https://github.com/android/play-billing-samples/tree/master/TrivialDriveJava
코드를 기반으로 구글 빌링 라이브러리 버전을 올렸습니다. 기능 구현 위주로 만들었기 때문에 코드가 다소 보기 어려울 수 있지만 천천히 정리해보겠습니다.
Sample for Google Play Billing Library version 4
This sample is provided to demonstrate using the Google Play Billing Library for in-app items and simple subscriptions. To read more visit https://developer.android.com/google/play/billing/index.html
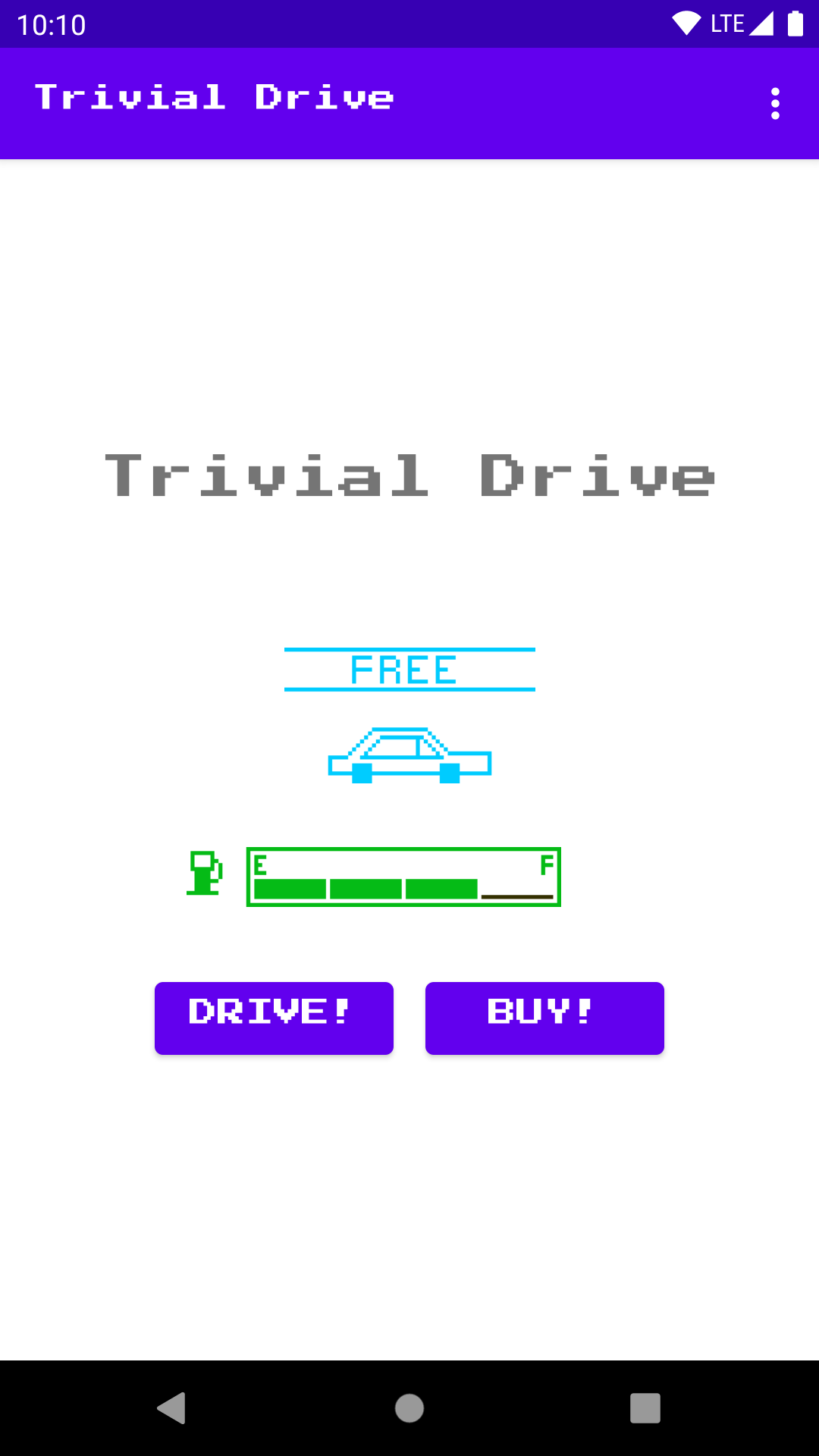
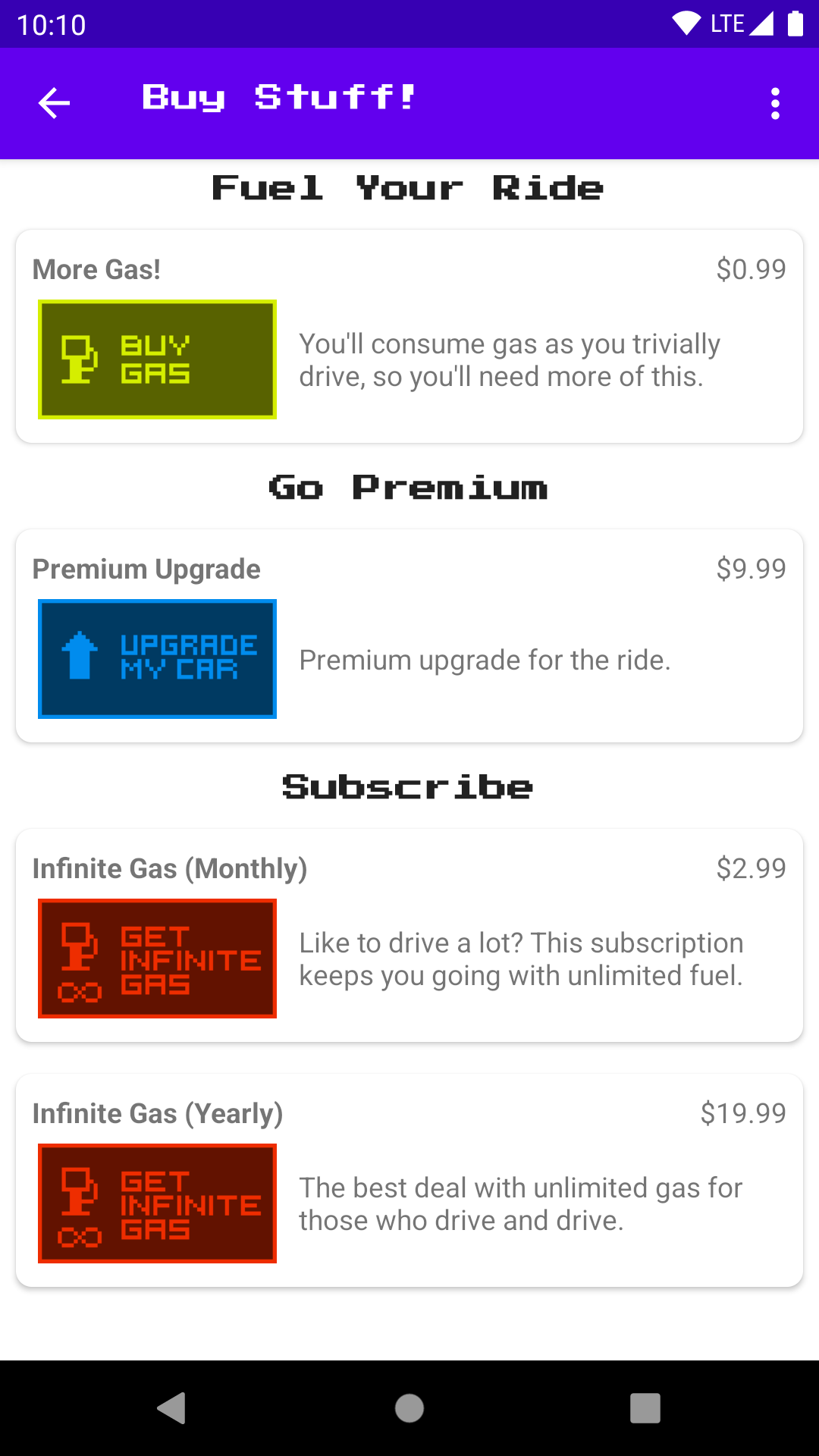
This game is a simple "driving" game where the player can buy gas and drive. The car has a tank which stores gas. When the player purchases gas, the tank fills up (1/4 tank at a time). When the player drives, the gas in the tank diminishes (also 1/4 tank at a time).
