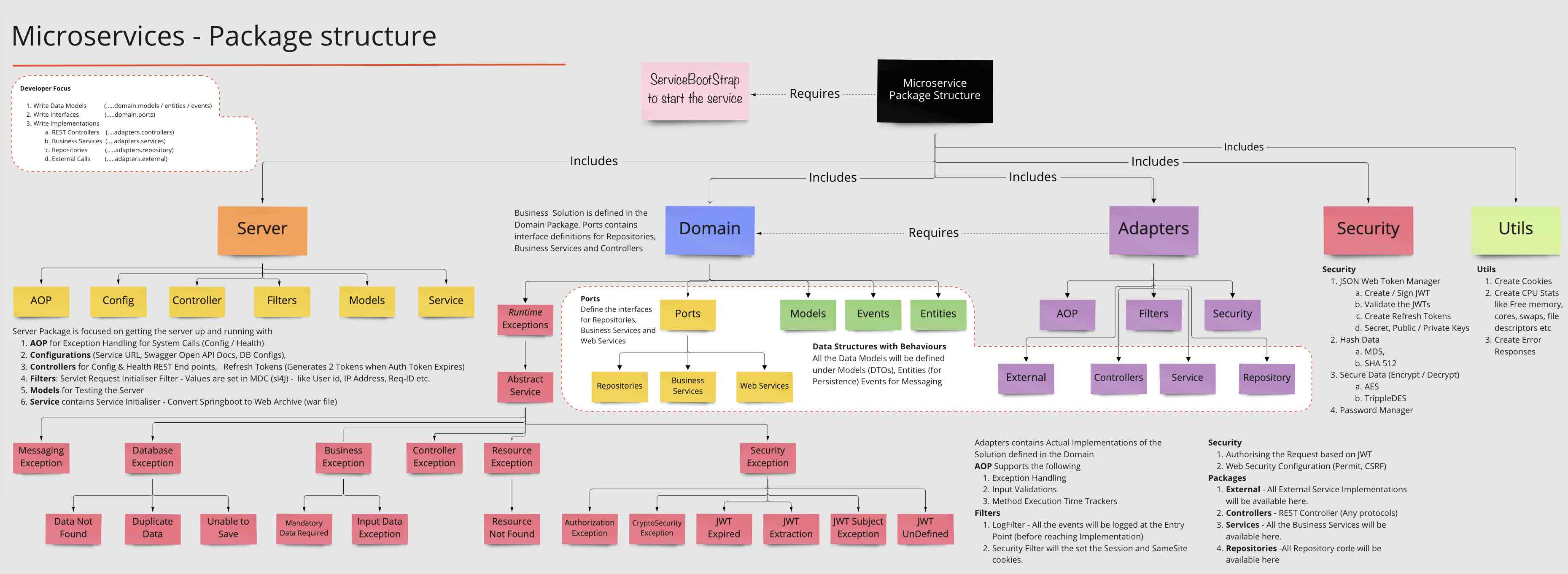
- Springboot App with Swagger Docs (...adapters.controllers)
- Exception Handling with Exception Framework using AOP ( ..adapters.aop)
- Log Management using Logback (...adapters.filters)
- Standardized REST Responses (...domain.models.StandardResponse)
- Security using JWT Tokens (...adapters.security)
- Encrypting Sensitive Data using Encryption Algorithms (...security)
- JPA configurations for H2 and PostgreSQL (...server.config)
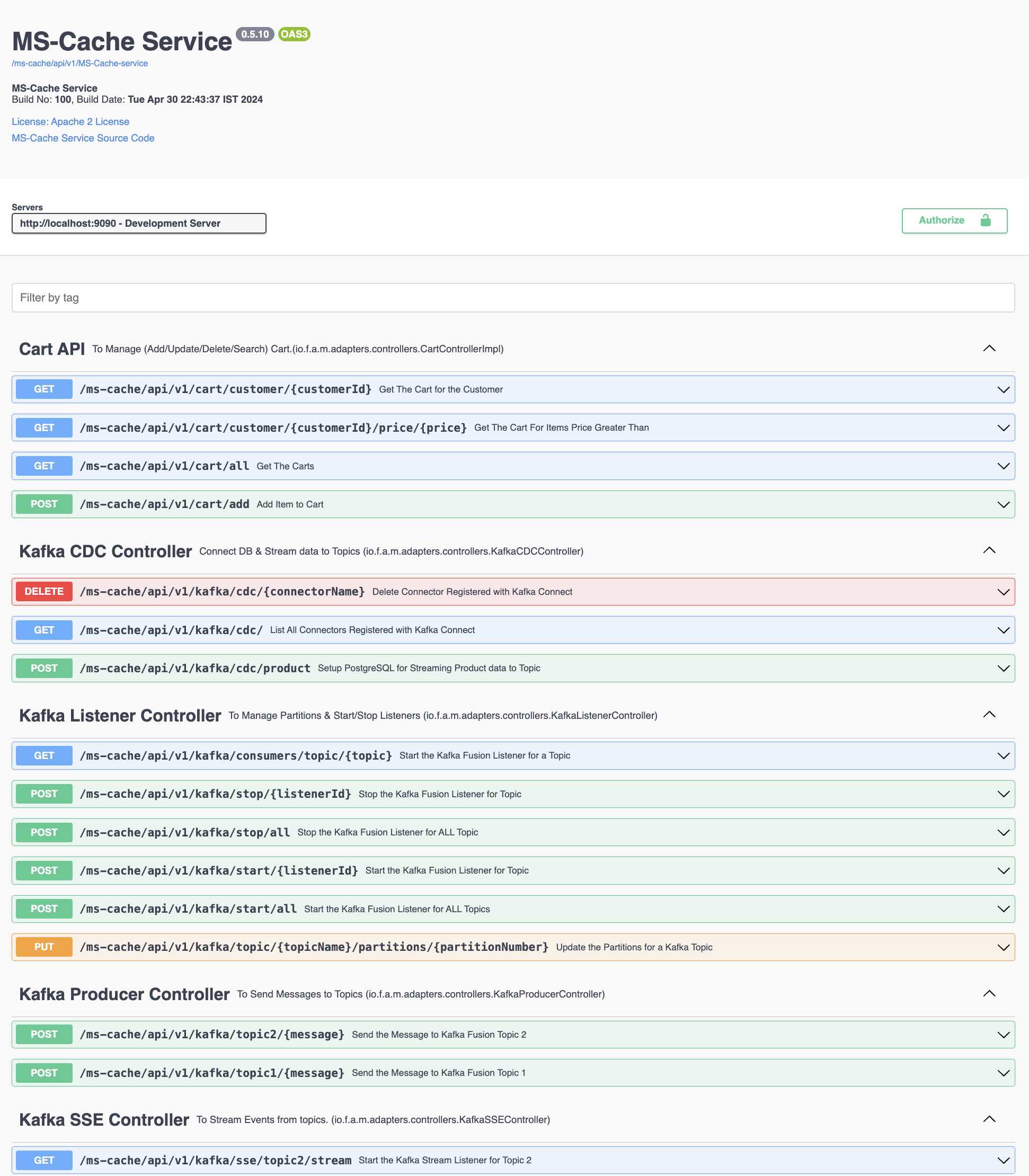
- Kafka Examples
- Springboot 2.7.2
- Java 8, Java 17 (To run)
