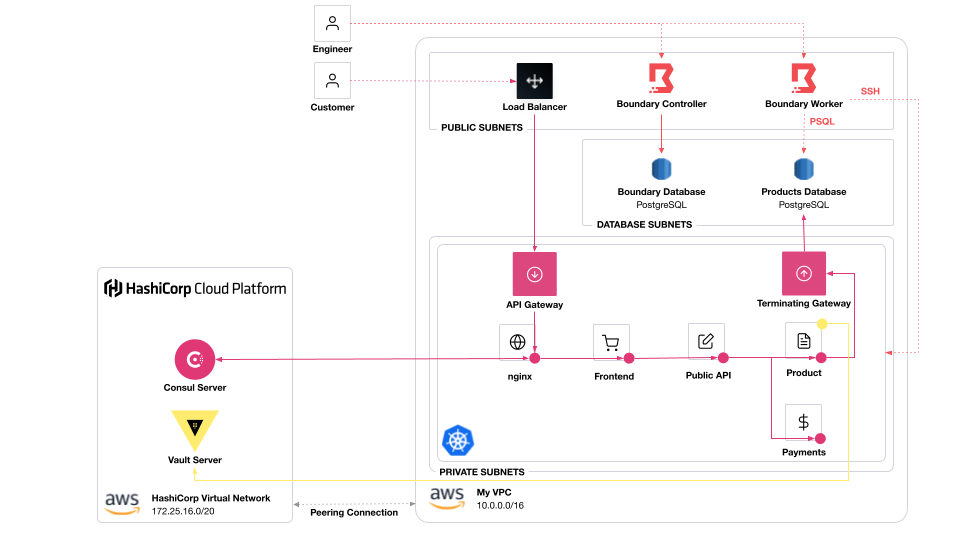
This is a demo of using Boundary, Consul, and Vault to secure an application on Kubernetes.
Boundary controls user access to databases and test endpoints. Consul secures service-to-service communication. Vault secures the Consul cluster and issues temporary credentials for an application to access a database
Each folder contains a few different configurations.
-
Terraform Configurations
-
infrastructure/: All the infrastructure to run the system.- VPC (3 private subnets, 3 public subnets)
- Boundary cluster (controllers, workers, and AWS RDS PostgreSQL database)
- AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service cluster
- AWS RDS (PostgreSQL) database for demo application
- HashiCorp Virtual Network (peered to VPC)
- HCP Consul
- HCP Vault
-
boundary: Configures Boundary with two projects, one for operations and the other for development teams. -
vault/setup/: Deploy a Vault cluster via Helm chart and set up Kubernetes auth method -
certs/: Sets up offline root CA and signs intermediate CA in Vault for Consul-related certificates. -
vault/consul/: Set up Consul-related secrets engines. -
consul/setup/: Deploys a Consul cluster via Helm chart. For demonstration of Vault as a secrets backend, deploys Consul servers + clients. -
consul/config/: Sets up external service to database. -
vault/app/: Set up secrets engines for applications. Archived in favor ofconsul/cts/.
-
-
Other
-
consul/cts/: Deploys CTS to Kubernetes for setting up Vault database secrets based on database service's address -
application/: Deploys the HashiCorp Demo Application (AKA HashiCups) to Kubernetes -
database/: Configures HashiCorp Demo Application database
-
Be sure to download the CLIs for the following.
- Terraform 1.4
- Consul 1.12 (on Kubernetes)
- Vault 1.10
- Boundary 0.8
- Kubernetes 1.22
- Terraform Cloud
- AWS Account
- HashiCorp Cloud Platform account
- You need access to HCP Consul and Vault.
- Create a service principal for the HCP Terraform provider.
jqinstalled- Fork this repository.
Start by setting up Terraform Cloud workspaces for all infrastructure. We divide the infrastructure provisioning from the deployment of services into separate states. This enforces a unidirectional dependency.
Before you start, make sure you:
- Create a Terraform Cloud account.
- Download the Terraform CLI.
- Log into Terraform Cloud from the CLI.
Go to the bootstrap directory.
cd bootstrapCopy tfvars.example to terraform.auto.tfvars.
cp tfvars.example terraform.auto.tfvarsUpdate terraform.auto.tfvars with the required variables
and credentials. DO NOT COMMIT THIS FILE AS IT CONTAINS
CREDENTIALS.
Note: For the HashiCorp folks, use doormat to push credentials up to the Terraform Cloud workspaces individually and leave AWS credentials blank in
terraform.auto.tfvars. The session tokens cannot be loaded into variable sets. Use the commanddoormat aws --account $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID tf-push --organization hashicorp-stack-demoapp --workspace infrastructure,boundary,consul-config,consul-setup,vault-setup.
vim terraform.auto.tfvarsInitialize Terraform.
terraform initRun Terraform and enter "yes" to apply.
terraform applyIf you log into Terraform Cloud and navigate to the hashicorp-stack-demoapp
organization, all the workspaces will be set up.
Next, set up all backends locally to point to Terraform Cloud. This demo needs access to output variables from specific workspaces in order to configure some things locally.
make terraform-initNote: If you are using a different organization name other than
hashicorp-stack-demoapp, update allbackend.tffiles to use the correct TFC organization.
Note: When you run this, you might get the error
Provider produced inconsistent final plan. This is because we're usingdefault_tags. Re-run the plan and apply to resolve the error.
Go to the infrastructure workspace in Terraform Cloud.
Update the infrastructure/terraform.auto.tfvars file with
your chosen region.
Commit it up to your fork.
Start a new plan and apply it. It can take more than 15 minutes to provision!
Go to the boundary workspace in Terraform Cloud.
