Technische Universität München
Computer Vision Challenge SoSe 22
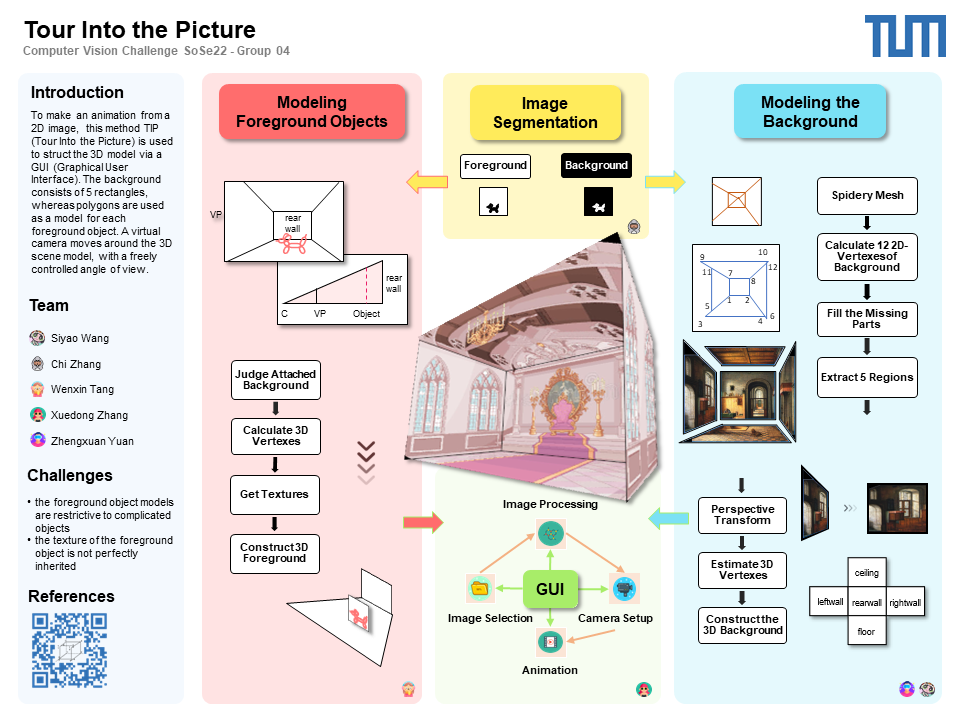
In this project we provide an interactive application, which enables the user to generate animation from a single 2D image. This application provides users with the following functions in the form of GUI: select an image, select the foreground object, select the vanishing point and inner rectangle, as well as change the perspective. Firstly, once the user has selected foreground objects, it's possible to distinguish foreground objects from background. Secondly, the user adds vanishing point and inner rectangle (rear wall) for the scene. Consequently, we can extract 5 regions from the picture. Based on the collection of polygons from background and foreground objects a simple scene model will be constructed.
- MATLAB_R2020a (at least)
- Toolbox Requirement:
- Computer Vision
- Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox
- Image Processing Toolbox
- Symbolic Math Toolbox
- Select an 2D image:
- The user can select a picture from the local folder of the computer;
- Specify the foreground object:
- There is a small input window for entering the number of foreground objects;
- After the number of objects is determined, the user is supposed to extract the foreground objects with a quadrilateral polygon in sequence;
- Once the foreground objects have been chosen, the background and foreground will be separated;
- Generate spidery mesh
- The user can change the position of vanishing point in the picture and drag to deform inner rectangle (rear wall);
- Four radial lines scatter from the vanishing point and intersect with the four vertices of inner rectangle. The rays will automatically change with the change of vanishing point and inner rectangle;
- Extract 5 regions
- Based on the determined vanishing point, inner rectangle, as well as radial lines, the left wall, rear wall, right wall, ceiling and floor are extracted then;
- Construct 3D room
- After user clicks "show 3D" button, the 3D model of room will be represented;
- User can change the value of X, Y, Z (virtual camera position) to obtain different perspectives;
- The button "Tour" provide user the animation of the room tour.
