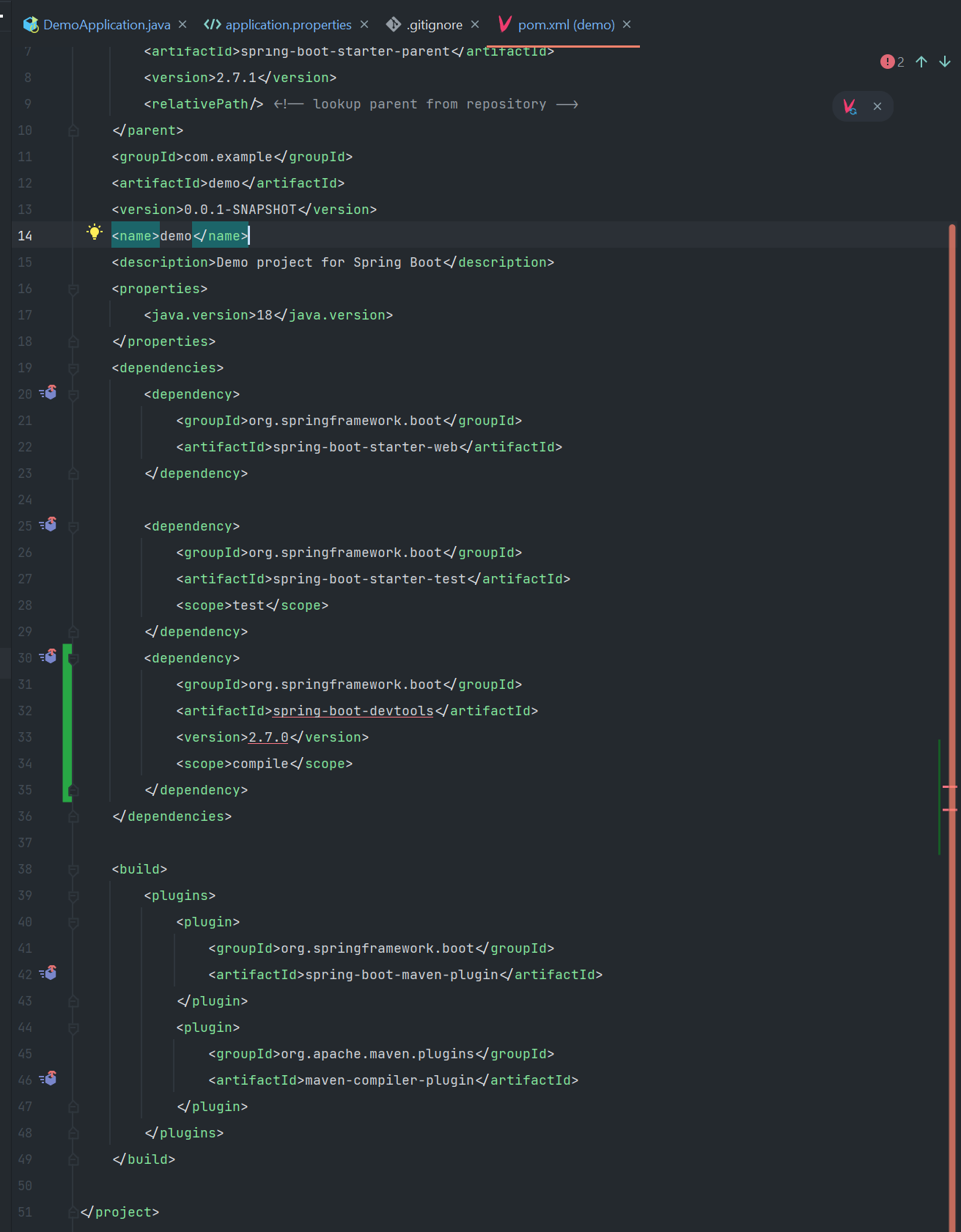
.gitignorein your project folder.- Copy the basic
pom.xmlfrom the reference - Run:
$ mvn packageto detects the Maven and gives you a working build$ mvn dependency:treeto check the pom file and install any dependency, what it is onlycom.example:myproject:jar:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
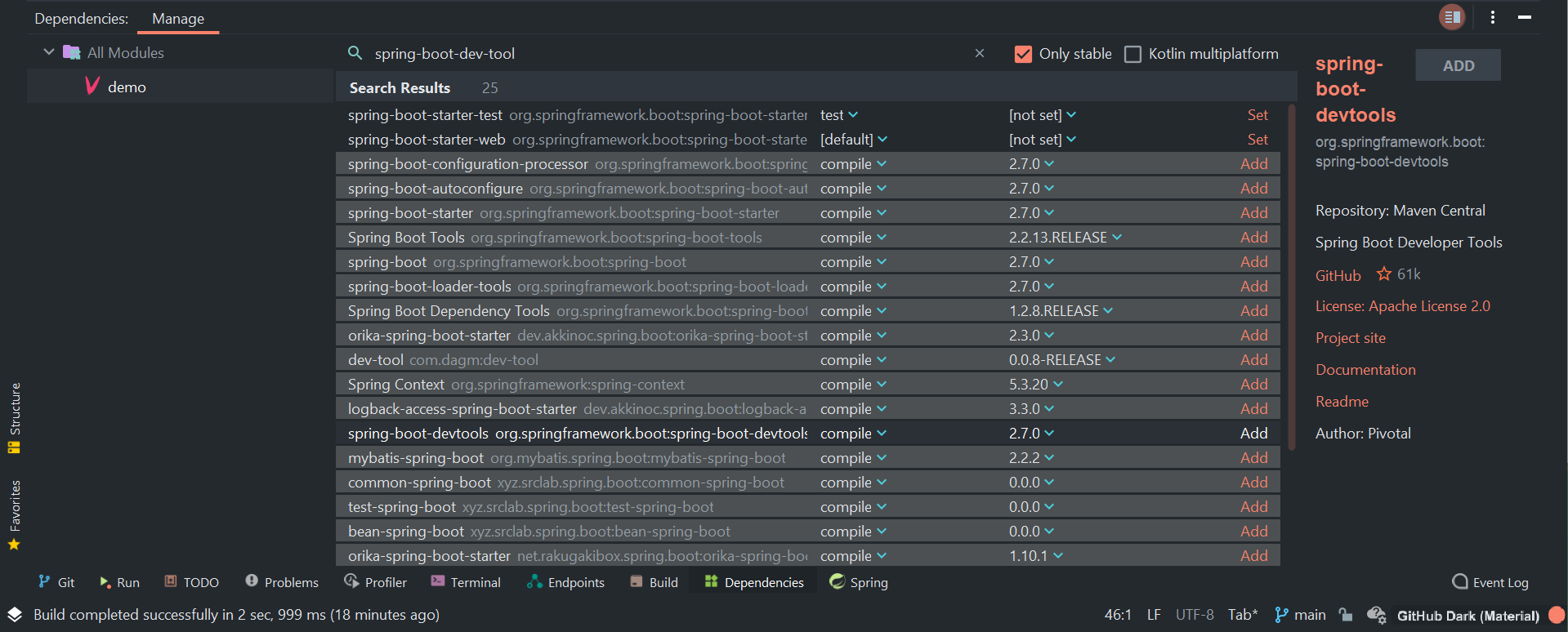
- Add the recommended dependencies and re-run the last command to install them
- Copy the basic
-
Create the main Java file
src/main/java/MyApplication.javawith the SpringBoot syntax and run$ mvn spring-boot:run -
Create a completely self-contained executable Jar that we could run in production
- Add the required plugins to the
pom.xml<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
- Click again the Maven button; run
$ mvn package; and finally$ java -jar ./target/myproject-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
- Add the required plugins to the
RESTful API
- Create a package called
Customerand a Spring Application (@SpringBootApplication):- Right button over
javafolder -> New > Package ->Customer
- Right button over
- Right button over
Customerpackage -> New > Java Class ->CustomerApplication. This must include the annotation@SpringBootApplication
-
Create a
Customerclass with getters and setters fornameandemail -
Create a customer controller:
- Right button over
Customerpackage -> New > Java Class ->CustomerController. This must include the@RestController
- Right button over
-
Use JPA (Java Persistence API) dependency:
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa(search for it underDependencies)- Install JPA dependency through IntelliJ Dependencies section
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa - Add the annotation
