- Manually improve the assembly
- Detect genetic diversity between maternal and paternal
- Annntate variants
- Identification of positively selected genes (PSGs)
- Compare diabetes-related genes among four species
you can download all scripts using
git clone https://github.com/comery/Nile_rat.git
and then set the binpath for below analyzing
bin=/xxx/xxx/Nile_rat/bin
Anchor more scaffolds onto chromosomes and prepare data to whole-genome alignment and SV identification.
mat=GCA_011750645.1_mArvNil1.mat_genomic.fna
pat=GCA_011762545.1_mArvNil1.pat_genomic.fna
p="Nile_Rat"
/share/app/MUMmer3.23/nucmer -maxmatch -l 100 -c 500 -p $p $mat $pat
/share/app/MUMmer3.23/delta-filter -m -i 90 -l 100 $p.delta > $p.delta.filt
/share/app/MUMmer3.23/dnadiff -d $p.delta -p $p.diff
This is a rough comparison to find the coordinate information of two assemblies quickly. Once we have found the missing scaffolds, we can link them up and detect genetic variations precisely.
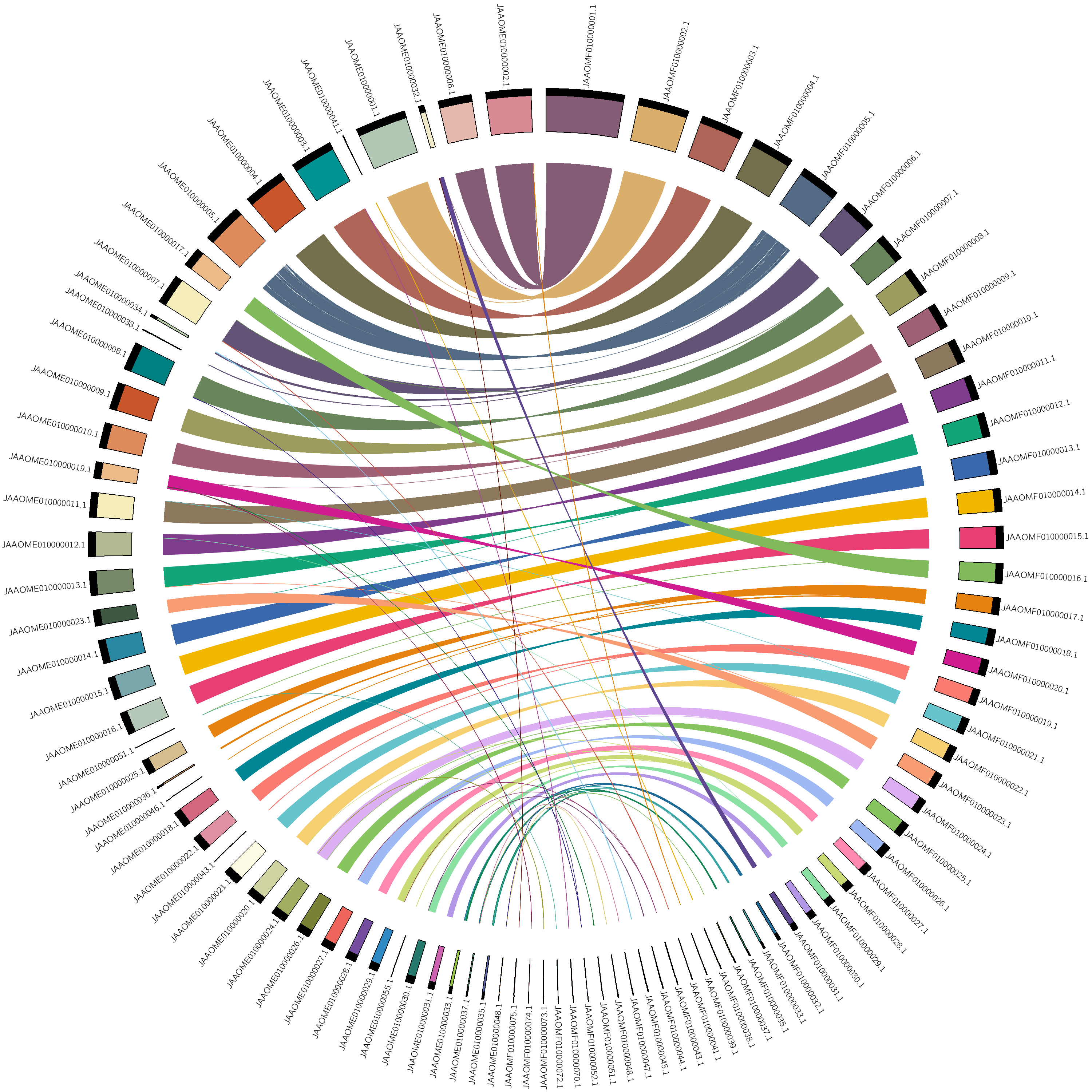
visualization of alignments
only keep scaffolds with length > 500 kb, and aligned block length > 10 kb
awk '($5>=10000||$6>=10000) && $7>98 && ($8>=500000 && $9>=500000){print $12"\t"$1"\t"$2"\t"$13"\t"$3"\t"$4}' Nile_Rat.diff.1coords > Nile_Rat.10k.id98.link
python3 Nile_Rat/bin/preCircosLink.sort.py --link Nile_Rat.10k.id98.link --scaf_len all.lens --minL 500000 --minB 10000 --rate 0.5
