#include <stdint.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <regex>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 参考代码:软件学院2019级-王一辉
#pragma pack(1) // 指定按 1 字节对齐,否则 struct 和 class 的成员变量按 4 字节对齐
const unsigned BYTES_PER_ENTRY = 32;
const int MAX_CONTENT_SIZE = 10000;
const int FINAL_TAG = 0xFF8; // FAT 表的坏簇标记
const char* COMMAND_ERROR = "ERROR: Cannot parse this command!\n";
const char* NO_FILE_ERROR = "ERROR: No such file!\n";
const char* FILE_TYPE_ERROR = "ERROR: File type error!!\n";
const char* EXIT_MESSAGE = "Bye!\n";
const string PATH_SEPARATOR = "/";
extern "C" {
void my_print(const char*, int);
void print(const char*);
void print_red(const char*);
}
inline void Print(const char* s, bool red = false) {
const char* colored = red ? ("\033[31m" + string(s) + "\033[37m").c_str() : s;
#ifdef EagleBear
printf("%s", colored);
#else
// my_print(colored, strlen(colored));
if (red) {
print_red(s);
} else {
print(s);
}
#endif
}
inline void readFromFile(void* dist, size_t size, FILE* fat12, uint32_t pos) {
fseek(fat12, pos, SEEK_SET);
fread(dist, 1, size, fat12);
}
// 参考代码:https://blog.csdn.net/Mary19920410/article/details/77372828
vector<string> split(const string& str, const string& delim) {
vector<string> res;
if (str.empty())
return res;
char strs[str.length() + 1];
strcpy(strs, str.c_str());
char d[delim.length() + 1];
strcpy(d, delim.c_str());
char* p = strtok(strs, d);
while (p) {
string s = p;
res.push_back(s); //存入结果数组
p = strtok(nullptr, d);
}
return res;
}
uint16_t bytesPerSector; // 每扇区字节数,一般为 512
uint8_t sectorsPerCluster; // 每簇扇区数,一般为 1
uint16_t reservedSectors; // Boot 记录占用的扇区数
uint8_t FATCount; // FAT 表个数,一般为 2
uint16_t directoryEntries; // 根目录最大文件数
uint32_t sectorsPerFAT; // FAT 扇区数
uint32_t FATBase; // FAT1 的偏移量
uint32_t rootDirectoryBase; // 根目录的偏移量
uint32_t dataBase; // 数据区偏移量