@Entityto theCustomerclass - Add a
@PostMappingin theCustomerController, what will require aCustomerRepositoryinterface<EntityType, EntityID> - Create a constructor in the
CustomerControllerto inject the previousCustomerRepositoryto be able to use all the available methods (dependency injection) like.save() - Add a DB dependency in the
pom.xmlfile, e.g.H2can be found using the initializr: ADD DEPENDENCIES > H2 Database
<dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency>
- Add the annotations
@Id @GeneratedValuein theCustomer Entityfor theidto provide the typeIdand autogenerate a new one every time; Also do not forget to create a defaultCustomerconstructor for the same entity - POST request example:
{ "name": "Manu", "email": "manukempo@gmail.com" }- Handle exceptions 404:
- Create a Handler Exception class under
Customerpackage calledCustomerNotFoundExceptionthat extendsRuntimeExceptionwith the customised message - Create a Controller Advice class under
Customerpackage calledCustomerNotFoundAdvicethat includes the annotations@ControllerAdvice,@ResponseBody(only when there is a response),@ExceptionHandler(CustomerNotFoundException.class)(only when theCustomerNotFoundExceptionis raised) and@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)(it will return a404)
- Create a Handler Exception class under
- Install JPA dependency through IntelliJ Dependencies section
-
Connect with a MySQL database
- Add MySQL dependency, what can be found through the initializr: ADD DEPENDENCIES > MySQL Driver, to the
pom.xmlfile - Specify the DB details in the
application.propertiesunder theresourcesdirectory undersrc/main
- Add MySQL dependency, what can be found through the initializr: ADD DEPENDENCIES > MySQL Driver, to the