FEDn is an open source, modular framework for Federated Machine Learning (FedML), developed and maintained by Scaleout Systems. It enables developers to configure and deploy FEDn networks to support different federated scenarios, ranging from cross-silo to cross-device use-cases.
Three key design objectives are guiding development in the project and is reflected in the core features:
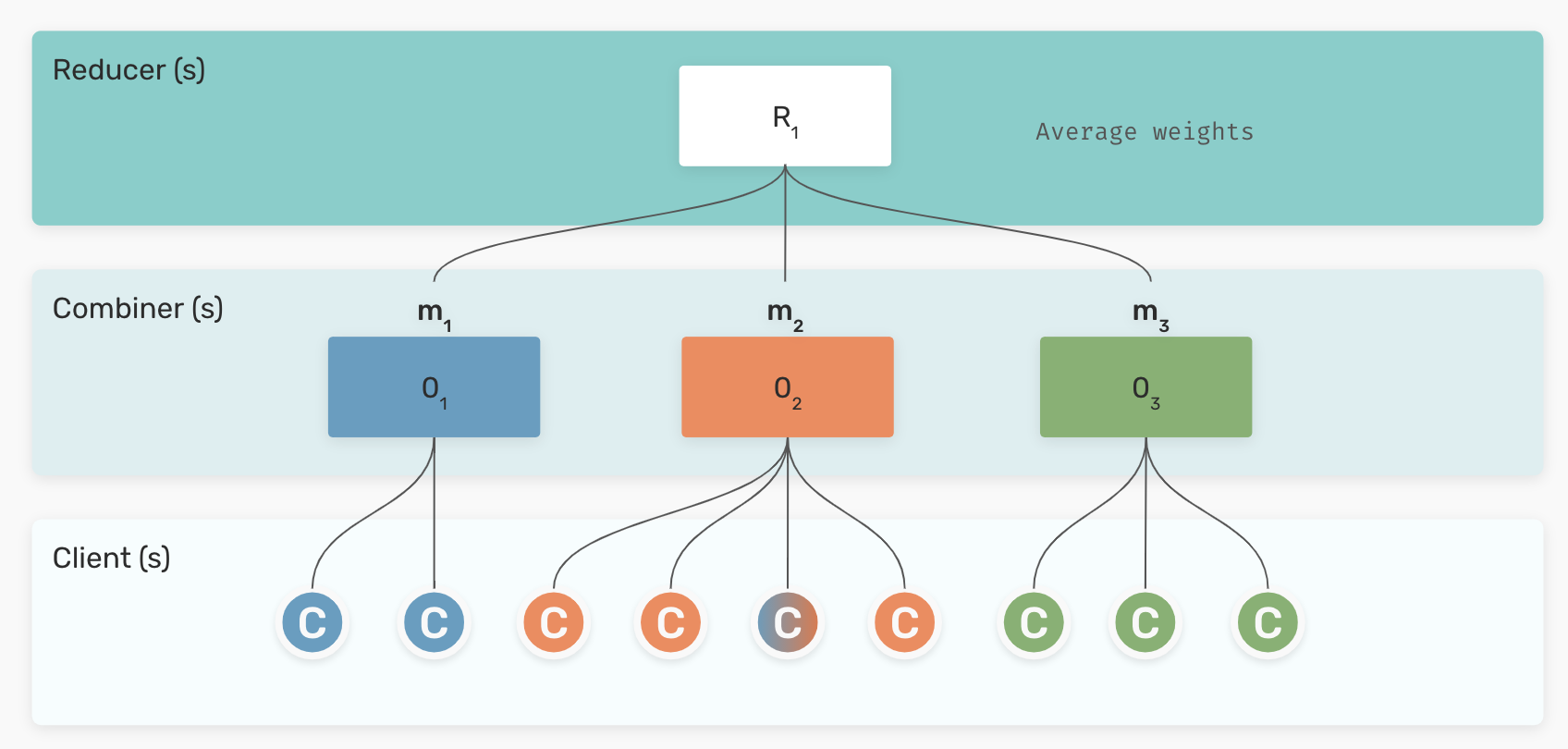
FEDn is designed to allow for flexible and easy scaling to meet both the demands from a growing number of clients, and from latency and throughput requirements spanning cross-silo and cross-device cases. This is addressed by allowing for a tiered model update and model aggregation scheme where multiple combiners divide up the work for global aggregation steps.