uint32_t bytesPerCluster; // 每簇字节数 = 每扇区字节数 * 每簇扇区数
inline int getFATValue(FILE* fat12, int num) {
uint32_t pos = FATBase + num / 2 * 3;
int FATValue = 0;
readFromFile(&FATValue, 3, fat12, pos);
if (num % 2) { // pos id odd
FATValue = FATValue >> 12;
} else { // pos is even
FATValue = FATValue & 0xfff;
}
return FATValue;
}
class BPB {
private:
uint16_t BPB_BytesPerSector; // 每扇区字节数,一般为 512
uint8_t BPB_SectorsPerCluster; // 每簇扇区数,一般为 1
uint16_t BPB_ReservedSectors; // Boot record 占用的扇区数
uint8_t BPB_FATCount; // FAT 表个数,一般为 2
uint16_t BPB_DirectoryEntries; // 根目录文件数的最大值
uint16_t BPB_TotalSectors; // 扇区数
uint8_t BPB_MediaDescriptor; //
uint16_t BPB_SectorsPerFAT; // FAT 扇区数,扇区数大于 65535 时该值为 0
uint16_t BPB_SectorsPerTrack;
uint16_t BPB_Heads;
uint32_t BPB_HiddenSectors;
uint32_t BPB_LargerSectorCount; // 如果 BPB_SectorsPerFAT 为 0,该值为 FAT 扇区数
public:
BPB(FILE* fat12) {
readFromFile(this, 25, fat12, 11);
bytesPerSector = BPB_BytesPerSector;
sectorsPerCluster = BPB_SectorsPerCluster;
reservedSectors = BPB_ReservedSectors;
FATCount = BPB_FATCount;
directoryEntries = BPB_DirectoryEntries;
if (BPB_SectorsPerFAT != 0) {
sectorsPerFAT = BPB_SectorsPerFAT;
} else {
sectorsPerFAT = BPB_LargerSectorCount;
}
FATBase = reservedSectors * bytesPerSector;
rootDirectoryBase = FATBase + sectorsPerFAT * FATCount * bytesPerSector;
dataBase = rootDirectoryBase + (directoryEntries * BYTES_PER_ENTRY + bytesPerSector - 1) / bytesPerSector * bytesPerSector; // dataBase = fileRootBase + ceil(1.0 * directoryEntries * BYTES_PER_ENTRY /bytesPerSector) * bytesPerSector;
bytesPerCluster = sectorsPerCluster * bytesPerSector;
};
}; // end of BPB
enum NodeType {
FILE_TYPE,
DIRECTORY_TYPE,
VIRTUAL,
};
struct Node {
const string name;
const string path;
size_t fileSize;
vector<Node*> children;
NodeType type;
int directoryCount = 0;
int fileCount = 0;
char content[MAX_CONTENT_SIZE]{};