note: 'all.lens' contains the length of all scaffolds
circos -conf circos.conf
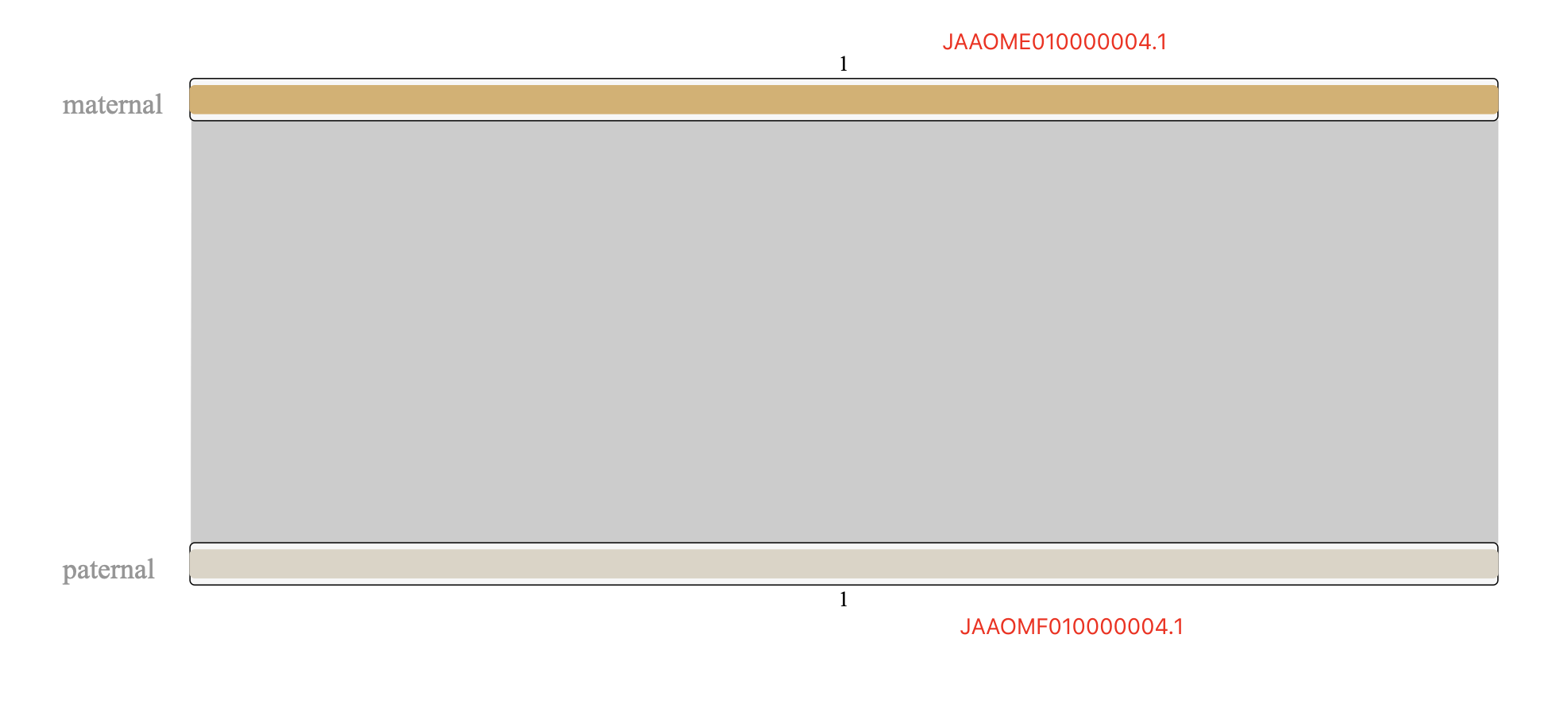
Figure 1. maternal vs. paternal alignmentNote: you can copy the circos.conf form here
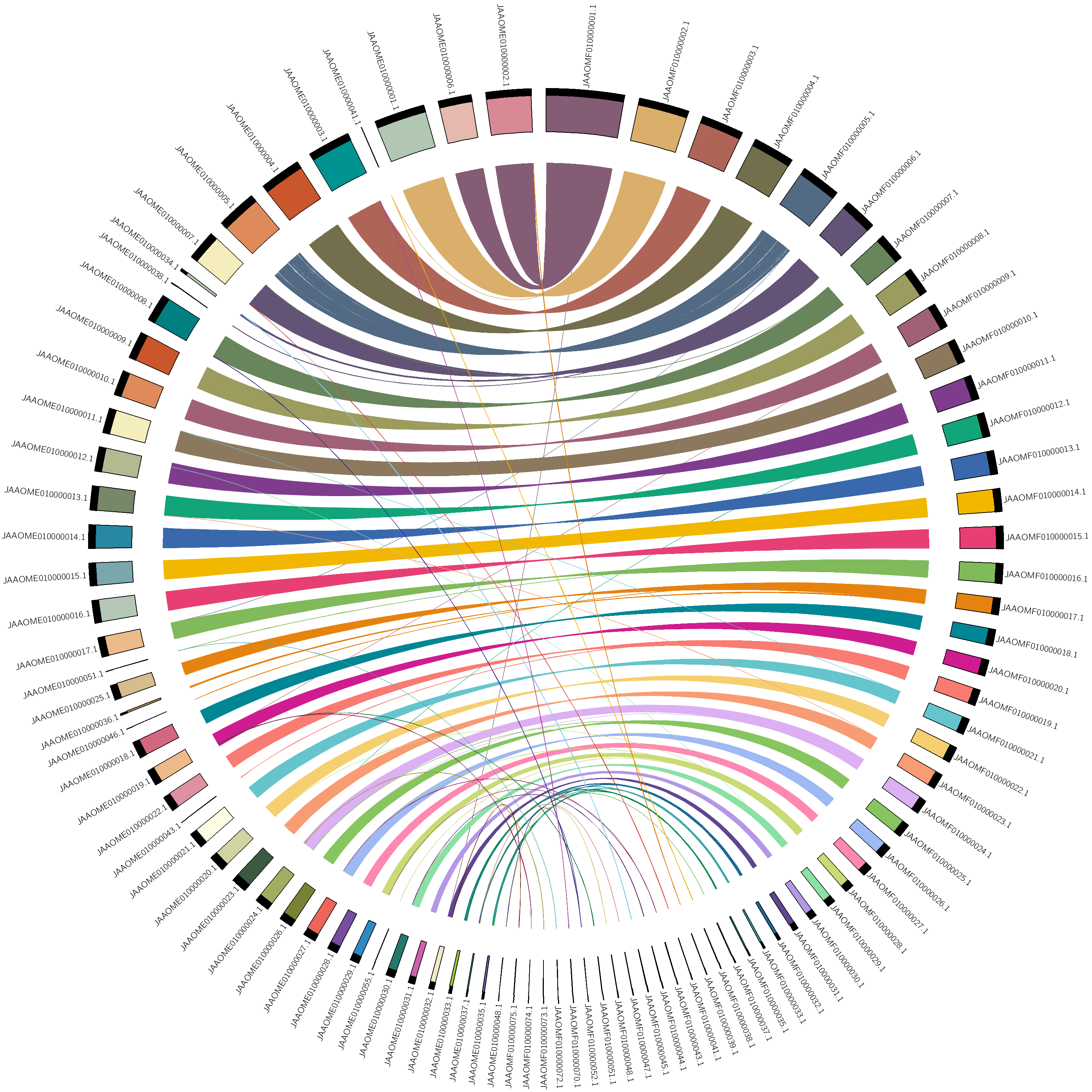
manually adjust the order, vi karyotype.txt
draw again using circos -conf circos.conf
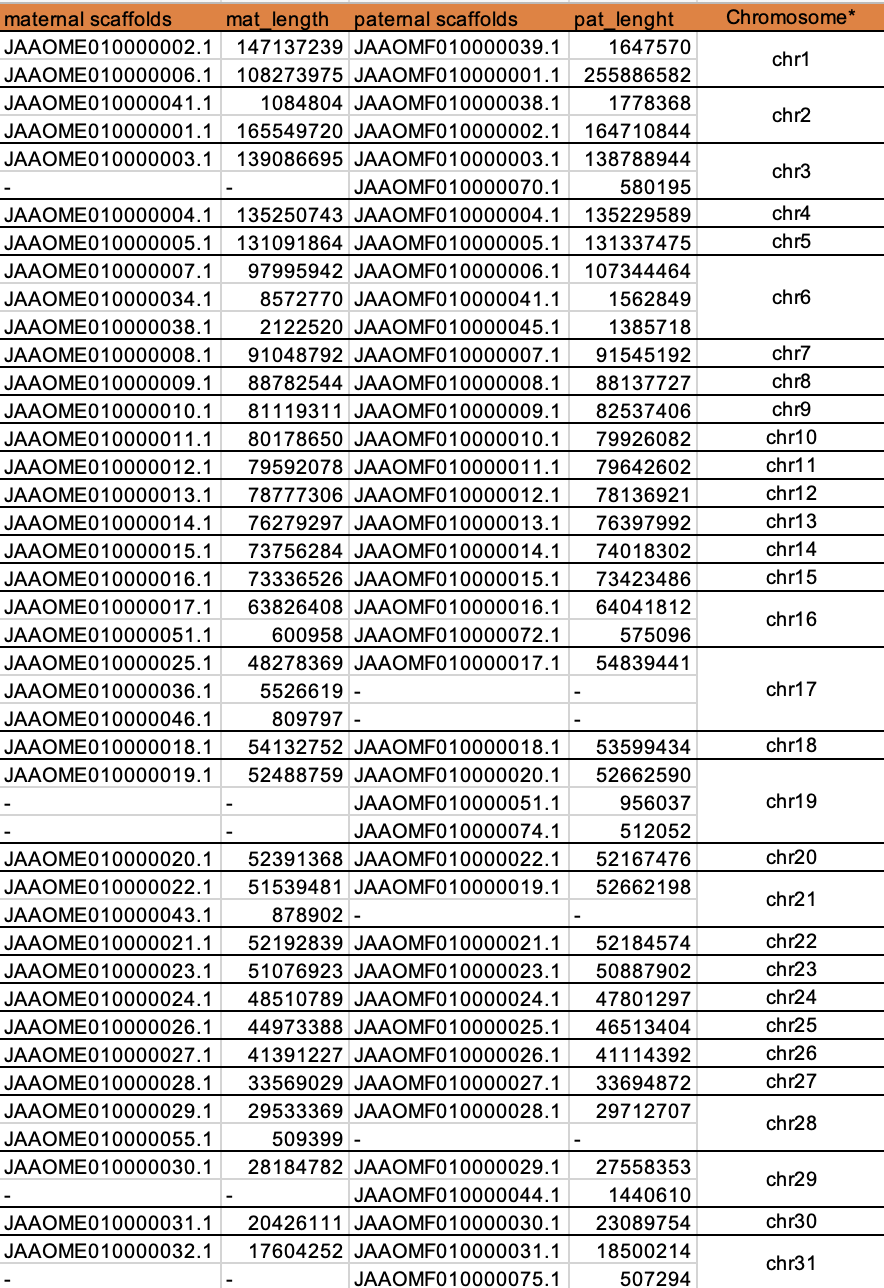
* hypothetical chromosomes order indicated by descending length, not biological chromosomes table file can find => assembly_stat.xlsx
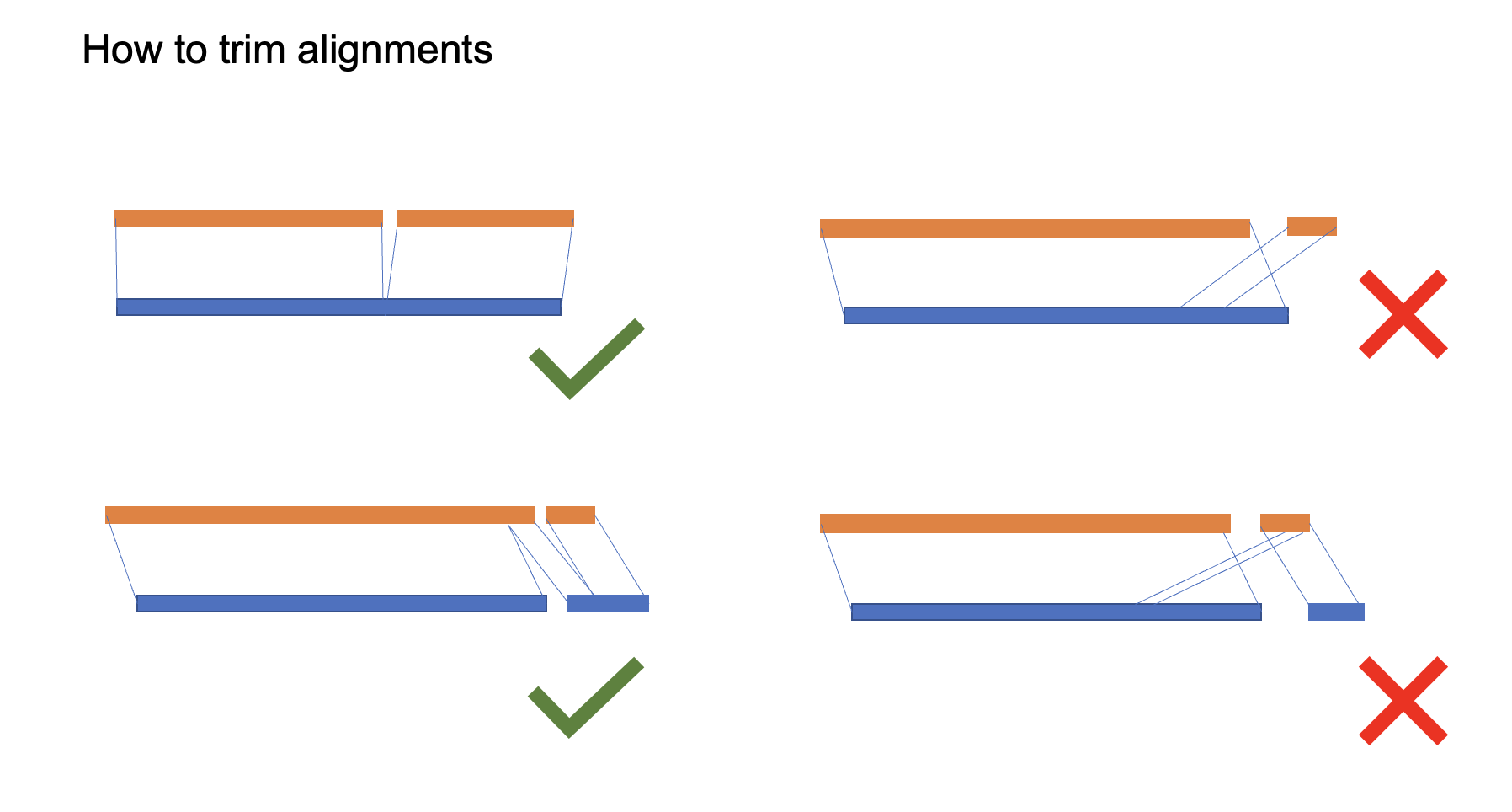
because of duplications and misassembly, we need to trim some improper alignments to avoid false-positive.