- Xuedong Zhang
- Chi Zhang
- Wenxin Tang
- Zhengxuan Yuan
- Siyao Wang
step 1: Image Segmentation
- function ImageSegment (Chi Zhang)
With the help of ‘drawpolygon’ function in ROI-Based Processing, the user can use a polygon to fit a foreground object. After that the foreground mask will be generated, which contributes to separating background and foreground objects. Consequently, the foreground mask, the pixel coordinates (2D position) of vertices of foreground objects, as well as the image of background without foreground objects will be available in workspace.
step 2: Modeling the Background
- function spidery_mesh (Zhengxuan Yuan)
This step is also based on ROI-Based Processing.drawpoint,drawrectangle, roiChange, etc. These functions enable the user to determine the vanishing point and inner rectangle in the picture and to move their positions or to deform the rectangle. Once the vanishing point and inner rectangle are certain, four radial lines scatter from the vanishing point and intersect with the four vertices of inner rectangle respectively. The points, which are intersections of the ray and the outer rectangle can also be adjusted. - function gen12Points (Zhengxuan Yuan)
To extract 5 regions, it's necessary to calculate the 2D coordinates of four vertices of each region respectively. Positions of point1,2,7,8 are determined after ROI-Based Processing, and 2D coordinates of other points can be calculated with straight line equation. So at the end of this step, we obtain 2D coordinated of 12 vertices and one vanishing point. - function get_image_pad (Siyao Wang)
Consider that some points are calculated with negative coordinates, which means those vertices are outside the image. To visualize all the points in the picture, the original image is supposed to be extended (add border) to include all the vertices. - function image_matting (Siyao Wang)
Take image with black border and 2D coordinates of points as input, generating mask for each regions(left wall, rear wall, right wall, ceiling, floor) respectively is possible. With the mask and input RGB image we can obtain individual image of 5 regions. - function Perspective_transfom (Siyao Wang)
To construct a model of 3D room, five rectangles are needed to compose the walls of room. In the view of trapeziform shape of each region, we should do tilt correction (perspective transform) firstly for each region to obtain rectangle. - function twoD2threeD (Chi Zhang)
We set a default value for focal length of virtual camera firstly, and then we specify the height and width of the rear wall plane in 3D model. Based on the properties of similar triangles, we can calculate the 3D coordinate of each point with the help of its 2D coordinate. - function construct_3D_room (Siyao Wang)
With 3D positions of vertices, positions of each surface are determined. Take 3D coordinates of vertices as input of function surface(), the five walls will be plotted in 3D-coordinate-system. Then function flipdim() contributes to mapping the textures of 2D images into 3D surfaces. In this step the model of background is constructed.
step 3: Modeling the Foreground Objects
- function get_polygon_function (Wenxin Tang)
Take 2D coordinates of two points on the plane and surface that vertical to foreground object as input, the plane equation of polygon that fits the foreground object is available. - function fg2Dto3D (Wenxin Tang)
With 2D coordinates of four vertices of foreground object, the polygon function of the plane, which is used to fit the foreground object is calculable. On the other hand, foreground objects are always attached to the floor, therefore we can calculate the 3D position of foreground object with its 2D coordinates and 3D coordinates of floor's vertices and plane equation of foreground object. - function plot_polygon (Wenxin Tang)
After calculating the 3D coordinates of foreground object, its position in 3D-coordinate-system can be determined. Function warp() is used here to plot foreground object, and to map the texture from 2D image into 3D surface for representing model of foreground object.
step 4: Animation
- animation in main.m (Chi Zhang)
Use function camproj, campos, camtarget and so on to control the virtual camera to move in the constructed 3D model. Once the user has moved to the desired view position, a photo (2D projection) can be taken.
step 5: GUI Design
(Xuedong Zhang)
Design the interactive interface in the application to enable user to do the following:
- Select an image: The user can select any picture in the computer;
- Determine foreground objects: The user can enter the number of foreground objects and then click four points in the picture to construct a quadrilateral to fit the foreground object;
- Generate spidery mesh: Vanishing point and inner rectangle are chosen and moved by user. Once the user has determined vanishing point and inner rectangle, 5 regions of the room will be extracted;
- Construct 3D room: After clicking button 'show 3D', the constructed 3D model for the room in input image will be represented. It's possible for user to control the virtual camera by changing the value of x, y, z. When user gets desired perspective, a photo can be taken.
- Animation: User can also click button 'Tour' to get variable transformed perspective of the room.