void list(const bool listSize) const {
char tmp[522];
if (listSize) {
sprintf(tmp, "%s %d %d:\n", path.c_str(), directoryCount, fileCount);
} else {
sprintf(tmp, "%s:\n", path.c_str());
}
Print(tmp);
for (Node* child : children) {
if (child->type == VIRTUAL) {
Print(child->name.c_str(), true);
Print(" ");
} else if (child->type == FILE_TYPE) {
if (listSize) {
sprintf(tmp, "%s %d", child->name.c_str(), child->fileSize);
} else {
sprintf(tmp, "%s ", child->name.c_str());
}
Print(tmp);
} else { // DIRECTORY
Print(child->name.c_str(), true);
if (listSize) {
sprintf(tmp, " %d %d", child->directoryCount, child->fileCount);
} else {
sprintf(tmp, " ");
}
Print(tmp);
}
if (listSize)
Print("\n");
}
Print("\n");
for (Node* child : children) {
if (child->type == DIRECTORY_TYPE) {
child->list(listSize);
}
}
}
Node(string name, string path, NodeType type, size_t fileSize)
: name(name), path(path), type(type), fileSize(fileSize) {}
inline void addChild(Node* child) {
if (child->type == DIRECTORY_TYPE) {
child->addChild(new Node(".", "", VIRTUAL, 0));
child->addChild(new Node("..", "", VIRTUAL, 0));
this->directoryCount++;
} else if (child->type == FILE_TYPE) {
this->fileCount++;
}
this->children.push_back(child);
}
string formatPath(string targetPath) const {
vector<string> names = split(targetPath, PATH_SEPARATOR);
stack<string> st;
for (string name : names) {
if (name == ".") {
continue;
} else if (name == "..") {
if (!st.empty())
st.pop();
} else {
st.push(name);
}
}
string res;
while (!st.empty()) {
res = PATH_SEPARATOR + st.top() + res;
st.pop();
}
return res;
}
const Node* findNode(string targetPath) const {
targetPath = formatPath(targetPath);
// printf("targetPath = %s\n", targetPath.c_str());
// printf("currentPath = %s\n", path.c_str());
if (this->type == FILE_TYPE && targetPath == this->path + this->name) {
// printf("find: %s\n", this->path.c_str());
return this;
}
if (this->type == DIRECTORY_TYPE && this->path == targetPath + PATH_SEPARATOR) {
return this;
}
if (targetPath.find(path) != 0) {
return nullptr;
}
for (Node* child : children) {
const Node* res = child->findNode(targetPath);
if (res != nullptr) {
return res;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
void readContent(FILE* fat12, int startCluster);
void readChildren(FILE* fat12, int startCluster);
}; // end of Node
struct DirectoryEntry {
static const int NAME_LENGTH = 11;
static const int DIRECTORY = 0x10;
char fileName[NAME_LENGTH]; // "xxxxxxxxyyy" as xxxxxxxx.yyy, where xxxxxxxx is filename and yyy is extention
uint8_t fileAttributes;
char reserved[14];
uint16_t firstCluster_low;
uint32_t fileSize;
DirectoryEntry() = default;
inline bool invalidName() const {
if (fileName[0] == '\0')
return true;
for (char ch : fileName)
if (ch != ' ' && !isalnum(ch))
return true;
return false;
}
void initRootEntry(FILE* fat12, Node* root) {
uint32_t base = rootDirectoryBase;
for (int i = 0; i < directoryEntries; ++i) {
readFromFile(this, BYTES_PER_ENTRY, fat12, base);
base += BYTES_PER_ENTRY;
if (this->invalidName())
continue;
string realName = this->transferName();
Node* child;
if (this->isFile()) {
child = new Node(realName, root->path, FILE_TYPE, fileSize);
root->addChild(child);
child->readContent(fat12, firstCluster_low);
} else {
child = new Node(realName, root->path + realName + PATH_SEPARATOR, DIRECTORY_TYPE, 0);
root->addChild(child);
child->readChildren(fat12, firstCluster_low);
}
}
}
inline bool isFile() const {
return (fileAttributes & DIRECTORY) == 0;
}
string transferName() const {
string res;
for (int i = 0; i < NAME_LENGTH; ++i) {
if (i == 8 && this->isFile())
res += '.';
if (fileName[i] != ' ')
res += fileName[i];
}
return res;
}
