Nodebook is a little python library which extracts characters from plain text books and uses graph theory to perform analyses on character types, importances and interactions.
Dependencies are SpaCy, matplotlib and networkx 1.11. Install using the commands below.
git clone https://github.com/Buroni/nodebook.git
pip install spacy
pip install networkx --version==1.11
pip install matplotlib
To run the library outside the root directory, you will need to update PYTHONPATH to point to the directory which contains the
nodebook folder:
PYTHONPATH=/path/to/parent/:$PYTHONPATH
There are several examples in the 'examples' directory which show some different usages.
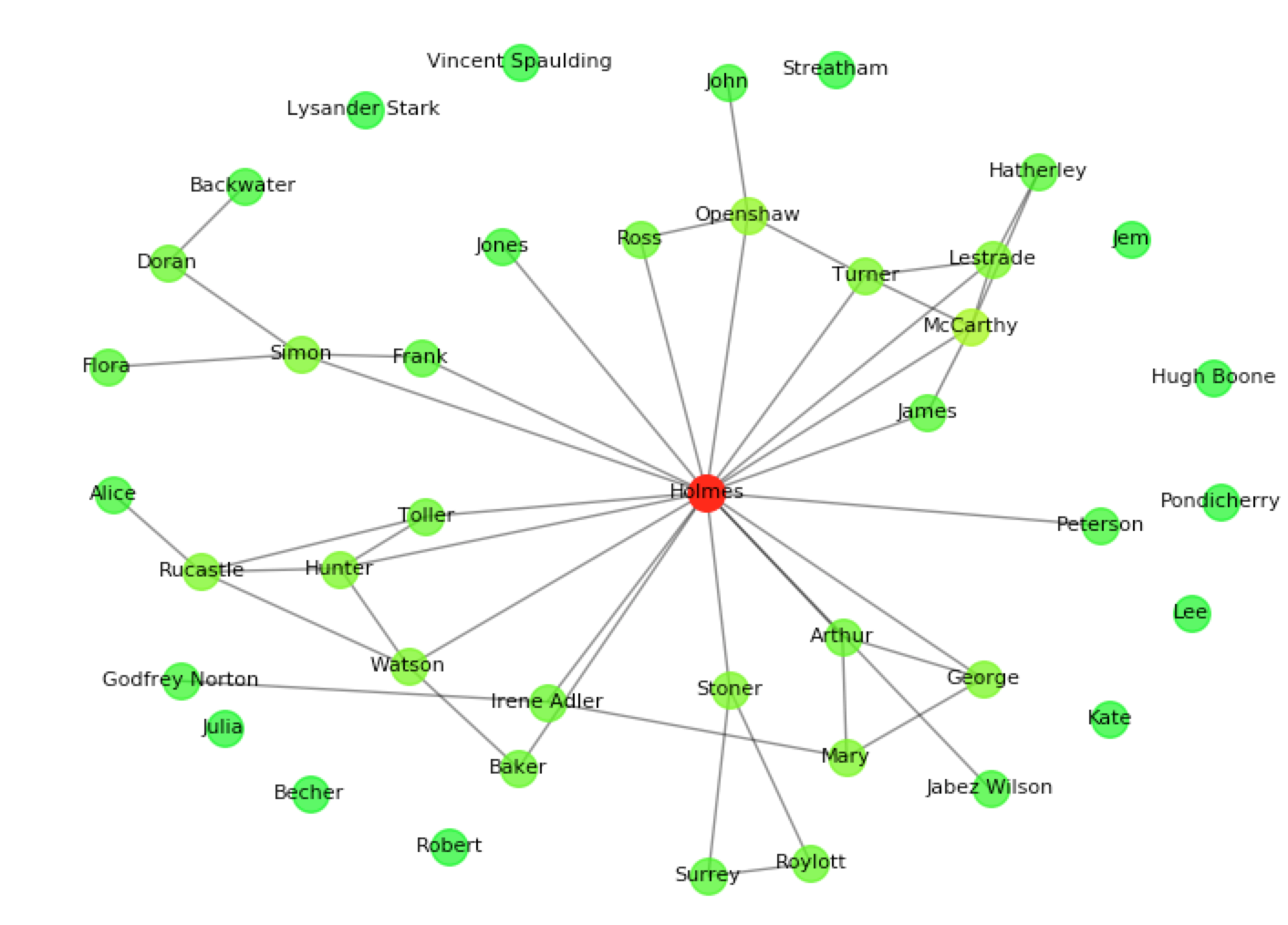
This quick example uses nodebook to find the main character in Arthur Conan Doyle's The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes, displays a graph of characters and dumps the graph into a json file.
from nodebook import book
sherlock = book("http://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/1661/pg1661.txt")
print("Most central characters: " + str(sherlock.important_characters(8)))
pov = "first person" if sherlock.is_first_person else "third person"
print("Point of view: " + pov)
sherlock.dump("sherlock.json")
sherlock.graph(with_labels=True, node_size=200)This example will produce the following:
Most central characters: [u'Holmes', u'McCarthy', u'Openshaw', u'Simon', u'Rucastle', u'Mary', u'Hunter', u'Watson']
Point of view: third personAfter the first time the plain text file is processed,
it is recommended to dump the graph into a json file and load
this rather than the original book in subsequent executions of
the program. The post-analysis json file is much quicker to read
than a full book.
lotr = book("fellowship.json")Initialise a new book object.
file_path can either be a local path or URL to a raw txt file of the book, or a local json dump file.
char_min_count is the number of times a character
should appear in the book before they are stored in the graph.
nodebook measures interactions between characters:
interaction_measure is the definition of an "interaction"
which should be used. It can either be "same_line", meaning
that two characters are seen as interacting if they appear on the same line,
or "verb", meaning that they interact if they appear as a subject
and object of the same transitive verb. For example, the sentence
"Jack talks to Jake" contains an interaction in both measure
methods, but specifically using the "verb" measure where Jack
interacts with Jake through the verb talks.
blacklist is a list of names which should be ignored when
looking for characters.
Dump the current book object into a json file with name specified
by the variable cache_file.
Draw a matplotlib graph of characters connected by edges representing interactions, and colour-coded by their degree.
Return a list of important characters in descending order by some metric. The metric can be:
"degree"-- measure a character's importance by the number of other characters they interacted with."clustering"-- measure by the local clustering co-efficient of each character in the graph."centrality"-- measure by the betweenness centrality of each character in the graph.
A list of strings representing the names of characters found during analysis of the book.
A string representing who nodebook thinks the first person is,
if the book is first person. Otherwise defaults to None. This
is worked out by calculating the character which has the highest
neighbourhood overlap with [FP] (the "first person" character tag).
A boolean representing whether nodebook believes the book is written in first person. This is worked out by counting the occurrences of the pronoun "I" outside quotation marks.
A book object contains a native NetworkX graph G, on which you can perform native Networkx methods. For example
myBook = book('my_book.json')
centrality = networkx.betweenness_centrality(myBook.G)