- Kafka 3.x (3.7.0)
- Java EE (javax.servlet., javax.persistence., javax.validation.*)
- Maven 3.8.6
- Git 2.31
- SpringBoot App template with
- Kafka Pub/Sub Examples
- Kafka Connect Examples
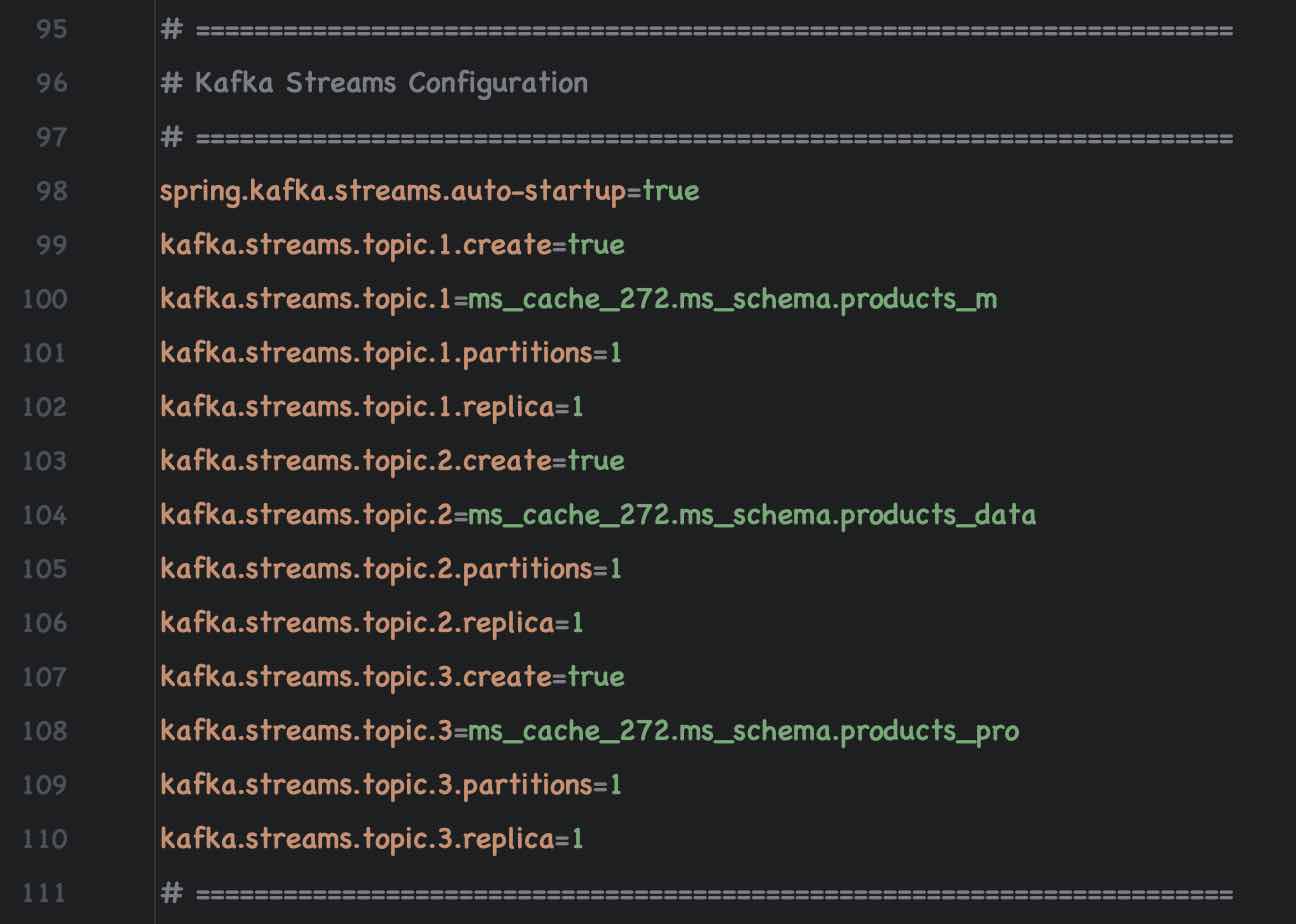
- Kafka Streams Examples
- Kafka Global Table Example
- Spring State Machine Examples (Reservation API)
- Spring Pagination Example (Country API)
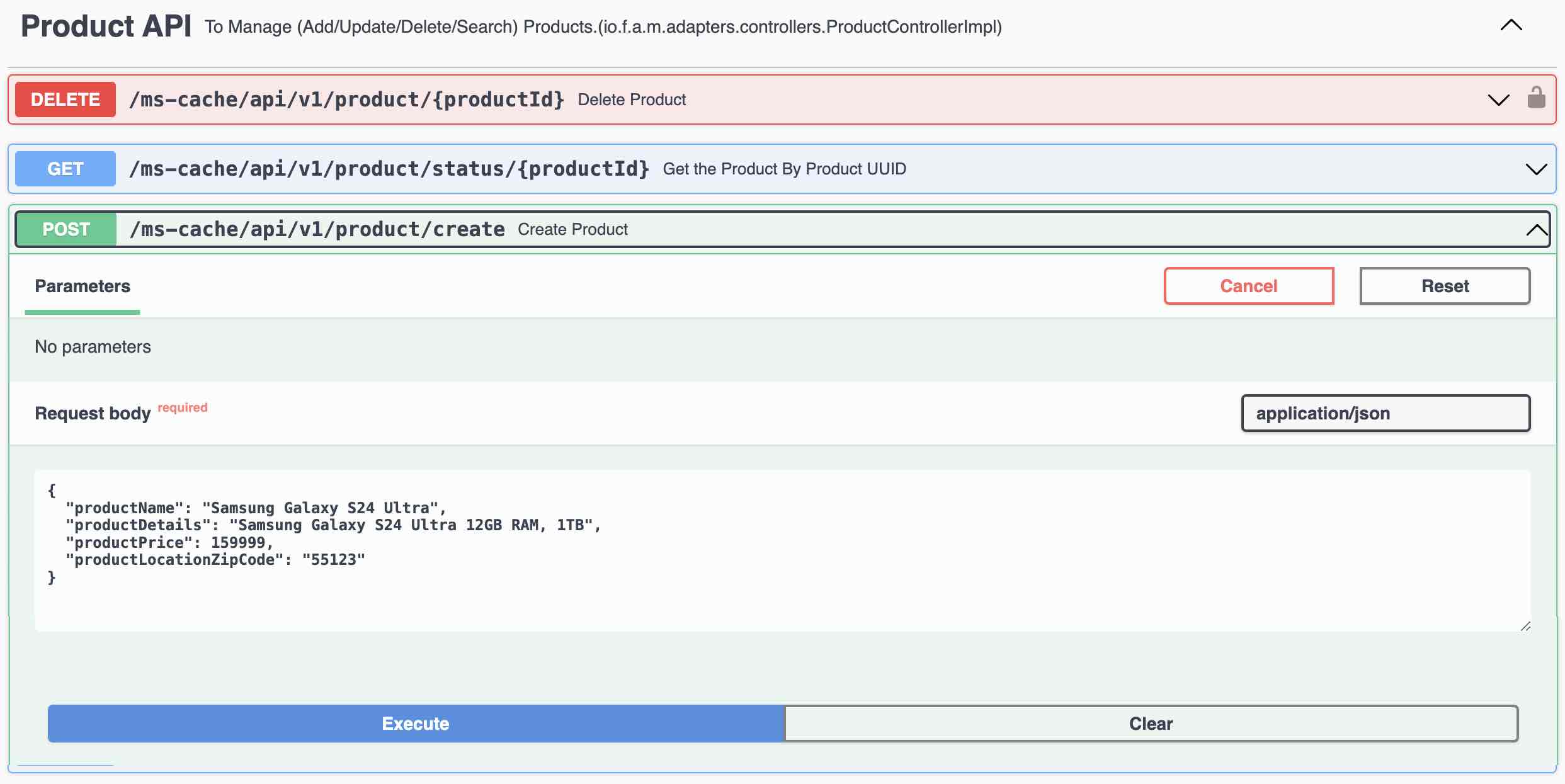
- CRUD Examples (Product API)
- Specification Design Pattern Example (Product API)
- SOLID Design Pattern Examples
- JWT Tokens Example (Secured Payments API )
- Spring Profiles works with H2 DB on Dev and PostgreSQL in Staging / Prod mode
- H2 In Memory Database & PostgreSQL Database Support
- Open API 3 Ex,
- Spring Actuator,
- Spring Sleuth and
- POM File with (SpringBoot) Fat and Thin (Maven) jar file creation and
- Dockerfile for containerisation.
- git clone https://github.com/arafkarsh/ms-springboot-272-java-8.git
- cd ms-springboot-272-java-8
Run the "compile" from ms-springboot-272-java-8
- compile OR ./compile (Runs in Linux and Mac OS)
- mvn clean; mvn -e package; (All Platforms)
- Use the IDE Compile options
- Clean up the target folder
- Generate the build no. and build date (takes application.properties backup)
- build final output SpringBoot fat jar and maven thin jar
- copy the jar files (and dependencies) to src/docker folder
- copy the application.properties file to current folder and src/docker folder
In Step 1.2.2 application.properties file will be auto generated by the "compile" script. This is a critical step. Without generated application.properties file the service will NOT be running. There is pre-built application properties file.