size_t getFileSize() const {
return fileSize;
}
}; // end of DirectoryEntry
void Node::readContent(FILE* fat12, int startCluster) {
if (startCluster == 0)
return;
char* pointer = this->content;
for (int currentCluster = startCluster; currentCluster < FINAL_TAG; currentCluster = getFATValue(fat12, currentCluster)) {
char tmp[bytesPerCluster];
uint32_t startByte = dataBase + (currentCluster - 2) * sectorsPerCluster * bytesPerSector;
readFromFile(tmp, bytesPerCluster, fat12, startByte);
memcpy(pointer, tmp, bytesPerCluster);
pointer += bytesPerCluster;
}
}
void Node::readChildren(FILE* fat12, int startCluster) {
for (int currentCluster = startCluster; currentCluster < FINAL_TAG; currentCluster = getFATValue(fat12, currentCluster)) {
uint32_t startByte = dataBase + (currentCluster - 2) * sectorsPerCluster * bytesPerSector; // 数据区的第一个簇的簇号是 2
for (int i = 0; i < bytesPerCluster; i += BYTES_PER_ENTRY) {
DirectoryEntry* rootEntry = new DirectoryEntry();
readFromFile(rootEntry, BYTES_PER_ENTRY, fat12, startByte + i);
if (rootEntry->invalidName()) {
continue;
}
string realName = rootEntry->transferName();
if (rootEntry->isFile()) {
Node* child = new Node(realName, this->path, FILE_TYPE, rootEntry->getFileSize());
addChild(child);
child->readContent(fat12, rootEntry->firstCluster_low);
} else {
Node* child = new Node(realName, this->path + realName + PATH_SEPARATOR, DIRECTORY_TYPE, 0);
addChild(child);
child->readChildren(fat12, rootEntry->firstCluster_low);
}
}
}
}
const char* handleCat(vector<string>& commands, const Node* root) {
if (commands.size() != 2) {
return COMMAND_ERROR;
}
string& path = commands[1];
const Node* res = root->findNode(path);
if (res == nullptr) {
return NO_FILE_ERROR;
}
if (res->type != FILE_TYPE) {
return FILE_TYPE_ERROR;
}
return res->content;
}
const char* handleList(vector<string>& commands, Node* root) {