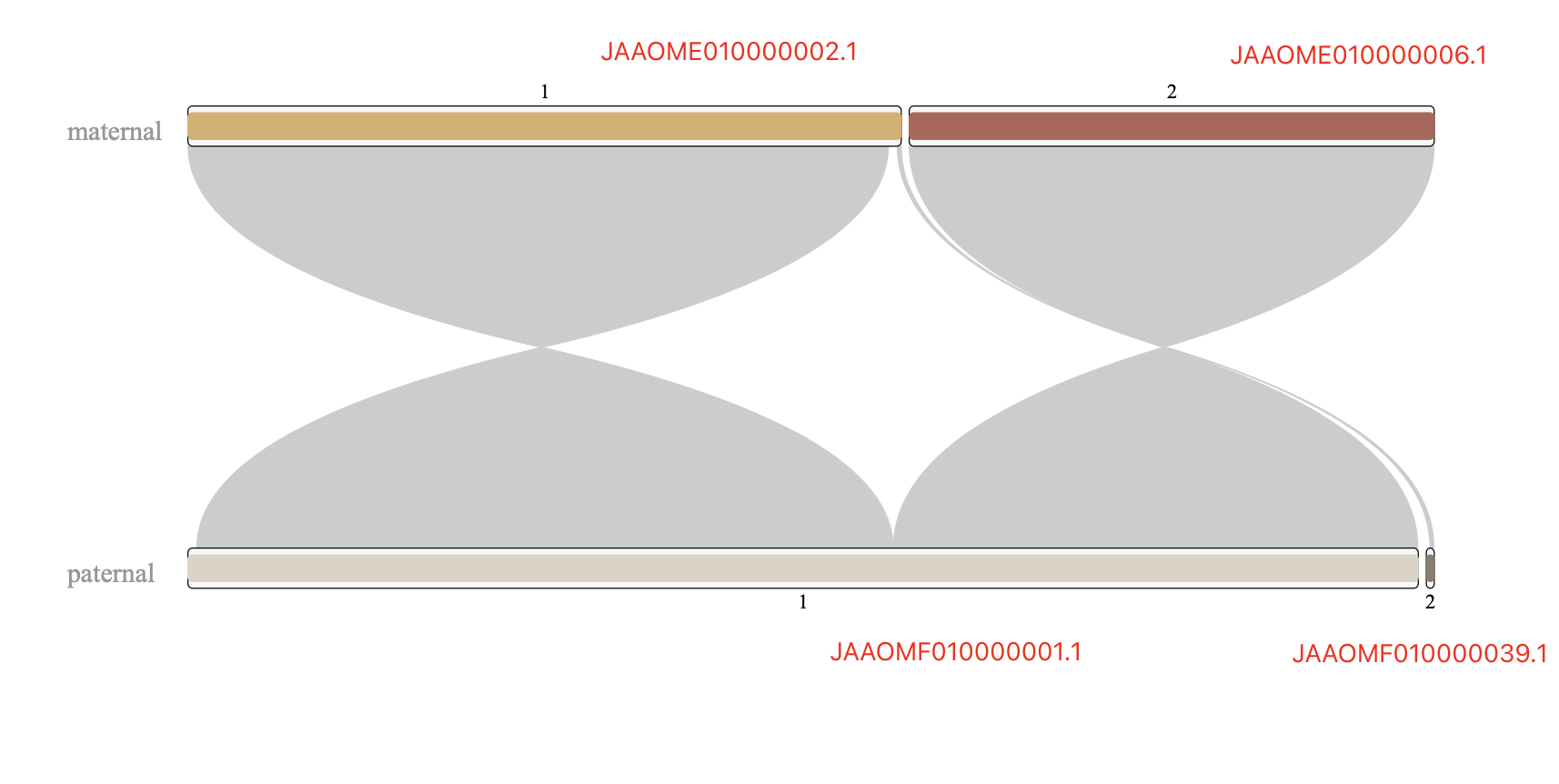
Figure 4. how to trim alignmentsAs expected, most chromosomes, only have one maternal scaffold and only one paternal scaffold, with the very close length, such as
chr4,chr5,chr7,chr8,chr9,chr10,chr11,chr12,chr13,chr14,chr15,chr18,chr20,chr22,chr23,chr24,chr25,chr26,chr27,chr30
But other cases are slightly complex, like chr1,chr2,chr3,chr6,chr16,chr17,chr19,chr21,chr28,chr29,chr31;
I found that chr6 is more complicated than other chrs, which could be a misassembly. However, I checked the breakpoints on the paternal #1 sequence, the pacbio reads aligned it continuously. so that is not likely to be a misassembly. thus, paternal #3 should be trimmed.
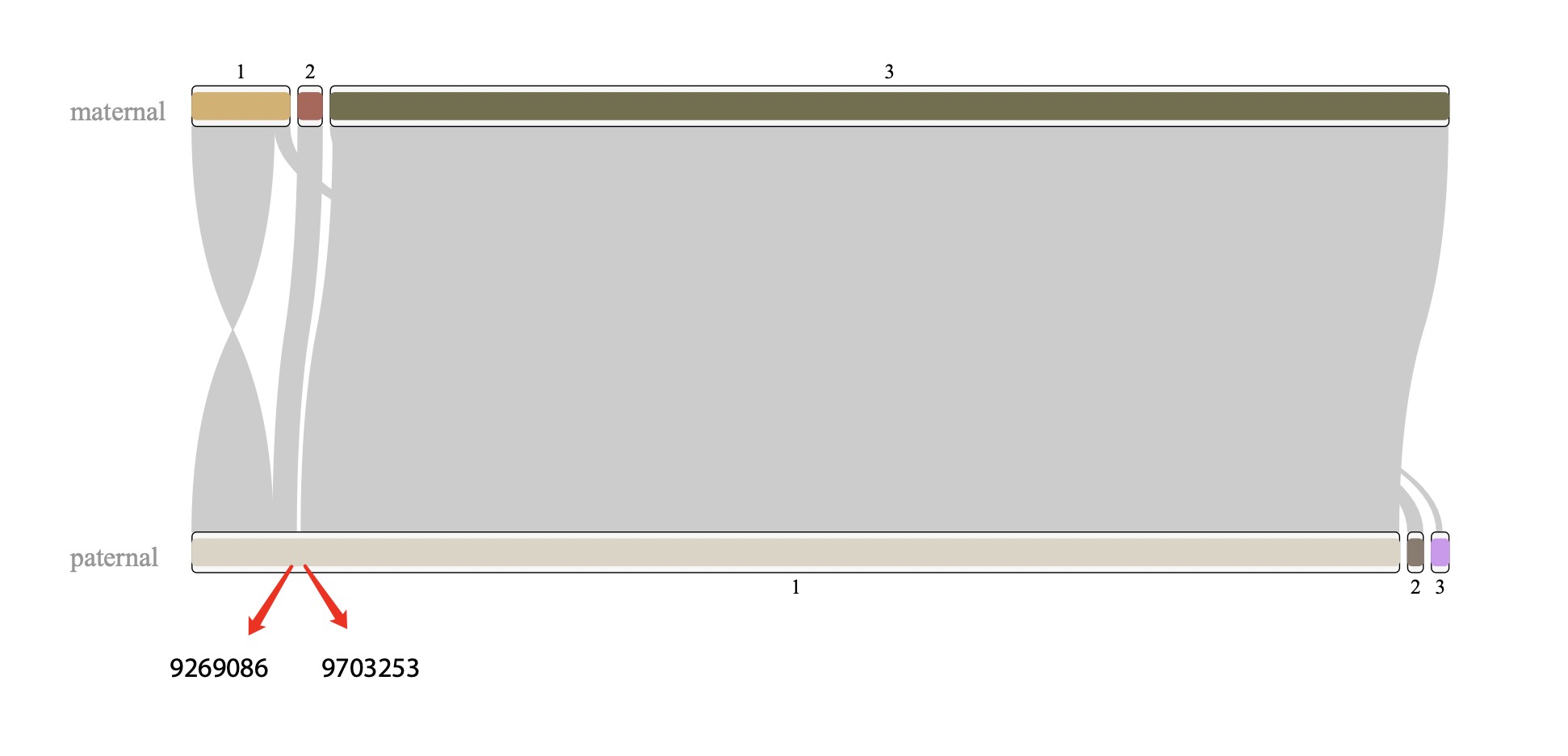
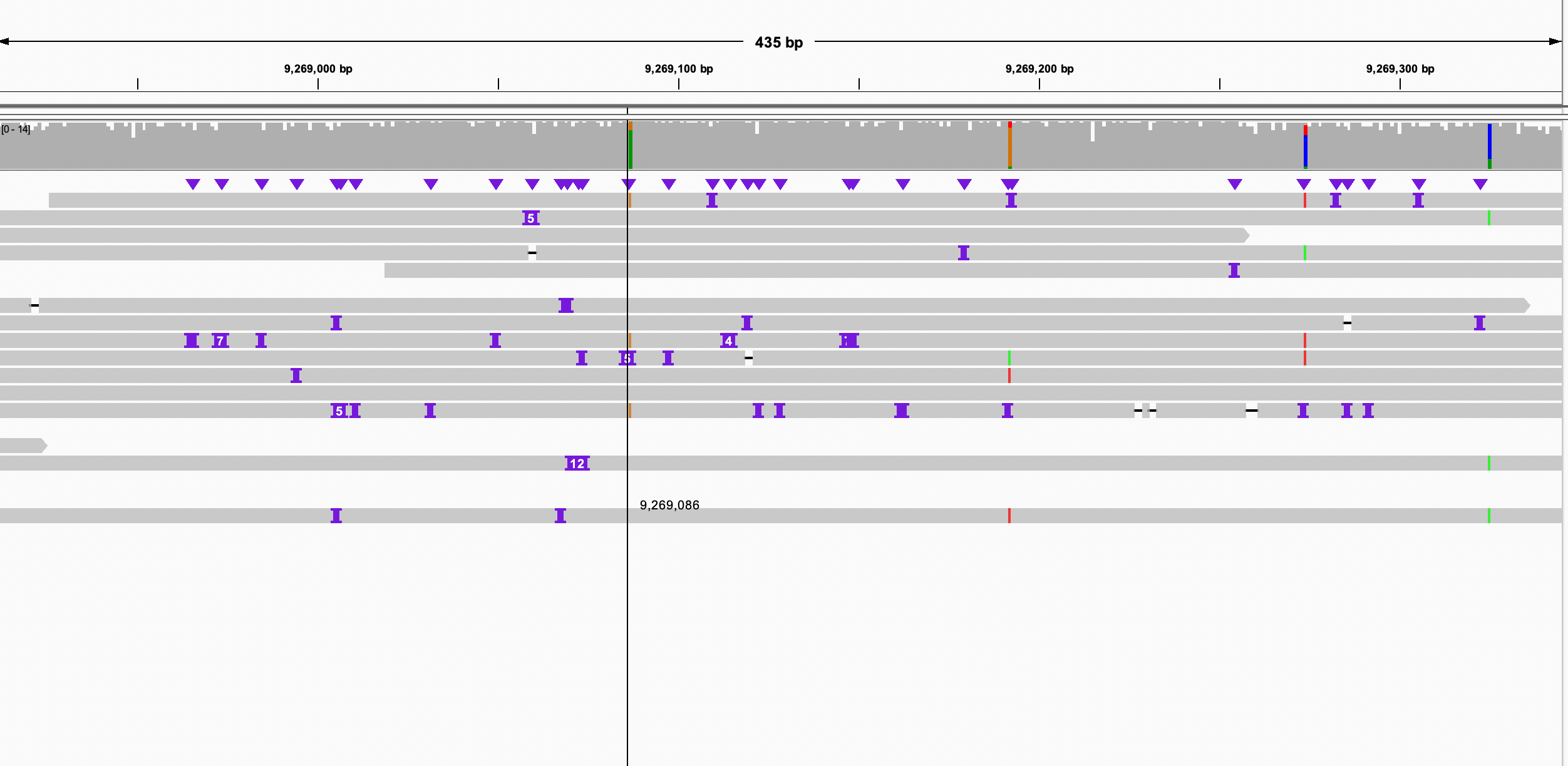
Figure 7. alignment of chr6 Figure 8. check left breakpoint on paternal #1 Figure 9. check right breakpoint on paternal #1Now we can concatenate these scaffolds into one super scaffold by 1000 Ns
Note: The *.mat.makeup.agp (give chr1 as example)file looks like below, it will generate one super scaffold, with two scaffolds (JAAOME010000002.1 & JAAOME010000006.1) linked by 1000 Ns.
superscaffold_chr1.mat 1 147137239 1 W JAAOME010000002.1 1 147137239 -
superscaffold_chr1.mat 147137240 147138239 2 N NA 1 1000 +
superscaffold_chr1.mat 147138240 255412214 3 W JAAOME010000006.1 1 108273975 -