Optionally, update the boundary/terraform.auto.tfvars file with
a list of users and groups you'd like to add.
Commit it up to your fork.
Start a new plan and apply it. This creates an organization with two scopes:
core_infra, which allows you to SSH into EKS nodesproduct_infra, which allows you to access the PostgreSQL database
Only product users will be able to access product_infra.
operations users will be able to access both core_infra
and product_infra.
Go to the vault/setup workspace in Terraform Cloud.
Start a new plan and apply it.
Terraform will set up Kubernetes authentication method and deploy the Vault Helm chart to the cluster.
As a best practice, store root CAs away from Vault. To demonstrate this, we generate a root CA offline. We use three separate root CAs:
-
Cluster Root CA
- Level 1 Intermediate CA (server root)
- Level 2 Intermediate CA (server intermediate)
-
Service Mesh Root CA for mTLS: This requires three levels because we will need to reconfigure the CA for the correct SPIFFE URI.
- Level 1 Intermediate CA
- Level 2 Intermediate CA (service mesh root)
- Level 3 Intermediate CA (service mesh intermediate)
-
API Gateway Root CA
- Level 1 Intermediate CA (gateway root)
- Level 2 Intermediate CA (gateway intermediate)
NOTE: This is a local Terraform command in order to secure the offline root CA.
Run the command to create a root CA as well as the intermediate CAs, and store the intermediate CAs in Vault. Enter "yes" for Terraform to configure Vault PKI secrets engine and add a passphrase as required.
make configure-certsGo to the vault/consul workspace in Terraform Cloud.
Start a new plan and apply it.
Terraform will set up the PKI secrets engine for TLS in the Consul cluster (not the service mesh).
Using kustomize, deploy the Gateway CRDs.
make configure-kubernetesGo to the consul/setup workspace in Terraform Cloud.
Start a new plan and apply it. This deploys Consul clients and a terminating gateway via the Consul Helm chart to the EKS cluster to join the HCP Consul servers.
The Helm chart will get stuck because of this issue. Patch the API gateway to resolve.
make configure-api-gatewayAPI Gateway requires a SPIFFE-compliant URI in the service mesh certificate. To bypass this issue, you will need to reconfigure the root CA with a SPIFFE URI that contains the correct Consul cluster ID.
make configure-certs-spiffeThis forces a root certificate rotation for Consul service mesh.
Update the terminating gateway with a write policy to the database.
make configure-terminating-gatewayGo to the consul/config workspace in Terraform Cloud.
Start a new plan and apply it. This does a few things, including:
- registers the database as an external service to Consul
- deploys the Consul API Gateway
- sets up the application intentions.
To add data, you need to log into the PostgreSQL database. However, it's on a private network. You need to use Boundary to proxy to the database.
-
Set up all the variables you need in your environment variables.
source set_terminal.sh -
Run the following commands to log in and load data into the
productsdatabase.make configure-db
If you try to log in as a user of the products team, you can print
out the tables.
make postgres-productsYou can use Consul-Terraform-Sync to read the database address from Consul and automatically configure a database secrets engine in Vault using a Terraform module.
To do this, deploy CTS to Kubernetes.
make configure-ctsTo deploy the example application, run make configure-application.
You can check if everything by checking the pods in Kubernetes.
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
## omitted for clarity
frontend-5d7f97456b-2fznv 2/2 Running 0 15m
nginx-59c9dbb9ff-j9xhc 2/2 Running 0 15m
payments-67c89b9bc9-kbb9r 2/2 Running 0 16m
product-55989bf685-ll5t7 3/3 Running 0 5m5s
public-64ccfc4fc7-jd7v7 2/2 Running 0 8m17sPort forward the nginx service to http://localhost:8080.
kubectl port-forward svc/nginx 8080:80You'll get a UI where you can order your coffee.
To set up a route on the API gateway, deploy
an HTTPRoute.
make configure-routeTo log into any of the machines in this demo, you'll need the SSH key.
make get-sshThis will save the private SSH key into id_rsa.pem at the top level
of this repository.
To use Boundary, use your terminal in the top level of this repository.
-
Set the
BOUNDARY_ADDRenvironment variable to the Boundary endpoint.source set_terminal.sh -
Use the example command in top-level
Makefileto SSH to the EKS nodes as the operations team.make ssh-operations
-
Go to the Boundary UI and examine the "Sessions". You should get an active session in the Boundary list because you accessed the EKS node over SSH.
Delete applications.
make clean-applicationRevoke Vault credentials for applications.
make clean-vaultDisable CTS task, remove resources, and delete CTS.
make clean-ctsGo into Terraform Cloud and destroy resources
for the consul-config workspace.
Remove additional Consul resources.
make clean-consulGo into Terraform Cloud and destroy resources
for the consul-setup workspace.
Remove API Gateway manifests.
make clean-kubernetesGo into Terraform Cloud and destroy resources
for the vault-consul workspace.
Remove certificates for Consul from Vault.
make clean-certsGo into Terraform Cloud and destroy resources
for the vault-setup workspace.
Go into Terraform Cloud and destroy resources
for the boundary workspace.
Go into Terraform Cloud and destroy resources
for the infrastructure workspace.
- The demo application comes from the HashiCorp Demo Application.
- portal.cloud.hashicorp.com/sign-up
- consul.io/docs/k8s/installation/vault
- vaultproject.io/docs/secrets/pki
- consul.io/docs/nia
- vaultproject.io/docs/auth/kubernetes
- consul.io/docs/security/acl/auth-methods/kubernetes
- hashi.co/k8s-vault-consul
- hashi.co/k8s-consul-api-gateway