PX-Developer is scale-out storage for containers. Run with container-granular controls for capacity, performance, and availability. Deploying the PX-Developer container on a server with Docker Engine turns that server into a scale-out storage node. Storage runs converged with compute and gives bare-metal drive performance.
PX-Developer aims to improve the storage experience for developer and DevOps teams using containers. This release is an open beta and we want to develop this solution with the community, including for enterprises. (More on our blog.) Contact us to share your feedback, work with us, and to request features. Stay tuned for updates on PX-Developer (PX-Dev for short) and our PX-Enterprise release.
As you develop and deploy your apps in containers, use PX-Dev for elastic storage capacity, managed performance, and high availability.
- See our quick start guides on installing PX-Dev:
- Launching PX-Dev with Docker Compose
- Detailed instructions for PX-Dev on Ubuntu or Red Hat
- Run stateful containers with Docker volumes:
- Scaling a Cassandra database with PX-Dev
- Running the Docker registry with high availability
- Use our pxctl CLI to directly:
- View the cluster global capacity and health
- Create, inspect, and delete storage volumes
- Attach policies for IOPs prioritization, maximum volume size, and enable storage replication
- Refer to the Technical FAQ and Troubleshooting guide if you run into an issue. Please also feel free to Contact us as well.
Portworx storage is deployed as a container and runs on a cluster of servers. Application containers provision storage directly through the Docker volume plugins API or the Docker command-line. Administrators and DevOps can alternatively pre-provision storage through the Portworx command-line tool (pxctl) and then set storage policies using the Portworx administrative interface.
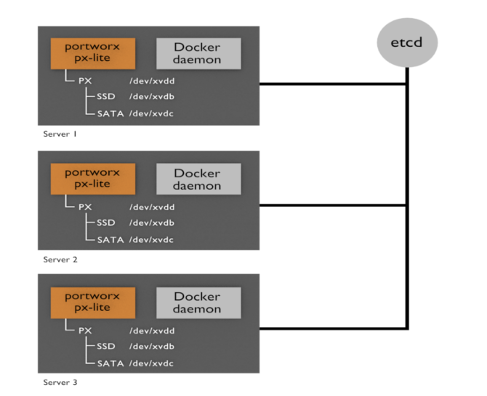
Portworx storage runs in a cluster of server nodes.
- Each server has the PX-Dev container and the Docker daemon.
- Servers join a cluster and share configuration through the key/value store, such as etcd.
- The PX-Dev container pools the capacity of the storage media residing on the server. You easily select storage media through the config.json file.
See Deployment Requirements for compatibility requirements.
Storage volumes are thinly provisioned, using capacity only as an application consumes it. Volumes are replicated across the nodes within the cluster, per a volume’s configuration, to ensure high availability.
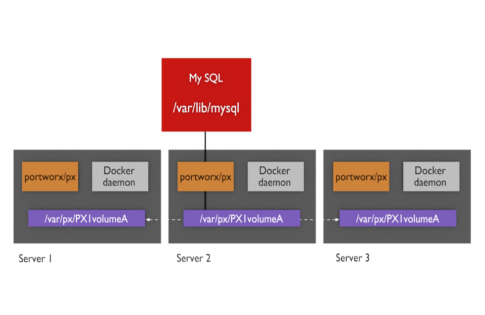
Using MySQL as an example, a PX-Dev storage cluster has the following characteristics:
- MySQL is unchanged and continues to write its data to /var/lib/mysql.
- This data gets stored in the container’s volume, managed by PX-Dev.
- PX-Dev synchronously and automatically replicates writes to the volume across the cluster.
Each volume specifies its request of resources (such as its max capacity and IOPS) and its individual requirements (such as ext4 as the file system and block size).
Using IOPS as an example, a team can chose to set the MySQL container to have a higher IOPS than an offline batch processing container. Thus, a container scheduler can move containers, without losing storage and while protecting the user experience.
As you use PX-Dev, please share your feedback and ask questions. Find the team on Google Groups.
If your requirements extend beyond the scope of PX-Dev, then please contact Portworx for information on PX-Enterprise.
| Field | Description | Example | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| ClusterID | A unique identifier for your cluster. Be sure to use the same identifier on all the nodes you want to cluster. | 5ac2ed6f-7e4e-4e1d-8e8c-3a6df1fb61a5 | required |
| mgtiface | The network interface for management data. | eth0 | optional |
| dataiface | The network interface for data transfers. | eth1 | optional |
| kvdb | The list of URIs to your etcd server cluster. | https://myetcd.example.com:4001 | required |
| devices | The list of devices that PX-Dev will use. Any disks listed will be reformatted for PX use. | /dev/xvda | required |
It is highly recommended that you run PX-Dev on a system with at least 4GB RAM.
| Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|
| Kernel Version | 3.10 or higher |
| Docker Version | 1.10 or higher |
| KV Database | Etcd 2.0 or higher. See https://github.com/coreos/etcd or try a hosted version at https://compose.io/etcd/ |
| CPU | 4 cores recommended |
| Memory | 4GB Minimum |
| Cloud | If running in the cloud, AWS Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (HVM) CentOS7 with Updates HVM |
| systemd | If using systemd, Docker should NOT be set to MountFlags=slave. PX-Dev exports mount points and requires shared mount flags. Tracking Docker issue 19625. |
Other limitations:
| Resource | Limit |
|---|---|
| Cluster Size | 3 |
| Per Volume Limit | 1TB |
| Max Volumes | 256 |
| Max local devices | 3 |