# make up the maternal super scaffold
python3 Nile_Rat/bin/link2superscaf.py chr1.mat.fa chr1.mat.makeup.agp > chr1.mat.superscaf.fa
python3 Nile_Rat/bin/link2superscaf.py chr1.pat.fa chr1.pat.makeup.agp > chr1.pat.superscaf.fa
For these chromosomes, the script link2superscaf.py utility can be used in such cases to generate pseudo-chromosomes. It can generate pseudo-genomes using the homology of an incomplete genome with the reference (chromosome-level assembled) genome as well as using the homology between two incomplete assemblies.
(why I do this? see more)
Now we have detected the missing scaffolds and anchored them to chromosome, then we can identify the large structural variations by comparing the maternal and paternal assemblies.
- avaliable codes, see github page
- *.agp files for making up super scaffolds, see "agp/all.makeup.agp"
- synteny plots for each chromosomes in this folder => synteny_comparison_figures
Recently, I find a tookit - RagTag can do the similar thing like I did above. if you have interest in it, you can play with it.
We compared the maternal and paternal assemblies to detect the full spectrum of genetic diversity. however, we only have the gene annotation of Refseq of Nile rat assembly (pat+X), so we need to generate the annotation for haploid assemblies by liftovering gene feature from Refseq based on genome alignment.
