Reference: W. Balmant, M. H. Sugai-Guérios, J. H. Coradin, N. Krieger, A. Furigo Junior, and D. A. Mitchell, "A Model for Growth of a Single Fungal Hypha Based on Well-Mixed Tanks in Series: Simulation of Nutrient and Vesicle Transport in Aerial Reproductive Hyphae", PLoS One, vol. 10, no. 3, p. e0120307, Mar. 2015. (https://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120307)
Fig 2. Description of a non-septate reproductive hypha as a series of well-mixed tanks.
Phenomena are denoted by capital letters: (i) Nutrient is provided by the vegetative hypha (tank 0) at the base of the reproductive hypha (tanks 1 to n) and moves towards the tip (tank n) by diffusion between the tanks and convective flow of the cytoplasm. This convective flow is due to evaporation at the hyphal tip; (ii) In the vesicle-producing zone (tanks i+1 to n-1), nutrient is used to produce vesicles containing cell wall precursors; (iii) The vesicles move towards the tip with a fixed velocity (i.e. there is no diffusive contribution to their transport) that can be different from that of the cytoplasm; (iv) The tip (tank n) extends due to the absorption of vesicles.
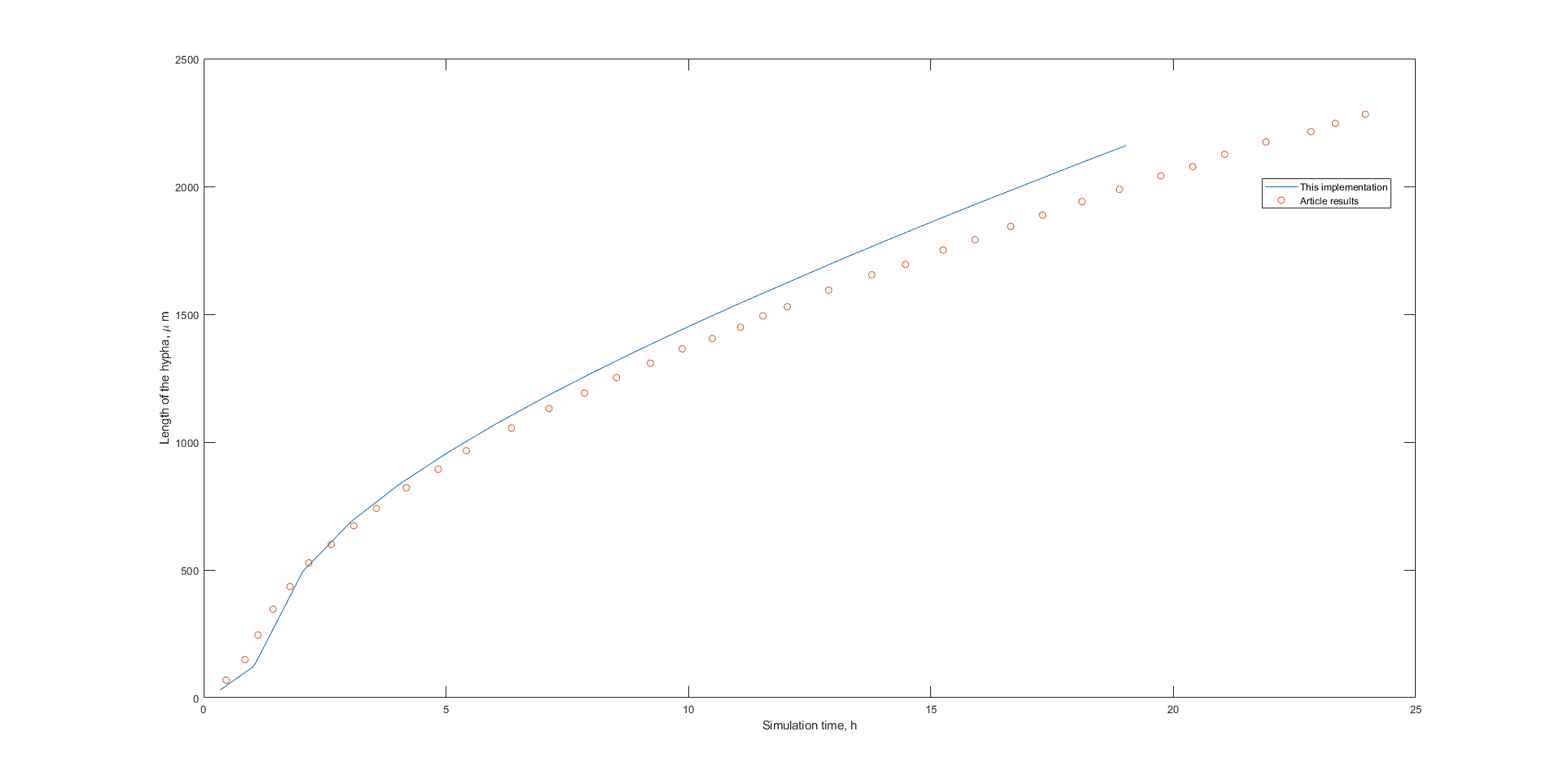
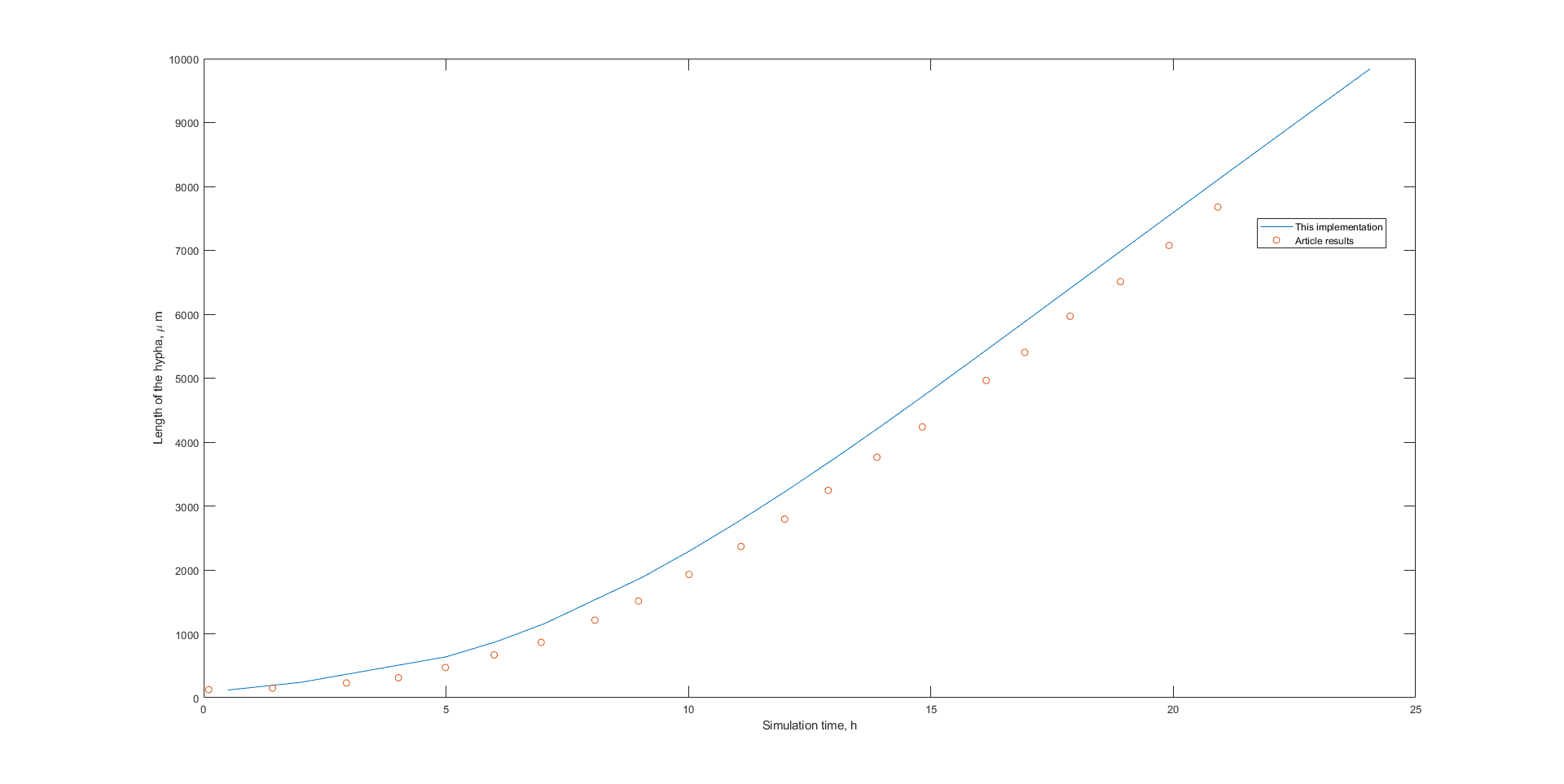
main is the simplified model implementation in which the simulation begins with N reactors (N > Nv) and the tip-tank reactor extends indefinitely until the defined time span tspan
mainWithEvent.m is the simplified model implementation in which the simulation begins with N reactors (N > Nv) and the simulation ends on time t in which the tip-tank reactor reaches twice its initial length.
mainWithEventAndLoop.m is the complete model implementation. N can be any positive integer and the simulation runs until the maximum number of reactors NMax (defined in row 19 as input parameter) is reached.
HyphalTanks.m comprises the system of Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) to be solved. The number of ODEs per loop depends on the number of reactors. The number of ODEs to solve at any given N is 2*N+1.