The framework treats client model updates and model validations as black-boxes. A developer can follow a structured design pattern to implement a custom helper class to support any ML model type or framework - the only requirement is that it should make sense from a machine learning perspective to average model parameters. Support for Keras Sequential models are available out-of-the box, and support for the TF functional API, PyTorch and SKLearn are in active development.
FEDn is built to support real-world, production deployments. FEDn relies on proven best-practices in distributed computing, uses battle-hardened components, and incorporates enterprise security features. There is no "simulated mode", only distributed mode. However, it is of course possible to run a local sandbox system in pseudo-distributed mode for convenient testing and devepment.
Constructing a federated model with FEDn amounts to a) specifying the details of the client side training code and data integrations, and b) deploying the reducer-combiner network. A FEDn network, as illustrated in the picture below, is made up of three main components: the Reducer, one or more Combiners and a number of Clients. The combiner network forms the backbone of the FedML orchestration mechanism, while the Reducer provides discovery services and provides controls to coordinate training over the combiner network. By horizontally scaling the combiner network, one can meet the needs from a growing number of clients.
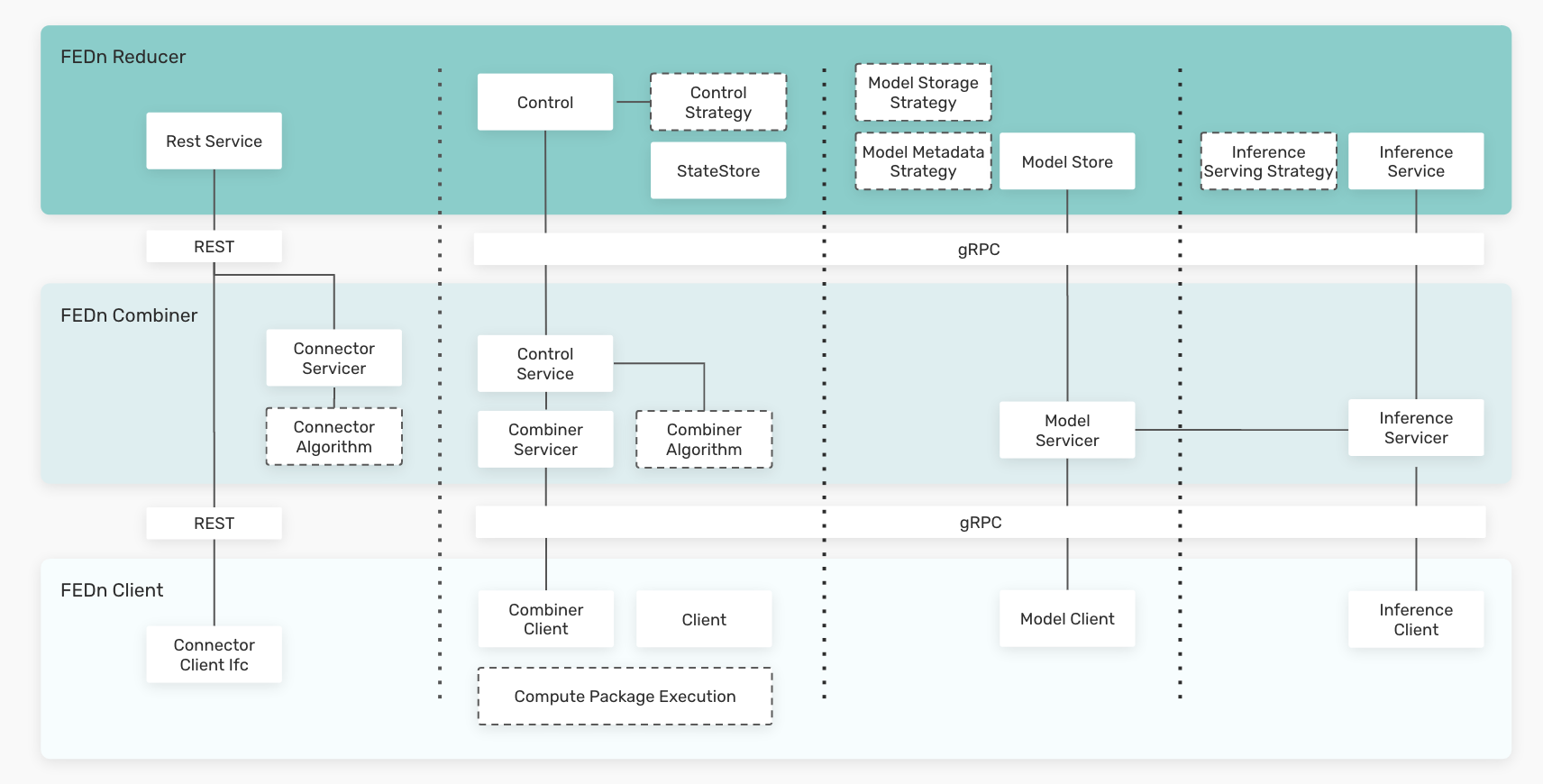
A Client is a data node, holding private data and connecting to a Combiner to recieve model update requests and model validation requests during trainig rounds. Clients do not require any open ingress ports, they recieve the code to be executed from its combiner, and they need to be configured prior to connection to read the local datasets in order to be able to execute model training and validation. Python3 clients are provided out of the box, and it is possible to write clients in a variery of languages to target different execution environments and hardware.
A combiner is an actor which main role is to orchestrate and aggregat model updates from a number clients during a training round. When and how to trigger such orchestration rounds are specified in the overall compute plan laid out by the Reducer. Each combiner in the network runs an independent gRPC server, providing RPCs for interacting with the alliance subsystem it controls. Hence, the total number of clients that can be accomodated in a FEDn network is proportional to the number of active combiners in the FEDn network. Combiners can be deployed anywhere, e.g. in a cloud or on a fog node to provide aggregation services near the cloud edge.