bool listSize = false, pathSet = false;
const Node* directory = root;
for (int i = 1; i < commands.size(); i++) {
string& arg = commands[i];
if (regex_match(arg.c_str(), regex("-l+"))) {
listSize = true;
} else if (!pathSet) {
pathSet = true;
directory = root->findNode(arg);
} else {
return COMMAND_ERROR;
}
}
if (directory == nullptr)
return NO_FILE_ERROR;
if (directory->type != DIRECTORY_TYPE)
return FILE_TYPE_ERROR;
directory->list(listSize);
return "";
}
int main() {
#ifdef EagleBear
freopen("test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("test.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
FILE* fat12 = fopen("./a2.img", "rb"); // 打开 FAT12 的映像文件
BPB bpb(fat12);
Node* root = new Node("", "/", DIRECTORY_TYPE, 0);
DirectoryEntry* rootEntry = new DirectoryEntry();
rootEntry->initRootEntry(fat12, root);
while (true) {
Print("> ");
string inputLine;
getline(cin, inputLine);
#ifdef EagleBear
Print(inputLine.c_str());
Print("\n");
#endif
vector<string> commandLine = split(inputLine, " ");
const char* res = COMMAND_ERROR;
if (commandLine.size() == 0) {
res = "";
} else if (commandLine[0] == "exit") {
if (commandLine.size() == 1) {
Print(EXIT_MESSAGE);
break;
}
} else if (commandLine[0] == "ls") {
res = handleList(commandLine, root);
} else if (commandLine[0] == "cat") {
res = handleCat(commandLine, root);
}
Print(res);
}
fclose(fat12);
#ifdef EagleBear
fclose(stdin), fclose(stdout);
#endif
return 0;
}
; 参考代码:https://blog.csdn.net/bedisdover/article/details/51287555
global print
global print_red
global my_print
section .data
color_red db 1Bh,'[31m',0
.len equ $-color_red
color_default db 1Bh,'[37m',0
.len equ $-color_default
section .text
print:
mov eax, 4
mov ebx, 1
mov ecx, color_default
mov edx, color_default.len
int 80h
mov ecx, [esp+4] ; ecx = str
mov eax, [esp+4]
call strlen
mov edx, eax ; edx = len
mov eax, 4