gene features of Refseq:
grep -v '#' Nile_Rat/01.assembly/pat.X/GCF_011762505.1_mArvNil1.pat.X_genomic.gff |awk '$3=="mRNA" {print $1"\t"$4"\t"$5}' |uniq |awk '{print $0"\tg"NR}' > refseq.mRNA.bed
grep -v '#' Nile_Rat/01.assembly/pat.X/GCF_011762505.1_mArvNil1.pat.X_genomic.gff |awk '$3=="CDS" {print $1"\t"$4"\t"$5}' |uniq |awk '{print $0"\tcds"NR}' > refseq.cds.bedliftover
liftOver refseq.mRNA.bed Nile_Rat/01.assembly/liftover/pat_as_query/refseq_vs_pat.chain pat.makeup.mRNA.bed pat.makeup.unMapped.mRNA.bed
liftOver refseq.cds.bed Nile_Rat/01.assembly/liftover/pat_as_query/refseq_vs_pat.chain pat.makeup.cds.bed pat.makeup.unMapped.cds.bed
liftOver refseq.mRNA.bed Nile_Rat/01.assembly/liftover/mat_as_query/refseq_vs_mat.chain mat.makeup.mRNA.bed mat.makeup.unMapped.mRNA.bed
liftOver refseq.cds.bed Nile_Rat/01.assembly/liftover/mat_as_query/refseq_vs_mat.chain mat.makeup.cds.bed mat.makeup.unMapped.cds.bedmake chr1 as an example
software='/path/your_software_installed'
$software/MUMmer3.23/nucmer --maxmatch -c 500 -b 500 -l 100 chr1.pat.fa chr1.mat.fa -p chr1
$software/MUMmer3.23/delta-filter -m -i 90 -l 100 chr1.delta > chr1.delta.filt
$software/MUMmer3.23/show-coords -THrd chr1.delta.filt > chr1.delta.filt.coords
$software/MUMmer3.23/dnadiff -d chr1.delta.filt -p chr1
mv chr1.snps chr1.var
python3 $bin/split_mummerVar2snpAndindel.py chr1.var chr1
python3 $bin/indel_statistic.py chr1.indel
awk '\$7<50' chr1.indel.report.txt >chr1.mummer.sm.indel
SV (INV, TRANS, INVTR) using Syri
$software/syri-1.0/syri/bin/syri -c chr1.delta.filt.coords -r chr1.pat.superscaf.fa -q chr1.mat.superscaf.fa -d chr1.delta.filt
# output files: syri.out, syri.log, syri.vcf
# filter by gap ratio (remove records with N's ratio > 0.5)
python3 $bin/filterN_syri_variants.py syri.out chr1.pat.fa chr1.mat.fa > chr1.syri.sv.tablarge indel & cnv using Assemblytics
# Assemblytics delta output_prefix unique_length_required min_size max_size
$software/Assemblytics-1.2.1/scripts/Assemblytics chr1.1delta chr1 10000 50 500000 && echo done!
# filter by gap ratio (remove records with N's ratio > 0.5)
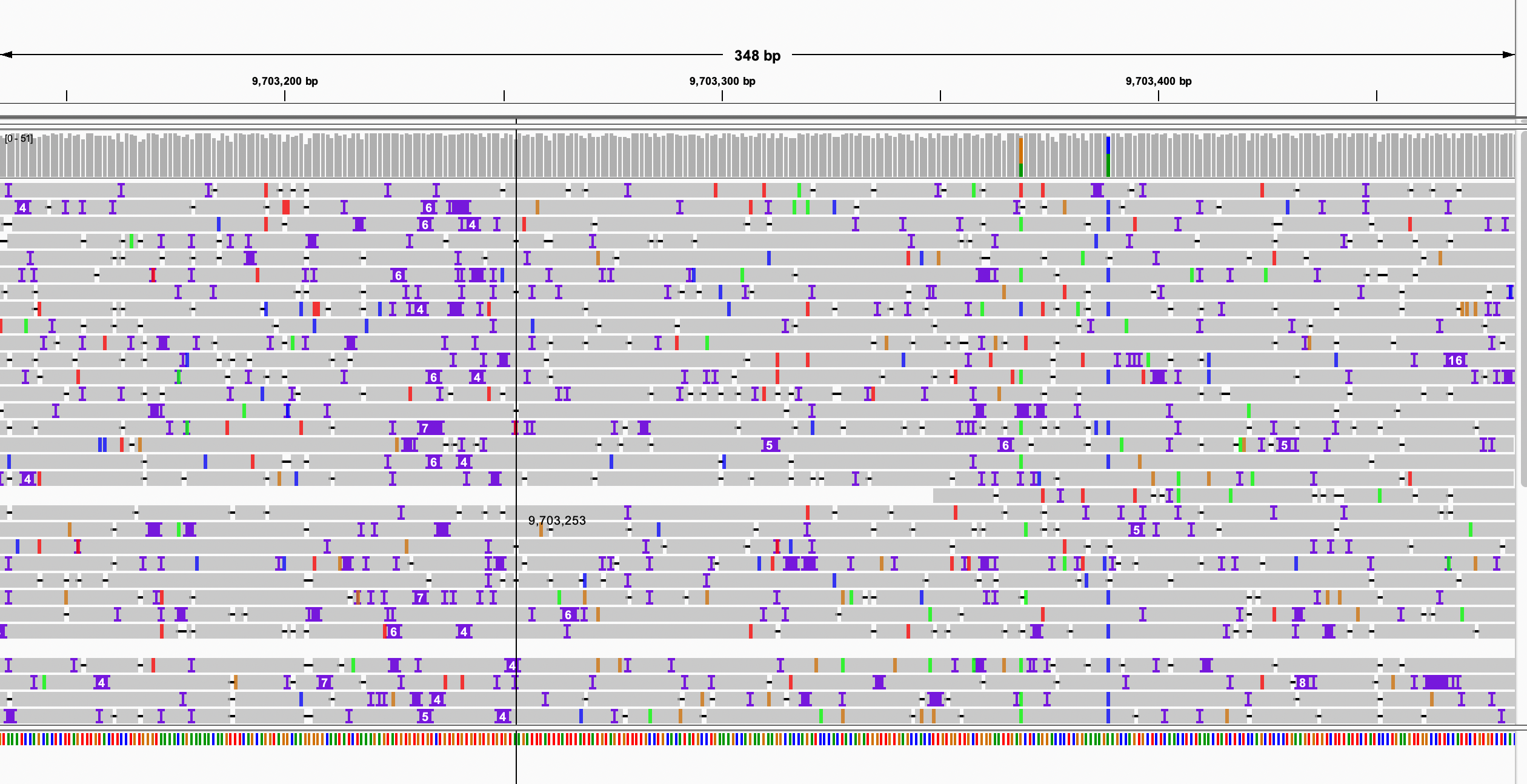
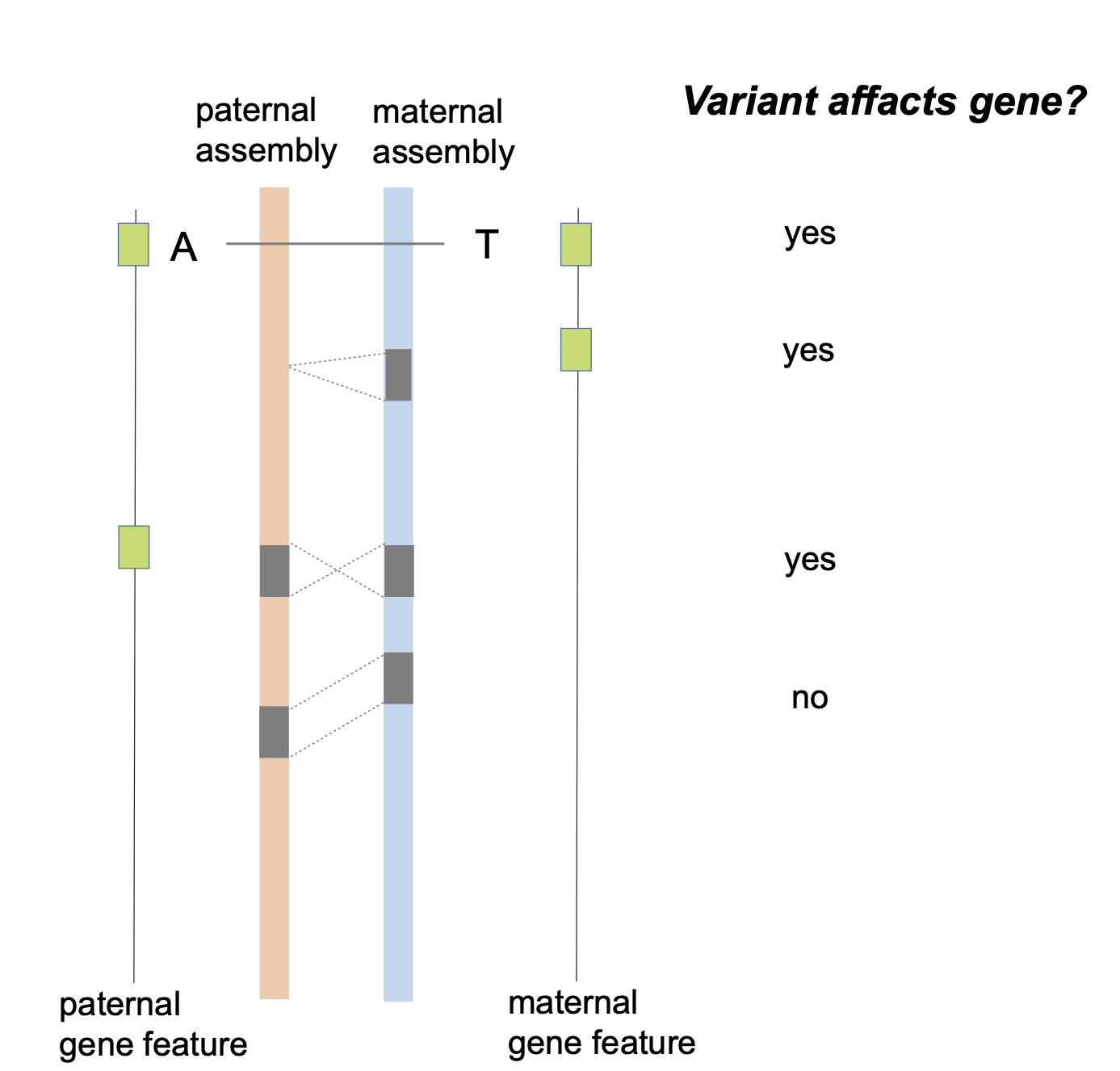
python3 $bin/filterN_assemblytics_variants.py chr1.Assemblytics_structural_variants.bed chr1.pat.fa chr1.mat.fa 0.5 >chr1.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bedI will think a variant may affact the gene if it has overlap with maternal gene features or has overlap with paternal gene features.
#cat ../list |while read a;do cat ../chromosomes/$a/$a.snp ;done > all.snp
echo "total snp count: " > summary.txt
wc -l all.snp >> summary.txt
# convert snp to bed format
awk '{print $11"\t"$1"\t"$1"\t"$12"\t"$4"\t"$4"\t"$2"\t"$3}' all.snp > all.snp.bed
cut -f 1-3 all.snp.bed > all.pat.snp.bed
cut -f 4-6 all.snp.bed > all.mat.snp.bed
# overlap with gene and cds
mat_mrna=Nile_rat/01.assembly/liftover/mat.makeup.mRNA.bed
pat_mrna=Nile_rat/01.assembly/liftover/pat.makeup.mRNA.bed
mat_cds=Nile_rat/01.assembly/liftover/mat.makeup.cds.bed
pat_cds=Nile_rat/01.assembly/liftover/pat.makeup.cds.bed
# overlap with mRNA
bedtools intersect -a all.pat.snp.bed -b $pat_mrna -wa -wb -loj | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse > pat.snp.mrna.overlap.bed
bedtools intersect -a all.mat.snp.bed -b $mat_mrna -wa -wb -loj | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse > mat.snp.mrna.overlap.bed
python3 $bin/combine_sv.annot.py all.snp.bed pat.snp.mrna.overlap.bed mat.snp.mrna.overlap.bed >all.snp.mRNA.annot
# either feature in paternal side is within a gene or feature in maternal side is within a gene, it will count
awk '$4!="." || $8!="."' all.snp.mRNA.annot > all.snp.annot.mRNA.overlap.txt
# overlap with cds
bedtools intersect -a all.pat.snp.bed -b $pat_cds -wa -wb -loj | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse > pat.snp.cds.overlap.bed