The reducer fills three main roles in the FEDn network: 1.) it lays out the overall, global training strategy and comminicates that to the combiner network. It also dictates the strategy to aggregate model updates from individual combiners into a single global model, 2.) it handles global state and maintains the model trail - an immutable trail of global model updates uniquely defining the FedML training timeline, and 3.) it provides discovery services, mediating connections between clients and combiners. For this purpose, the Reducer exposes a standard REST API.
The figure below provides a logical archiecture view of the services provided by each agent and how they interact.
FEDn is desinged to allow customization of the FedML algorithm, following a specified pattern, or programming model. Model aggregation happens on two levels in the system. First, each Combiner can be configured with a custom orchestration and aggregation implementation, that reduces model updates from Clients into a single, combiner level model. Then, a configurable aggregation protocol on Reducer level is responsible for combining the combiner-level models into a global model. By varying the aggregation schemes on the two levels in the system, many different possible outcomes can be achieved. Good staring configurations are provided out-of-the box to help the user get started.
The currently implemented default scheme uses a local SGD strategy on the Combiner level aggregation, and a simple average of models on the reducer level. This results in a highly horizontally scalable FedAvg scheme. The strategy works well with most artificial neural network (ANNs) models, and can in general be applied to models where it is possible and makes sense to form mean values of model parameters (for example SVMs). Additional FedML training protocols, including support for various types of federated ensemble models, are in active development.
The easiest way to start with FEDn is to use the provided docker-compose templates to launch a local sandbox / simulated environment consisting of one Reducer, two Combiners, and five Clients. Together with the supporting storage and database services (currently Minio and MongoDB), this consitutes a minimal system for training a federated model and learning the FEDn architecture. FEDn projects are templated projects that contain the user-provided model appplication components needed for federated training. This repository bundles a number of such test projects in the 'test' folder. These projects can be used as templates for creating your own custom federated model.
