Letsconsul
Tool that helps you automatically renew LetsEncrypt certificates and serve them in consul K/V storage.
Note: It is tightly integrated with proxy-server (nginx in this case) and consul-template tool. Please read below for full understanding of certificate issuing and installation process.
Get started
At first create following K/V structure in Consul:
letsconsul
|_
| \_renew_interval = 168h
|_
| \_reload_interval = 10s
|_
| \_service = letsconsul
|_
| \_domains_enabled = ["example.com", "qlean.ru"]
|_
\_domains
|_
| \_example.com
| |_
| | \_domain_list = ["www.example.com", "example.com"]
| |_
| | \_email = admin@example.com
| |_
| \_timestamp = 0
|_
\_qlean.ru
|_
| \_domain_list = ["qlean.ru", "www.qlean.ru", "assets.qlean.ru"]
|_
| \email = webmaster@qlean.ru
|_
\_timestamp = 0
Consul configuration keys:
renew_interval- domain certificate expiration timereload_interval- time after letsconsul reloading domains information from consulservice- consul service namedomains_enabled- domains fromletsconsul/domainsthat can be validated and renewed with certs/keys
When letsconsul starting it reading particular command line arguments:
-b- host:port variable that validation web-server will listen (by default 0.0.0.0:8080)-c- consul address (by default 127.0.0.1:8500)
Also, you can specifly consul ACL token with CONSUL_TOKEN environment variable.
Example of usage:
$ wget https://github.com/hypersleep/letsconsul/releases/download/0.0.2/letsconsul-linux-64.zip
$ unzip letsconsul-linux-64.zip
$ ./letsconsul -b 0.0.0.0:8080 -c 127.0.0.1:8500
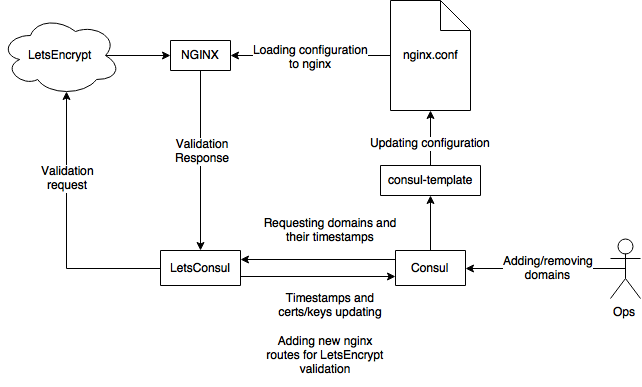
Workflow description
After app starts, it fetching domains information from consul by given consul_service key, checking certificate expiration time and if more than renew_interval then starts certificate renew process.
Updating and receiving certificates is based on LetsEncrypt HTTP validation.
After validation request has sent to LetsEncrypt, letsconsul starts a validation web-server on address -b that should receive a LetsEncrypt validation request.
Ensure that validation web-server available from internet! You can simply do this with combination of nginx proxy and consul-template:
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.example.com example.com;
{{range service "letsconsul"}}
location /.well-known/acme-challenge {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_pass http://{{.Address}}:{{.Port}};
}
{{end}}
}
If validation will be made successfully, letsconsul writes received certificates and keys to fullchain and private_key consul keys.
After that you can use values of fullchain and private_key as cert/key files for nginx using consul-template:
/etc/ssl/example.com.crt.ctmpl:
{{key "letsconsul/domains/example.com/fullchain"}}
rendering to: /etc/ssl/example.com.crt
/etc/ssl/example.com.key.ctmpl:
{{key "letsconsul/domains/example.com/private_key"}}
rendering to: /etc/ssl/example.com.key
Finally, you're got fully automated and distributed by many servers/proxies HTTPS certificates!
You can see full workflow on following chart: