| languages | page_type | description | products | urlFragment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
sample |
This sample shows how to use the Microsoft Authentication Library for .NET to get an access token and call the Microsoft Graph from a UWP app. |
|
uwp-signing-in-graph-aad |
Universal Windows Platform application signing in users with Microsoft and calling the Microsoft Graph
| Getting Started | Library | Docs | Support |
|---|
This simple sample demonstrates how to use the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) for .NET to get an access token and call the Microsoft Graph (using OAuth 2.0 against the Azure AD v2.0 endpoint) from a Universal Windows Platform (UWP) application.
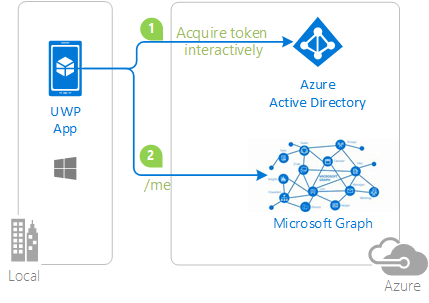
- The .NET client UWP application uses the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) to obtain a JWT access token from Azure Active Directory (Azure AD):
- The access token is used as a bearer token to authenticate the user when calling the Microsoft Graph.
You can get full explanation about this sample, and build it from scratch by going to Call the Microsoft Graph API from a Universal Windows Platform (UWP) application. You would have to change a few things (see below, build from scratch)
To run this sample, you'll need:
- Visual Studio 2017
- An Internet connection
- An Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant. For more information on how to get an Azure AD tenant, see How to get an Azure AD tenant
- A user account in your Azure AD tenant or a Microsoft account (formerly Windows Live account). Therefore, if you signed in to the Azure portal with a Microsoft account and have never created a user account in your directory before, you need to do that now.
From your shell or command line:
git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/active-directory-dotnet-native-uwp-v2.gitor download and exact the repository .zip file.
Given that the name of the sample is pretty long, and so are the name of the referenced NuGet packages, you might want to clone it in a folder close to the root of your hard drive, to avoid file size limitations on Windows.
There is one project in this sample. To register it, you can:
- either follow the steps Step 2: Register the sample with your Azure Active Directory tenant and Step 3: Configure the sample to use your Azure AD tenant
- or use PowerShell scripts that:
- automatically creates the Azure AD applications and related objects (passwords, permissions, dependencies) for you
- modify the Visual Studio projects' configuration files.
If you want to use this automation:
-
On Windows run PowerShell and navigate to the root of the cloned directory
-
In PowerShell run:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process -Force
-
Run the script to create your Azure AD application and configure the code of the sample application accordinly.
.\AppCreationScripts\Configure.ps1
Other ways of running the scripts are described in App Creation Scripts
-
Open the Visual Studio solution and click start
If ou don't want to use this automation, follow the steps below
As a first step you'll need to:
- Sign in to the Azure portal using either a work or school account or a personal Microsoft account.
- If your account is present in more than one Azure AD tenant, select
Directory + Subscriptionat the top right corner in the menu on top of the page, and switch your portal session to the desired Azure AD tenant.
- Navigate to the Microsoft identity platform for developers App registrations page.
- Select New registration.
- In the Name section, enter a meaningful application name that will be displayed to users of the app, for example
UWP-App-calling-MSGraph. - In the Supported account types section, select Accounts in any organizational directory and personal Microsoft accounts (e.g. Skype, Xbox, Outlook.com).
- Select Register to create the application.
- In the Name section, enter a meaningful application name that will be displayed to users of the app, for example
- On the app Overview page, find the Application (client) ID value and record it for later. You'll need it to configure the Visual Studio configuration file for this project.
- In the list of pages for the app, select Authentication.
-
- In the Redirect URIs list, select for TYPE Public client (mobile & desktop). Then paste this value urn:ietf:wg:oauth:2.0:oob in the REDIRECT URI column.
-
- Select Save.
- In the list of pages for the app, select API permissions
- Click the Add a permission button and then,
- Ensure that the Microsoft APIs tab is selected
- In the Commonly used Microsoft APIs section, click on Microsoft Graph
- In the Delegated permissions section, ensure that the right permissions are checked: User.Read. Use the search box if necessary.
- Select the Add permissions button
In the steps below, "ClientID" is the same as "Application ID" or "AppId".
Open the solution in Visual Studio to configure the projects
-
In the
App.xaml.csfile from the cloned repo, set your application/client ID copied from the App Registration Portal where you will have registered an application and added the native platform.private const string ClientId = "[Application Id pasted from the application registration portal]" -
(Optionally): Enable Windows Integrated Authentication when using a federated Azure AD tenant
Out of the box, this sample is not configured to work with Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) when used with a federated Azure Active Directory domain. To work with IWA the application manifest must enable additional capabilities. These capabilities are not configured by default for this sample because applications requesting the Enterprise Authentication or Shared User Certificates capabilities require a higher level of verification to be accepted into the Windows Store, and not all developers may wish to perform the higher level of verification. To enable Windows-Integrated Authentication, in Package.appxmanifest, in the Capabilities tab, enable:
- Enterprise Authentication - Private Networks (Client & Server) - Shared User CertificatesAlso,
MainPage.xaml.cs, when building the application, ensure that the following line of code:.WithUseCorporateNetwork(true)
- Run the application from Visual Studio (Debug | Start without Debugging), directly on the local machine, or after deploying to a device or an emulator.
If sign-in with your work or school account and your organization requires conditional access, you are asked to provide a certificate:
-
If you have not enabled UWP-specific considerations above, you will get this error:
No valid client certificate found in the request. No valid certificates found in the user's certificate store. Please try again choosing a different authentication method. -
On Windows 10 desktop UWP application, if you enabled the settings described above, the list of certificates is presented, however if you choose to use your PIN, the PIN window is never presented. This is a known limitation with Web authentication broker in UWP applications running on Windows 10 (this works fine on Windows Phone 10). As a work-around, you will need to click on the sign-in with other options link and then choose Sign-in with a username and password instead, provide your password and go through the phone authentication.
-
we plan to remove this limitation in the future by integrating the Web Account Manager (WAM)
Follow the instructions given in Windows desktop .NET guided walkthrough, but:
- Instead of creating a WPF project, you will need to create a UWP project
- Instead of using a Label in the
MainWindow.xaml, you will need to use a TextBock (as Labels are not supported in the UWP platform). Instead of the Label Content property, use the TextBlock's Text property - With UWP applications, you don't need to add a cache as it's already managed by MSAL.Net
We use Stack Overflow with the community to provide support. We highly recommend you ask your questions on Stack Overflow first and browse existing issues to see if someone has asked your question before. Make sure that your questions or comments are tagged with [msal.dotnet].
If you find and bug in the sample please raise the issue on GitHub Issues.
If you find a bug in msal.Net, please raise the issue on MSAL.NET GitHub Issues.
To provide a recommendation, visit our User Voice page.
If you'd like to contribute to this sample, see CONTRIBUTING.MD.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
For more information see MSAL.NET's conceptual documentation: