Maximum coverage location problem (MCLP)
A fork of Can Yang's - "Maximum Coverage Location" repository using python-mip instead of gurobipy.
This repository provides a Python implementation of solving a classical instance of the maximum coverage location problem described in Church 1974.
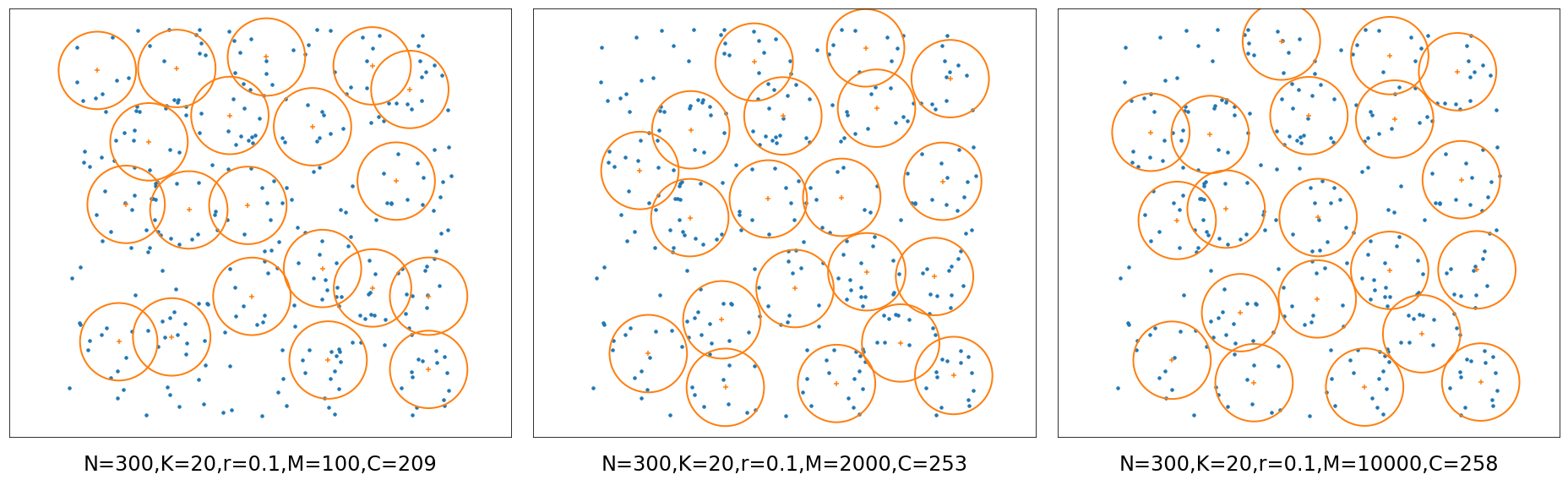
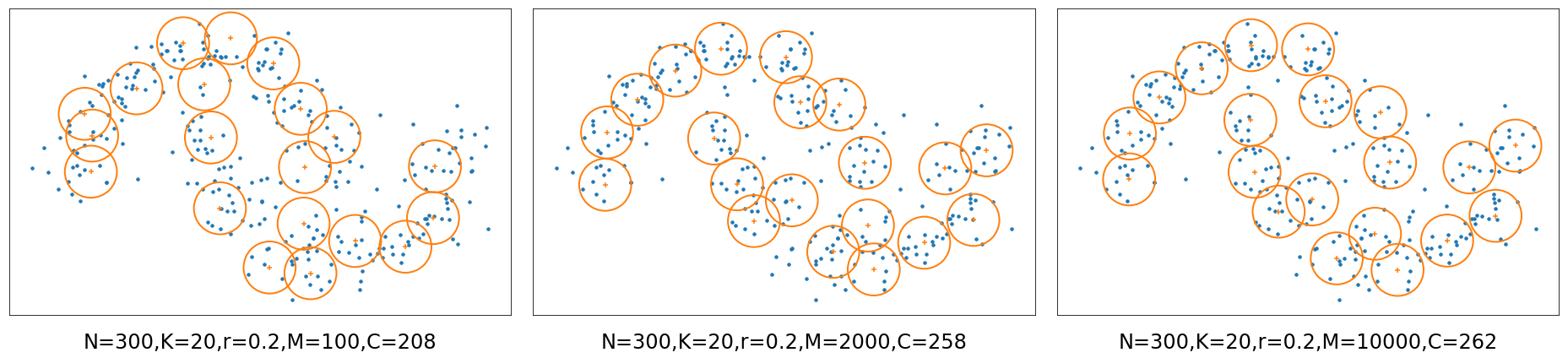
The problem is defined as: given N points, find K circles with radius of r to cover as many points as possible.