The user can also purchase a "premium upgrade" that gives them a red car instead of the standard blue one (exciting!).
The user can also purchase a subscription ("infinite gas") that allows them to drive without using up any gas while that subscription is active. The subscription can either be purchased monthly or yearly.
This sample will warn you if you don't supply a base64EncodedPublicKey in your local.properties, which is used for purchase signature validation. If you just want to run the sample, you can put anything in there to get past the Gradle build check, but in order to get the rest of the sample to function, you need to create an application instance in the Google Play Developer Console and add matching in-app-purchase SKUs.
ON THE GOOGLE PLAY DEVELOPER CONSOLE
-
Create an application on the Developer Console, available at https://play.google.com/apps/publish/.
-
Copy the application's public key (a base-64 string). You can currently find this under Monetization Setup->Licensing.
IN THE CODE
-
Create or open local.properties. Add base64EncodedPublicKey=the key value you copied"
-
Change the sample's package name to your package name. To do that, update the package name in AndroidManifest.xml and correct the references (especially the references to the R object).
-
Export an APK, signing it with your PRODUCTION (not debug) developer certificate. This cert is only used for securely communicating with Google Play App Signing, and will not be used for publishing by Google Play.
BACK TO THE GOOGLE PLAY DEVELOPER CONSOLE
-
Upload your APK to Google Play for Internal Testing. Any other track will require that your app has complete assets and metadata for publishing. Add testers here.
-
Go into the main developer console settings and go to License Testing. Add accounts here that will be used for testing. These accounts will get to make test purchases and can used builds signed with a different signature.
-
Under In-app Products, create products with these Product IDs: premium, gas
-
Under Subscriptions, create SUBSCRIPTION items with these IDs: infinite_gas_monthly, infinite_gas_yearly
-
Publish your APK to the internal testing channel. It should be ready to test almost immediately.
TEST THE CODE
- Install the APK signed with your debug certificate, to a test device with a test account on it.
- Run the app.
- Make (test) purchases!
If you make any real purchases, you can refund them. You can use the tester functionality within the Google Play console to define test Google Accounts that won't be charged. When using the tester functionality make sure to look for "Test" language appended to each purchase in the device UI and in the receipt. If you don't see "Test" then you will need to be sure to refund/cancel the charge.
This sample app implements signature verification but does not demonstrate how to enforce a tight security model. When releasing a production application to the general public, we highly recommend that you implement the security best practices described in our documentation at:
https://developer.android.com/google/play/billing/security
In particular, you should set developer payload strings when making purchase requests and you should verify them when reading back the results. This will make it more difficult for a malicious party to perform a replay attack on your app.
If you've found an error in this sample, please file an issue: https://github.com/googlesamples/android-play-billing/issues
Patches are encouraged, and may be submitted by forking this project and submitting a pull request through GitHub.
Copyright 2021 Google, Inc.
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
2012-11-29: Initial release 2013-01-08: Updated to include support for subscriptions 2015-03-13: Updated to new dev console and added yearly subscriptions 2015-08-27: Ported to gradle and prepped for transitioning to GitHub 2021-04-28: Rewritten and updated to support Google Play Billing Library V3 2021-05-15: Updated to support Google Play Billing Library V4