mov ebx, 1
int 80h
ret
print_red:
mov eax, 4
mov ebx, 1
mov ecx, color_red
mov edx, color_red.len
int 80h
mov ecx, [esp+4]
mov eax, [esp+4]
call strlen
mov edx, eax
mov eax, 4
mov ebx, 1
int 80h
mov eax, 4
mov ebx, 1
mov ecx, color_default
mov edx, color_default.len
int 80h
ret
;; strlen(str: eax) -> len: eax
strlen:
push ebx
mov ebx, eax
.nextchar:
cmp byte [eax], 0
jz .finished
inc eax
jmp .nextchar
.finished:
sub eax, ebx
pop ebx
ret
my_print:
push ebp
mov edx, [esp+12]
mov ecx, [esp+8]
mov ebx, 1
mov eax, 4
int 80h
pop ebp
retMain: main.cpp my_print.asm
nasm -felf32 my_print.asm -o my_print.o
g++ main.cpp my_print.o -o main -std=c++11
rm -rf my_print.o
clean:
rm -rf main该实验实现了附加功能:cat 命令支持输出超过 512 字节的文件。
- 使用
#pragma pack(1)指令,编译时对成员变量按 1 字节对齐,而不是按 4 字节对齐。 - 在汇编中实现输出红色字体,避免在 C++ 代码中实现输出红色字体带来的错误
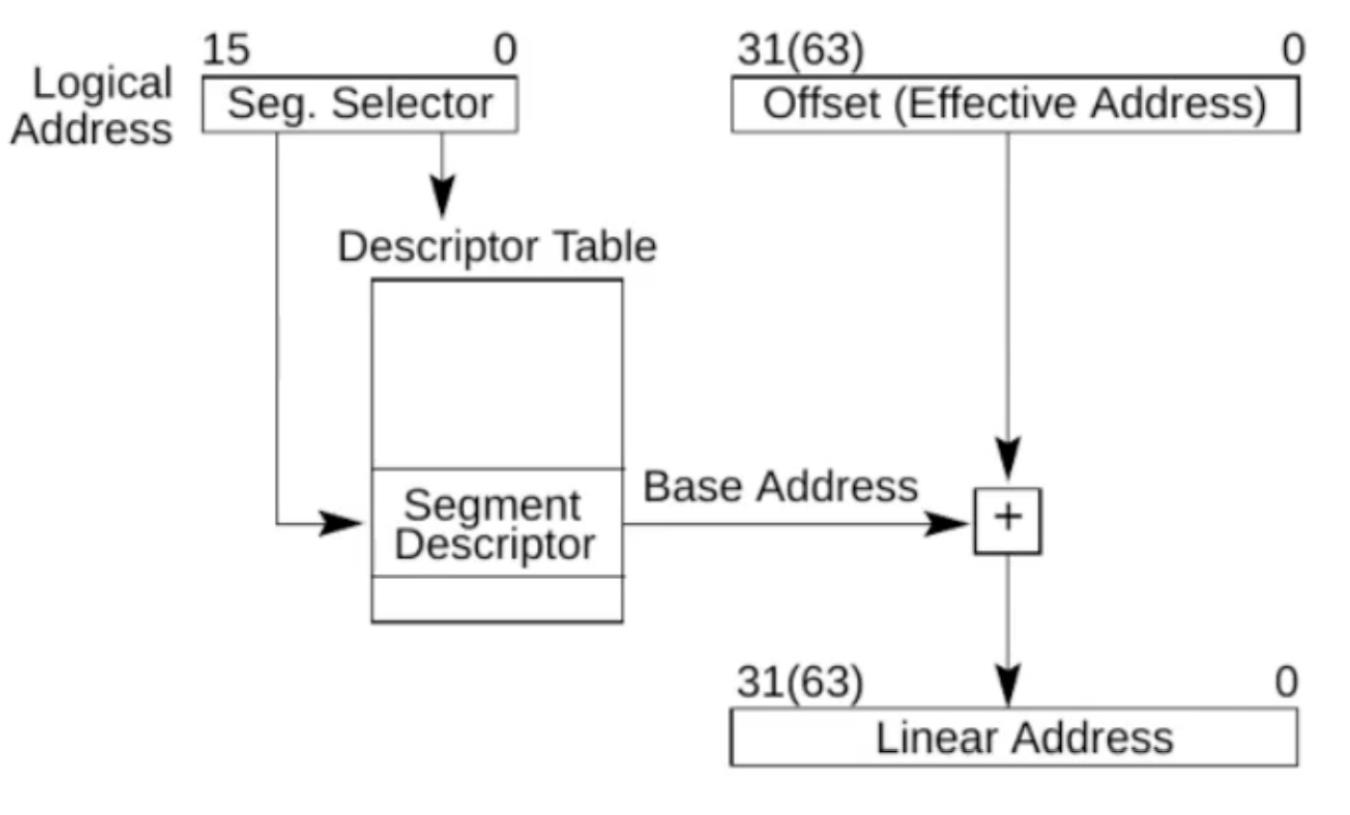
- 实模式:基地址+偏移量可以直接获得物理地址的模式。缺点:非常不安全
- 保护模式:不能直接拿到物理地址,需要进行地址转换。从 80286 开始,是现代操作系统的主要模式
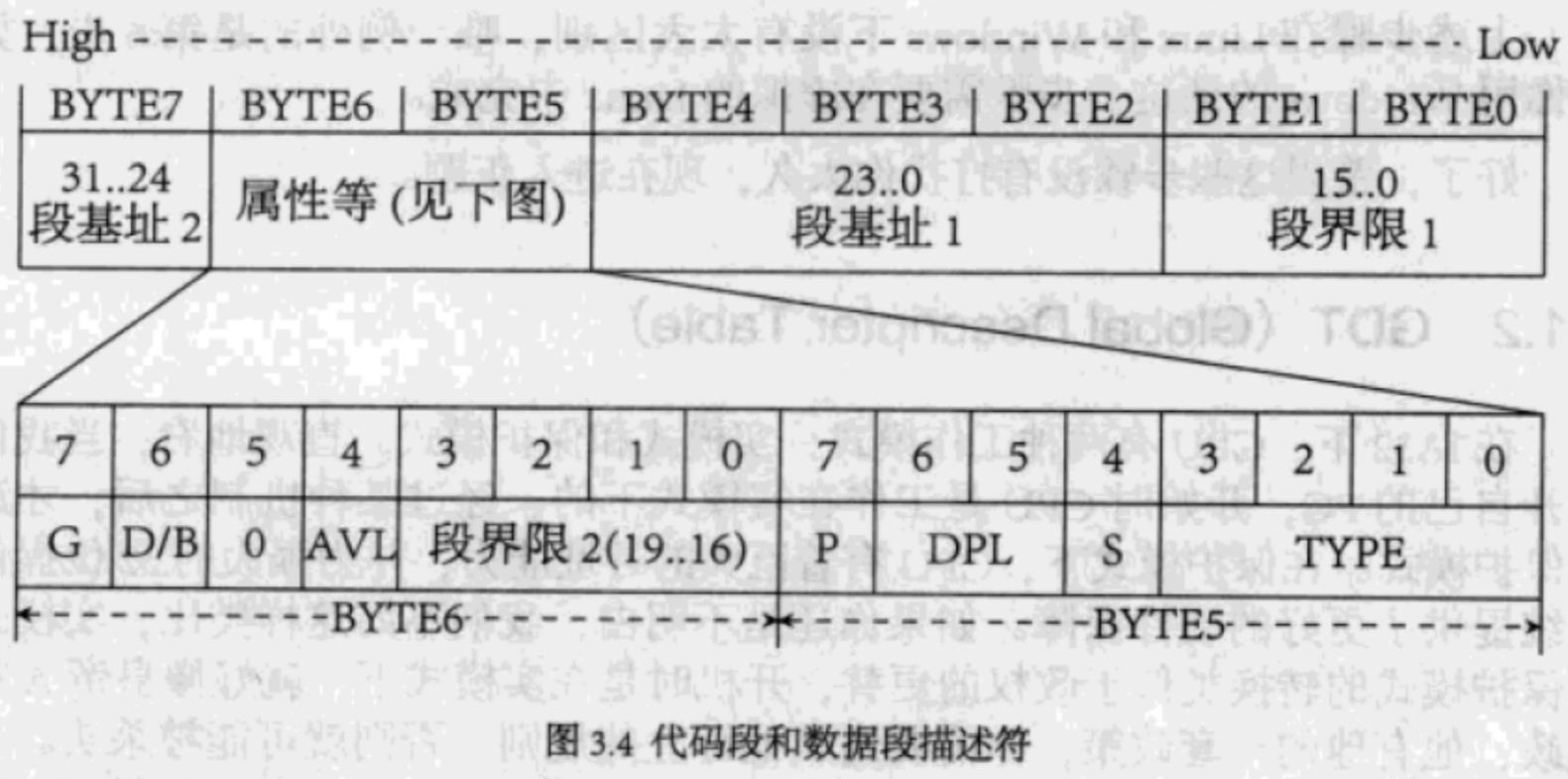
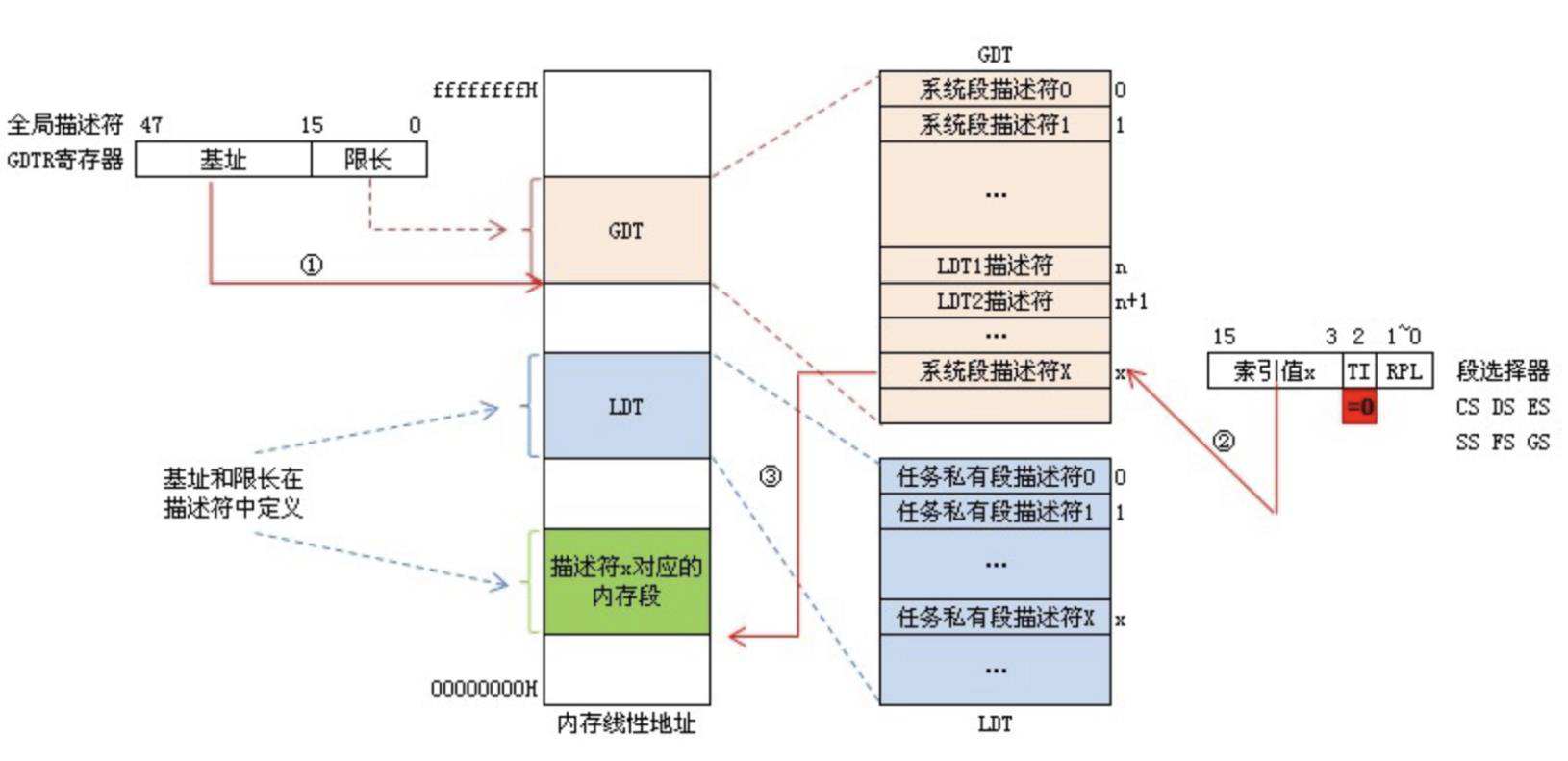
- 选择子共 16 位,放在段选择寄存器里
- 低 2 位表示请求特权级
- 第 3 位表示选择 GDT 还是 LDT 方式
- 高 13 位表示在描述符表中的偏移
- 故描述符表的项数最多是 2^13^
GDT:全局描述符表,是全局唯一的。存放一些公用的描述符,和包含各进程局部描述符表首地址的描述符。
LDT:局部描述符表,每个进程都可以有一个。存放本进程内使用的描述符。
GDTR:48 位寄存器,高 32 位放置 GDT 首地址,低 16 位放置 GDT 限长。限长决定了可寻址的大小,注意低 16 位放的不是选择子
LDTR:16 位寄存器,放置一个特殊的选择子,用于查找当前进程的 LDT 首地址。
- 给出段选择子(放在段选择寄存器里)+ 偏移量
- 若选择了 GDT 方式,则从 GDTR 获取 GDT 首地址,用段选择子中的 13 位做偏移,拿到 GDT 中的描述符
- 如果合法且有权限,用描述符中的段首地址加上第 1 步中的偏移量找到物理地址,寻址结束
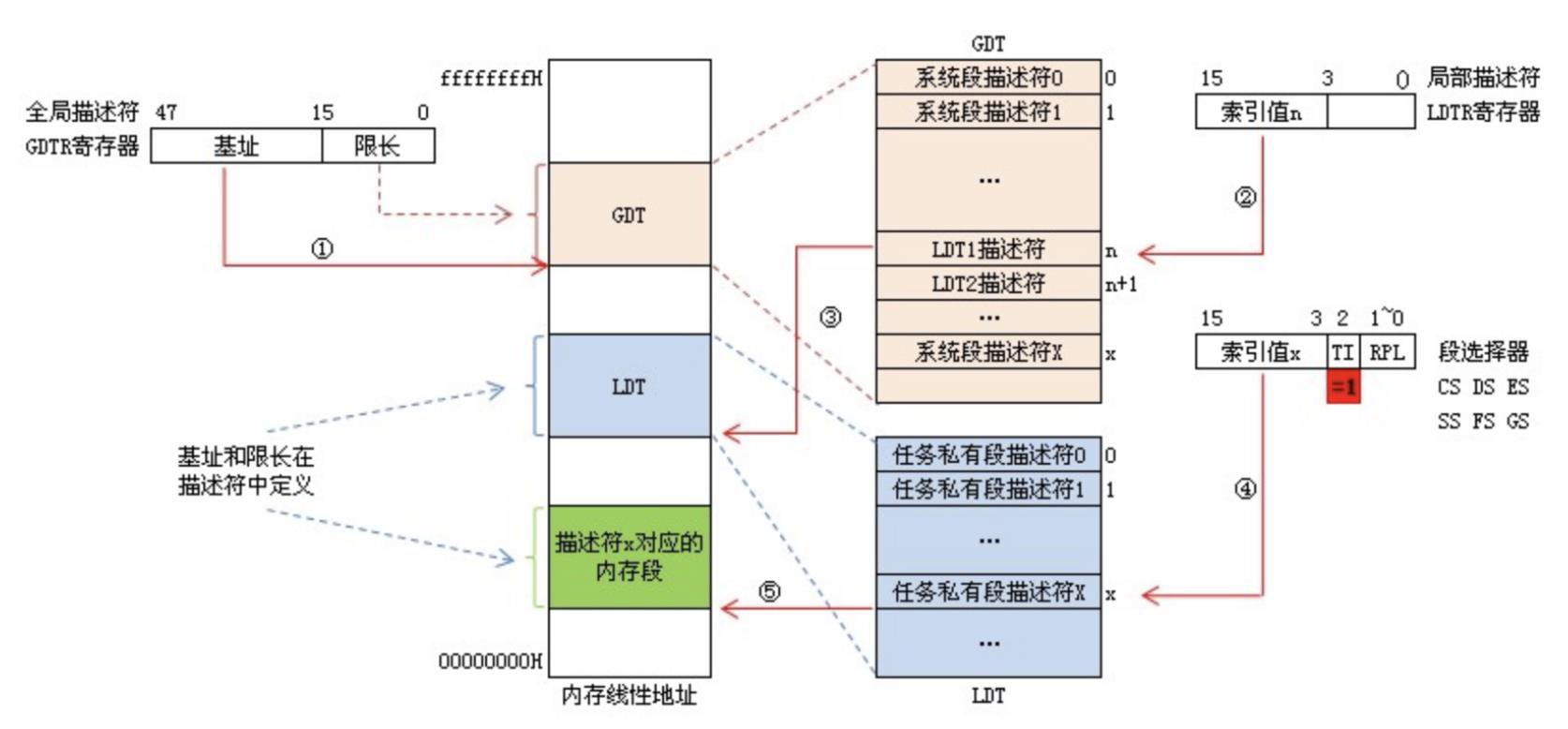
- 给出段选择子(放在段选择寄存器中)+ 偏移量
- 若选择了 LDT 方式,则从 GDTR 获取 GDT 首地址,用 LDTR 中的偏移量做偏移,拿到 GDT 中的描述符 1
- 从描述符 1 中获取 LDT 首地址,用段选择子中的 13 位做偏移,拿到 LDT 中的描述符 2
- 如果合法且有权限,用描述符 2 中的段首地址加上第 1 步中的偏移量找到物理地址。寻址结束
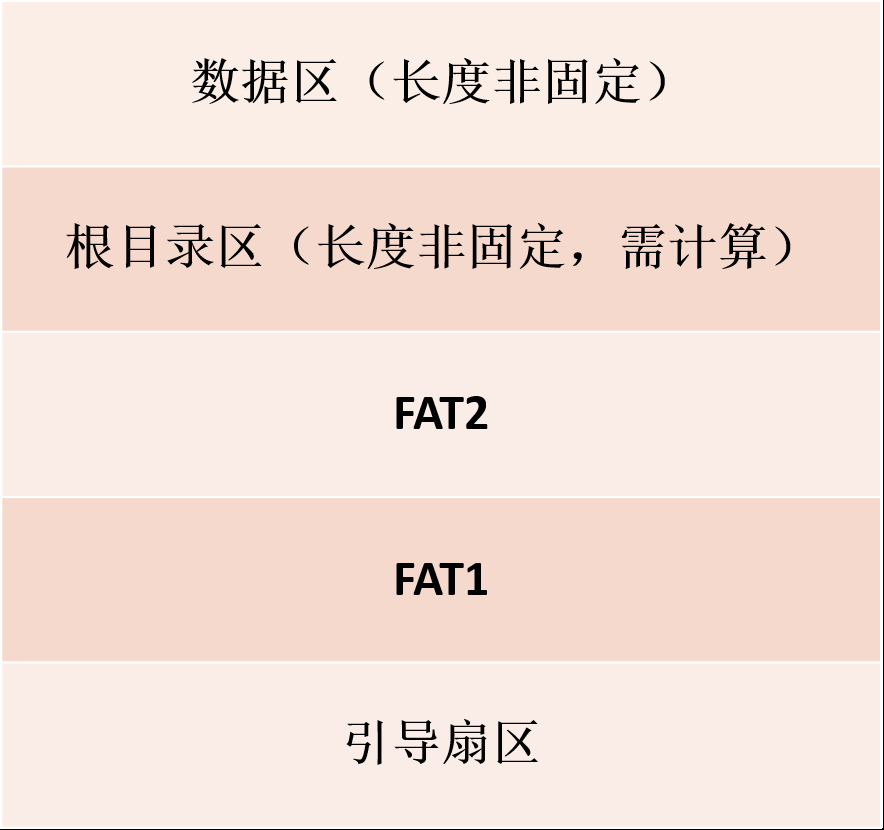
根目录区长度不是一定的,需要根据 BPB 中规定的根目录最大文件数计算。
下面代码求出根目录区的起始字节数。
FATBase = reservedSectors * bytesPerSector;