- Example 1: Select 20 circles with radius of 0.1 to cover 300 points (uniform distribution)
(M is the number of candidate sites and C is the number of points covered)
- Example 2: Select 20 circles with radius of 0.2 to cover 300 points (moon distribution)
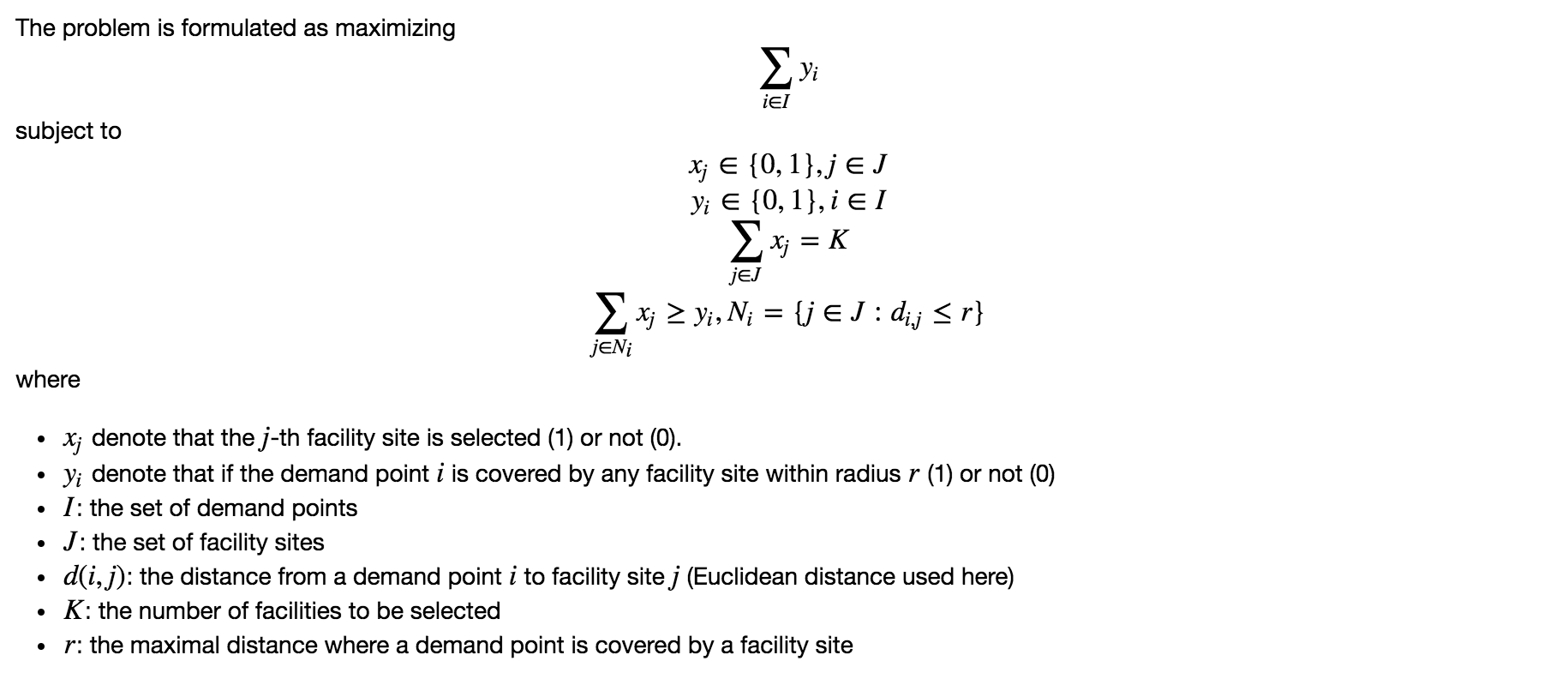
Problem formulation
The method randomly generates a set of candidate sites within the region of the input points. The problem is then solved by integer programming.
The mathematical formulation is given below:
Demo and usage
from mclp import *
import numpy as np
Npoints = 300
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
points,_ = make_moons(Npoints,noise=0.15)
# Number of sites to select
K = 20
# Service radius of each site
radius = 0.2
# Candidate site size (random sites generated)
M = 100
# Run mclp
# opt_sites is the location of optimal sites
# f is the number of points covered
opt_sites,f = mclp(points,K,radius,M)
# Plot the result
plot_result(points,opt_sites,radius)