bedtools intersect -a all.mat.snp.bed -b $mat_cds -wa -wb -loj | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse > mat.snp.cds.overlap.bed
python3 $bin/combine_sv.annot.py all.snp.bed pat.snp.cds.overlap.bed mat.snp.cds.overlap.bed >all.snp.cds.annot
# either feature in paternal side is within a CDS or feature in maternal side is within a CDS, it will count
awk '$4!="." || $8!="."' all.snp.cds.annot > all.snp.annot.cds.overlap.txt
echo "SNV within mRNA:" >> summary.txt
wc -l all.snp.annot.mRNA.overlap.txt >> summary.txt
echo "SNV within CDS:" >> summary.txt
wc -l all.snp.annot.cds.overlap.txt >> summary.txtcat ../../list |while read a;do cat ../../chromosomes/$a/$a.mummer.sm.indel ;done > all.mummer.sm.indel
# convert file format
python3 $bin/small_indel_Pos2bed.py all.mummer.sm.indel
bedtools intersect -a ins.mat.pos.bed -b $mat_mrna -wa -wb | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse> ins.matPos.mRNA.bed
bedtools intersect -a del.pat.pos.bed -b $pat_mrna -wa -wb | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse> del.patPos.mRNA.bed
bedtools intersect -a ins.mat.pos.bed -b $mat_cds -wa -wb | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse> ins.matPos.cds.bed
bedtools intersect -a del.pat.pos.bed -b $pat_cds -wa -wb | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse> del.patPos.cds.bed
cat ../../list |while read a;do cat ../../chromosomes/$a/assemblytics/$a.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bed ;done > all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bed
grep 'Insertion' all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bed > all.Insertion.bed
grep 'Deletion' all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bed > all.Deletion.bed
grep -v -e 'Insertion' -e 'Deletion' all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bed > all.cnv.bed
echo "total:" >readme.txt
wc -l all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bed >> readme.txt
# overlap with mRNA
cut -f 1-3 all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bed > pat.sv.bed
cut -f 4-6 all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bed > mat.sv.bed
bedtools intersect -a pat.sv.bed -b $pat_mrna -wa -wb -loj | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse > pat.sv.mrna.overlap.bed
bedtools intersect -a mat.sv.bed -b $mat_mrna -wa -wb -loj | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse > mat.sv.mrna.overlap.bed
python3 $bin/combine_sv.annot.py all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bed pat.sv.mrna.overlap.bed mat.sv.mrna.overlap.bed >all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.mRNA.annot
awk '$4!="." || $8!="."' all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.mRNA.annot > all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.annot.mRNA.overlap.txt
echo "overlap with mRNA" >> readme.txt
cut -f 9 all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.annot.mRNA.overlap.txt|sort |uniq -c |sort -rn >> readme.txt
# overlap with cds
bedtools intersect -a pat.sv.bed -b $pat_cds -wa -wb -loj | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse > pat.sv.cds.overlap.bed
bedtools intersect -a mat.sv.bed -b $mat_cds -wa -wb -loj | bedtools groupby -i - -g 1-3 -c 7 -o collapse > mat.sv.cds.overlap.bed
python3 $bin/combine_sv.annot.py all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.bed pat.sv.cds.overlap.bed mat.sv.cds.overlap.bed >all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.cds.annot
awk '$4!="." || $8!="."' all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.cds.annot > all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.annot.cds.overlap.txt
echo "overlap with CDS" >> readme.txt
cut -f 9 all.Assemblytics_structural_variants.filterN.annot.cds.overlap.txt|sort |uniq -c |sort -rn >> readme.txtI downloaded the rat RefSeq genome (GCF_015227675.2_mRatBN7.2_genomic.fna.gz), and the mouse RefSeq genome (GCF_000001635.27_GRCm39_genomic.fna.gz) and others you need.