Clone the repository (make sure to use git-lfs!) and follow these steps:
- Create a file named '.env' in the repository root folder and set the following variables (alter values as necessary):
ALLIANCE_UID=ac435faef-c2df-442e-b349-7f633d3d5523
FEDN_REDUCER_HOST=reducer
FEDN_REDUCER_PORT=8090
FEDN_MONGO_USER=fedn_admin
FEDN_MONGO_PASSWORD=password
FEDN_MONGO_HOST=mongo
FEDN_MONGO_PORT=27017
FEDN_ME_USERNAME=fedn_admin
FEDN_ME_PASSWORD=password
FEDN_MINIO_HOST=minio
FEDN_MINIO_PORT=9000
FEDN_MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=fedn_admin
FEDN_MINIO_SECRET_KEY=password
FEDN_ALLIANCE_AUTH_TOKEN=auth_token
FEDN_ALLIANCE_ADMIN_AUTH_TOKEN=auth_token
EXAMPLE=mnist
CLIENT_NAME_BASE=client-fedn1-
you set the EXAMPLE variable to the example you are working on imported with base path from test/your_example or start all commands below by prepending
EXAMPLE=mnistlike$ EXAMPLE=data_center docker-compose up
We provide templates for a minimal standalone Docker deployment, useful for local testing and development.
- To deploy the supporting services (Minio and MongoDB):
$ docker-compose up Make sure you can access the following services before proceeding to next steps:
- Minio: localhost:9000
- Mongo Express: localhost:8081
- Start a Reducer
$ docker-compose -f reducer.yaml up - Attach two combiners:
$ docker-compose -f combiner.yaml up - Attach a number of Clients (assuming you are running the MNIST example):
$ docker-compose -f client.yaml up --scale client=5Make sure that you can access the Reducer UI at https://localhost:8090, and that the combiner and clients are up and running, before proceeding to the next step.
Navigate to the Minio dashboard and log in. To prepare FEDn to run training, we need to upload a seed model via this endpoint (https://localhost:8090/seed). Creating and staging the seed model is typically done by founding members of the ML alliance. For testing purposes, you find pre-generated seed model in "test/mnist/seed" (and correspondingly for the other examples).
Navigate to the Reducer UI. To initialize the federated model we need to upload a seed model. For testing purposes, you find a pre-generated seed model in "test/mnist/seed" (and correspondingly for the other examples).
- Creating and staging the seed model in the FEDn network is typically done by one of the founding members of the ML alliance, or the user deploying and managing the FEDn network. There is a script "test/mnist/seed/init_model.py" that you can edit if you would like to alter the neural network achitecture of the seed model.*
To start training, navigate to the Reducer REST API endpoint: localhost:8090/start. You can follow the progress of training visually in from the "Dashboard" menu (https://localhost:8090/plot)
The actual deployment, sizing and tuning of a FEDn network in production depends heavily on the use case (cross-silo, cross-device etc), the size of models, and on the available infrastructure and the desired strategy to provide end-to-end security. To deploy a FEDn network across different hosts in a live environment, first analyze the use case and create an appropriate architecture plan. Then deploy reducers and combiners as needed by modifying the .env files and docker-compose files accordingly for each host/service. Reference deployment descriptions for representative scenarios and hardware are coming soon.
Warning, there are many additional security considerations when deploying a live FEDn network, external to core FEDn functionality. Make sure to include these aspects in your deployment plans.
Explore our other example models, or use them as templates to create your own project.
Reach out to Scaleout (https://scaleoutsystems.com) to learn how to configure and deploy zero-trust FEDn networks in production based on FEDn, and how to adapt FEDn to support a range of use-case scenarios.
All pull requests will be considered. We are currently managing issues in an external tracker (Jira). Reach out to one of the maintainers if you are interested in making contributions, and we will help you find a good first issue to get started.
FEDn is licensed under Apache-2.0 (see LICENSE file for full information).