- Refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-minikube/ for installation steps.
- Before the installation, ensure the preferred hypervisor (virtualbox is preferred) is installed on your local machine unless you would like to install it on the local machine without hypervisor. In this case, you need docker or podman for minikube to run on the local machine.
- Next, download the minikube binary following the steps of the OS of your local machine, in my case MacOS,
$ curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-darwin-amd64then make the file executable$ chmod +x minikube. Lastly, add the minikube to your path$ sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin/.
- Kubernetes CLI tool
kubectlis needed to for the administration of the K8 cluster and application deployment. - Refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl/#before-you-begin for the installation steps.
- Again, since I'm using MacOS, download the binary
$ curl -LO "https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/darwin/amd64/kubectl"then make the file executable$ chmod +x ./kubectl. Lastly, add the kubectl to your path$ sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
- Once minikube and kubectl are ready, it's time to bring up the minikube cluster (i mean node..).
- In the terminal, run
minikube start --driver=<driver_name>, the driver_name is the name of the hypervisor installed on the local machine. eg. virtualbox - Check that the minikube node is running normally by running
minikube status. If the output is like this, it's all set!
host: Running
kubelet: Running
apiserver: Running
kubeconfig: Configured
- Firstly, Nginx Hello World application must be deployed as Deployment in kubernetes in order to define ReplicaSet to handle self-healing and replication.
- In this demo, the replicas is set as 2 so that 2 Nginx pods will be deployed as defined in deploy_nginx.yml file.
- Run
kubectl apply -f deploy_nginx.ymlto trigger the deployment to the cluster. - Check that there are 2 pods running in the cluster by running
kubectl get deployment nginx-hello-world
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-hello-world 2/2 2 2 69m
- Next, the Nginx Hello World deployment must be exposed as Service because pods come and go and same goes to the IP addressess that are assigned to the pods. A stable IP and domain name are needed to route the traffic to the intended pods that are serving the application. There are many ways to handle container networking but for the scope of this demo, NodePort is used to allow connection outside of the cluster.
- As seen in nginx_service.yml, the NodePort is exposed as 32042 and it will forward to port 80 of the Nginx endpoint.
- Run
kubectl apply -f nginx_service.ymlto expose the Nginx deployment as service. - Check that the nginx-hello-world service has been assigned a cluster IP and the port mapping of 32042 to 80 by running
kubectl get svc nginx-hello-world
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-hello-world NodePort 10.101.125.102 <none> 80:32042/TCP 80m
- The cluster IP assigned to the nginx-hello-world is non-routable from outside the cluster because it's a virtual network in the cluster. Hence, the minikube ip must be used to access the service. To check the minikube ip, run
minikube ip.
192.168.99.100
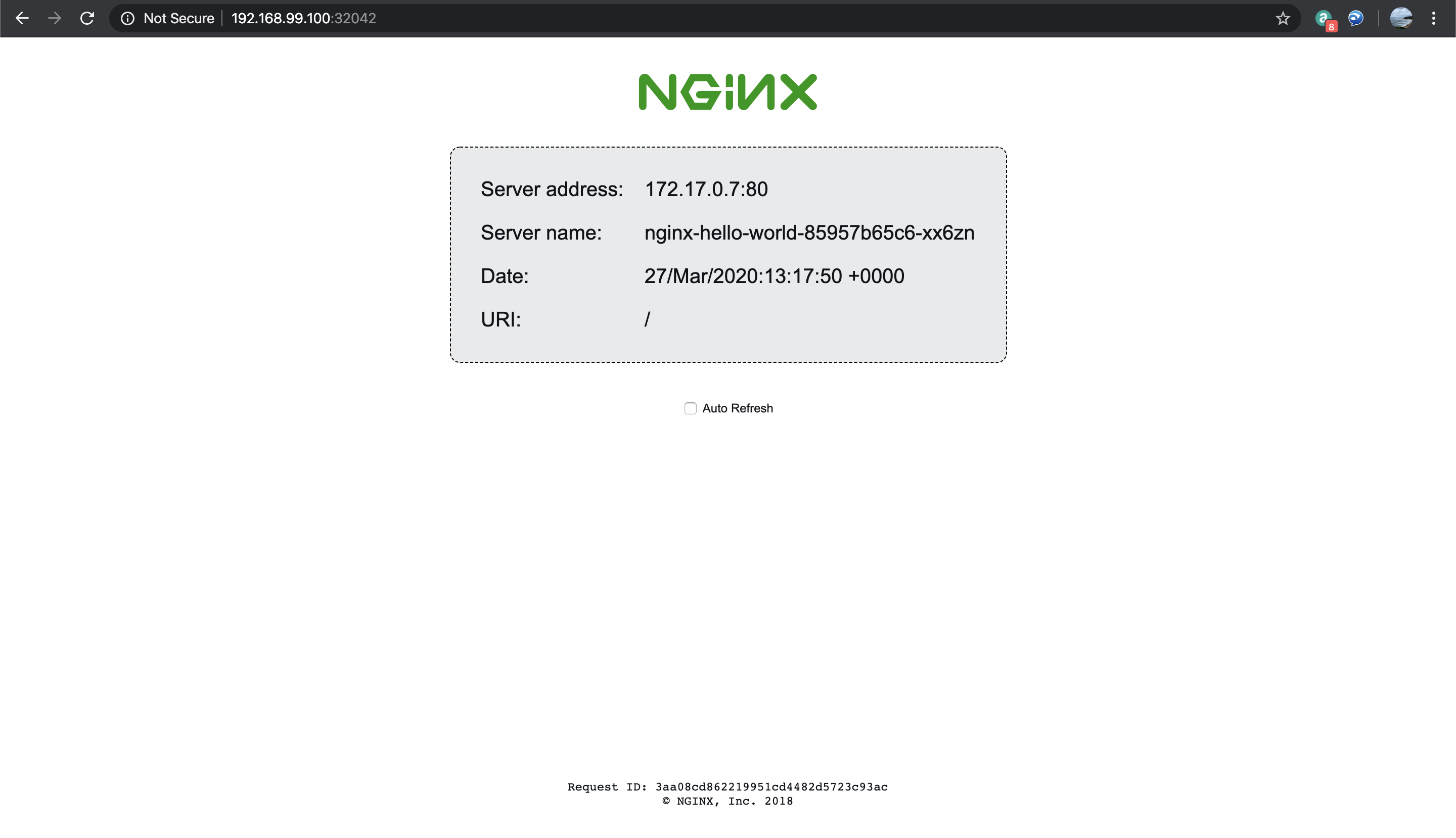
- Using your favorite browser, type
<minikube_ip>:<node_port>eg. 192.168.99.100:32042 then you will see a nice Nginx page as seen below.