I did not retrieve the genes and protein sequences from NCBI GFF data, instead, I did the reannotation for the rat, mouse, and Nile rat using human protein as reference. Although the RefSeq version has a very detailed annotation, isoforms they reported will make it problematic to identify orthologous genes among four species. It could happen that an isoform is a positively selected gene (PSG), but not in another isoform of the same gene. So, the simplest way to avoid this problem is to reannotate genes using the same standard pipeline. This issue was also raised by one of reviewers of the marmoset paper.
To achieve this goal, I generated a dataset of 20,426 genes of human by selecting the longest transcript as the representative transcript. Then annotated rat, mouse, and Nile rat genomes using exonerate.
For an orthologous gene, protein alignment will conduct at first, then protein sequence alignment will guide nucleotide sequence alignment to make sure alignment is based on codon.
First, each included gene had to map to the human sequence alignments including at least 70% of its coding sequence (CDS). Second, frameshift indels in CDSs were prohibited. Third, CDSs with premature stop codons were excluded. In addition, final alignments shorter than 150 bp were discarded.
The positive selection sites within a specific lineage were detected by the branch-site model in PAML. Genes with an FDR-adjusted p-value less than 0.05 were treated as candidates for positive selection. To minimize the effects of assembly and alignment, we filtered candidate PSGs if 1) the positive selective site was gap in more than two species; 2) the PS sites have more than two nonsynonymous substitution forms.
make rat genome as an example
genome="GCF_015227675.2_mRatBN7.2_genomic.fna"
shortname="mRatBN"
[ -d $shortname ] || mkdir $shrotname
cd $shortname
ln -s ../$genome ./$shortname.fa
$software/exonerate-2.4.0/bin/exonerate --model protein2genome --bestn 1 --showalignment TRUE --showtargetgff TRUE --showvulgar TRUE ../homo_sapiens.best.pep $shortname.fa >$shortname.exonerate
python3 bin/exonerate_parse.py ../homo_sapiens.best.pep $shortname.exonerate ./
perl bin/getGene.pl $shortname.exonerate.gff $shortname.fa | awk '{print \$1}' > $shortname.exonerate.cds
fastaKit -ap $shortname -o tmp $shortname.exonerate.cds
mv tmp $shortname.exonerate.cds
perl bin/cds2aa.pl $shortname.exonerate.cds | awk '{print \$1}' > $shortname.exonerate.pep
date"annotate other species using above pipeline, and then merge all cds together (all.cds)
# add a tag to human sequence's header
bin/fastaKit -ap human -o human.cds homo_sapiens.best.cds
# merge all cds together
find ../01.annot/ -name "*.exonerate.cds" |xargs cat > tmp
cat human.cds tmp > all.cds
# split sequences into subdir by ortholog
python3 ../../bin/getMSAfromCDS.py all.cds MSA
# remove these orthologs which has gene missing at least one species
grep -v '#' ortholog.matrix.txt|awk '$2!="na"'|cut -f 1,2 > all.right.ortholog.list
# protein alignment [1]
wk=`pwd`
cat all.right.ortholog.list|while read a b
do
cd $b
perl $bin/cds2aa.pl $a.cds > $a.pep
$software/mafft/7.471/bin/mafft --anysymbol --maxiterate 1000 --localpair --quiet --thread 2 $a.pep > $a.pep.aln
perl $bin/pepMfa_to_cdsMfa.pl $a.pep.aln $a.cds > $a.cds.aln
perl $bin/pal2nal.pl $a.pep.aln $a.cds -output paml -nogap > pal2nal.seq
cp $wk/codeml.ctl .
$software/paml-4.8/bin/codeml codeml.ctl
python3 $bin/parse_codeml_output_raw.py codeml.txt > $a.pairwise.val0
python3 $bin/parse_codeml_output.py codeml.txt > $a.pairwise.val
cd $wk
done
# positively seleceted genes
# filter genes by alignment
## 1, each gene has more than 70% align rate with human
## 2, framshif, stop codon exclude
## 4, alignment (aa) < 50 bp, exclude
cat all.right.ortholog.list|while read a b
do
# give a report
python3 $bin/MSAexamine.py -minL 50 -rate 0.70 -rid human -a $b/$a.pep.aln -f tab
done > all.filter.report.tab
# keep filtered orthology
grep 'PASS' all.filter.report.tab|cut -f 1 >all.filtered.ortholog.list
python3 $bin/getLine_by_ColumnInTab.py all.right.ortholog.list 1 all.filtered.ortholog.list 1 >all.filtered.ortholog.path.list
# PSGs
wk=`pwd`
cat all.filtered.ortholog.path.list|while read a b
do
python3 $bin/paml_single.py $wk/tree/tree.nwk $b/$a.cds.aln $b
cd $b
sh paml.sh
cd $wk
done
# p-value
cat all.filtered.ortholog.path.list|while read a b
do
perl $bin/paml.lrt.pl $b/H1.mlc $b/H0.mlc 1
done > all.ortholog.pvalue
# q-value, find the significant positively selected genes
perl $bin/paml.fdr.pl all.ortholog.pvalue BH 0.05 > all.ortholog.qvalue
awk '$3 == "significant" && $1==0 {print $2}' all.ortholog.qvalue > all.significant.gene
# visulization of phylogeny and alignment around each PSG site
[ -d "significant" ] || mkdir "significant"
grep -f all.significant.gene all.filtered.ortholog.path.list > all.significant.gene.list
cd significant
# collect all significant genes together
cat ../all.significant.gene.list|while read a b
do
ln -s ../$b ./
done
cd ..
find significant/ -type l >draw.og.list
# generate images that contain phylogenetic tree and local sequence alignment
cat draw.og.list|while read a
do
b=`echo $a|awk -F "/" '{print $2}'`
python3 $bin/draw_phytree_with_align_mlc.py $a/H1.mlc $a/$b.cds.aln paternal $b
done > draw.log
# some genes may no have sites, if will give error report in draw.logWe have obtained the gene alignment and calculated the dnds values when conducting PSG analysis. now we can collect them to find diverse genes among four species.
# cat them together..., got 3054gene.pairwise.val0
awk '$3>1' 3054gene.pairwise.val0 |grep -e 'maternal' -e 'paternal' |grep -v 'nan' >Nile_rat.compared.val
# filter val
# do filtering, see reference
awk '$3<10 && $3>1 && $5 <2 && $5>0.01' Nile_rat.compared.val > Nile_rat.compared.filtered.val