rootDirectoryBase = FATBase + sectorsPerFAT * FATCount * bytesPerSector;一般来说,0 扇区为引导扇区,每个 FAT 表占用 9 个扇区,则根目录区从 19 扇区开始。
下面代码求出数据区的起始字节数。
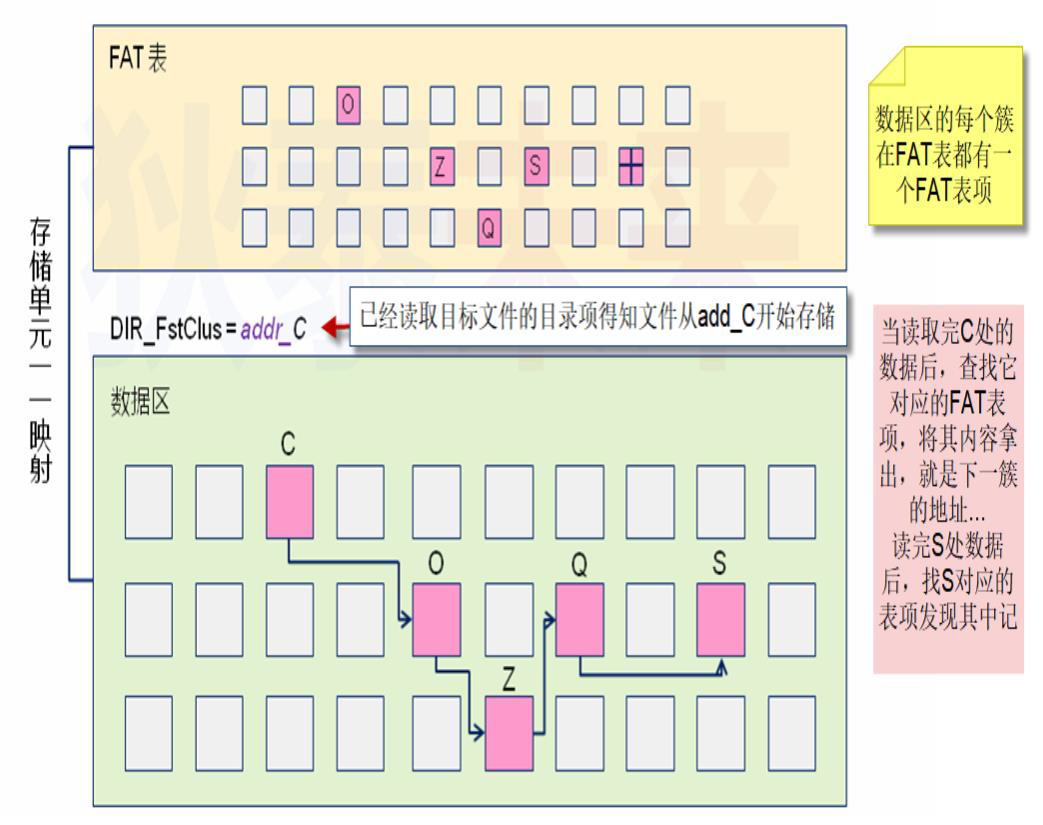
dataBase = rootDirectoryBase + (directoryEntries * BYTES_PER_ENTRY + bytesPerSector - 1) / bytesPerSector * bytesPerSector; // dataBase = fileRootBase + ceil(1.0 * directoryEntries * BYTES_PER_ENTRY /bytesPerSector) * bytesPerSector;文件分配表被划分为紧密排列的若干个表项,每个表项都与数据区中的一个簇相对应,而且表项的序号也是与簇号一一对应的。
每 12 位成为一个 FAT 项(FATEntry),代表一个簇。所以 2 个 FAT 项会占用 3 个字节。
FAT 项的值代表文件的下一个簇号:
- 值大于或等于
0xFF8,表示当前簇已经是本文件的最后一个簇 - 值为
0xFF7,表示它是一个坏簇
静态链接是指在编译阶段直接把静态库加入到可执行文件中去,这样可执行文件会比较大。
静态链接时发生空间和地址分配,符号解析和重定位。
动态链接是指链接阶段仅仅只加入一些描述信息,而程序执行时再从系统中把相应动态库加载到内存中去。
动态链接分为装载时动态链接和运行时动态链接。
ld 是 gcc 工具链的一部分。
从 0x08048000 开始分配。
在 386 系统上,文本基地址为 0x08048000,这允许文本下方有一个相当大的堆栈,同时仍保持在地址 0x08000000 上方,从而允许大多数程序使用单个二级页表。 (回想一下,在 386 上,每个二级表映射 0x00400000 个地址。)
class BPB {
private:
uint16_t BPB_BytesPerSector; // 每扇区字节数,一般为 512
uint8_t BPB_SectorsPerCluster; // 每簇扇区数,一般为 1
uint16_t BPB_ReservedSectors; // Boot record 占用的扇区数
uint8_t BPB_FATCount; // FAT 表个数,一般为 2
uint16_t BPB_DirectoryEntries; // 根目录文件数的最大值
uint16_t BPB_TotalSectors; // 扇区数
uint8_t BPB_MediaDescriptor; // Media Descriptor 的种类
uint16_t BPB_SectorsPerFAT; // FAT 扇区数,扇区数大于 65535 时该值为 0
uint16_t BPB_SectorsPerTrack;
uint16_t BPB_Heads; // Number of heads or sides on the storage media.
uint32_t BPB_HiddenSectors; // Number of hidden sectors.
uint32_t BPB_LargerSectorCount; // 如果 BPB_SectorsPerFAT 为 0,该值为 FAT 扇区数
...
};在初始化时已经利用 class Node 构建了逻辑上的文件树。在处理命令时直接对构建好的文件树进行遍历,不再访问二进制文件。
在初始化时已经利用 class Node 构建了逻辑上的文件树。在处理命令时直接对构建好的文件树进行遍历,不再访问二进制文件。
findNode 成员函数为根据目标路径,对当前节点及其子节点进行查找。
使用 [esp+4] 获取函数的唯一一个参数。函数没有返回值。
使用基本同实验一的方式进行 I/O,与输出颜色相关的代码如下:
section .data
color_red db 1Bh,'[31m',0
.len equ $-color_red
color_default db 1Bh,'[37m',0
.len equ $-color_default