- run OR ./run (Runs in Linux or Mac OS,
- run prod (to use PostgreSQL DB)
- mvn spring-boot:run (All Platforms)
- test OR ./test (Runs in Linux or Mac OS)
- Execute the curl commands directly (from the test script)
- Setting up Postman with REST Endpoints for Testing
- CRUD Examples
- JWT Token Examples
Check the CRUD_Examples.md
Install the latest version of Kafka. This version is tested with Kafka 3.7.0
- change the envkafka.sh in the kafka-scripts folder to set the Kafka Path
$ cd kafka-scripts
$ vi envkafka.sh OR nano envkafka.sh
Change the Kafka Path
#!/bin/sh
KV=-3.7.0
KAFKAPATH=~/Softwares/kafka$KV
echo $KAFKAPATH
- start Zookeeper Server
$ kafka-scripts/start-zc.sh
- start Kafka Broker
$ kafka-scripts/start-ka.sh
- start Kafka Connect (java 17+)
$ kafka-scripts/start-kc.sh
- run (to test with H2 In-Memory Database)
- run prod (to test with PostgreSQL Database) Check the application-prod.properties for PostgreSQL Config
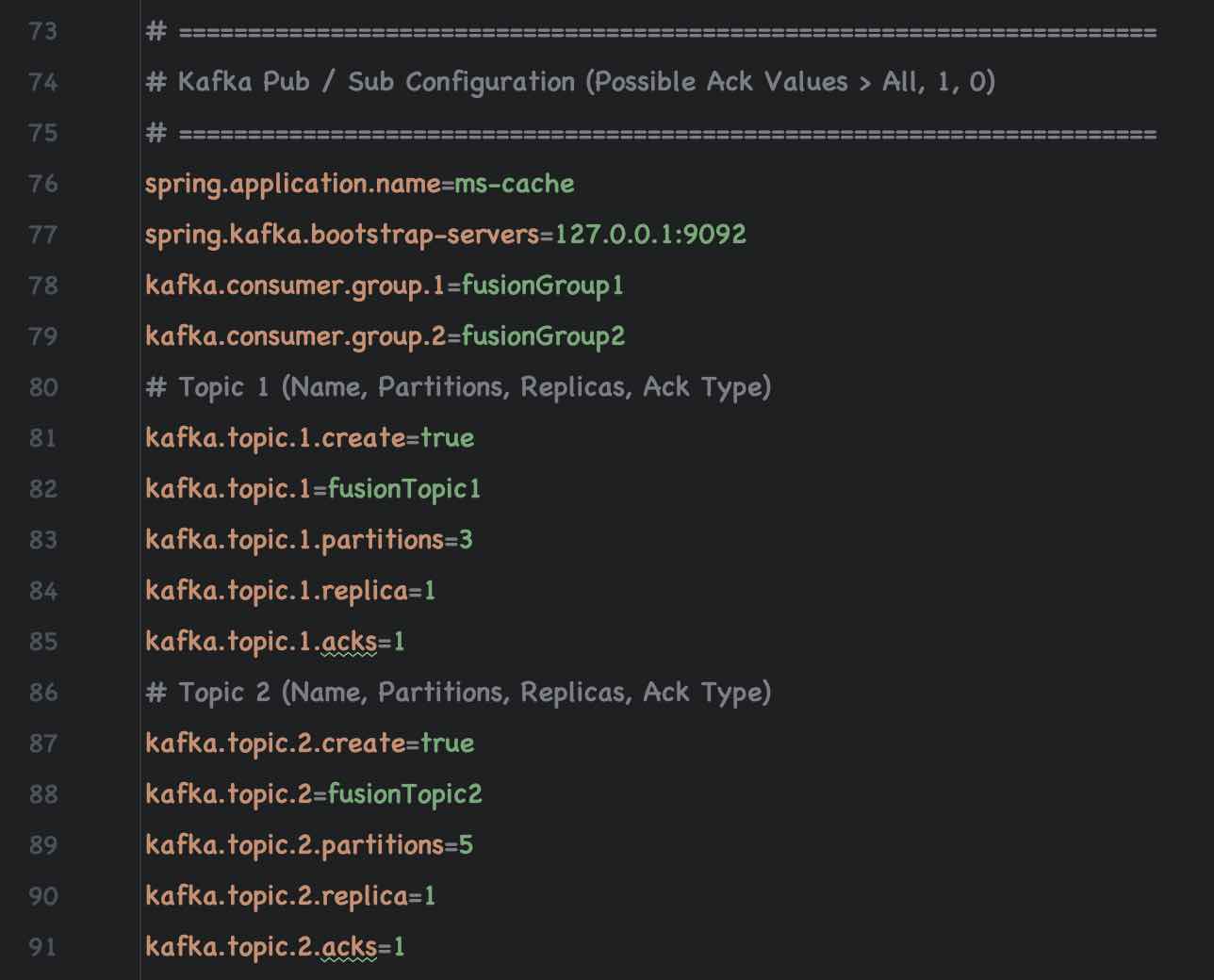
| Topic Name | Partitions | Replica | Acks | Consumer Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fusionTopic1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | fusionGroup1 |
| fusionTopic2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | fusionGroup2 |
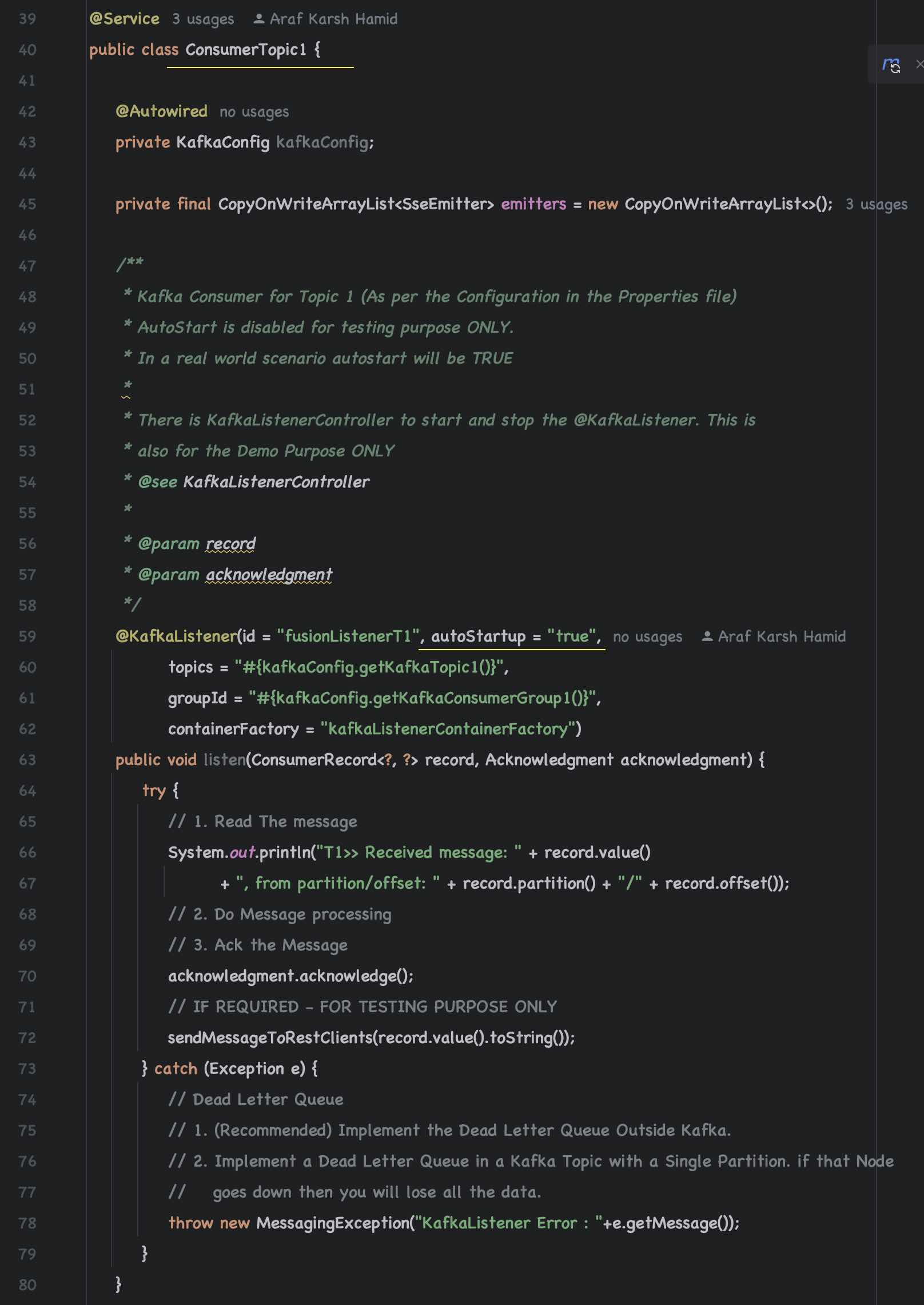
Ensure that Kafka Consumers are enabled (autostart = true) For Consumer Topic 1 and Topic 2
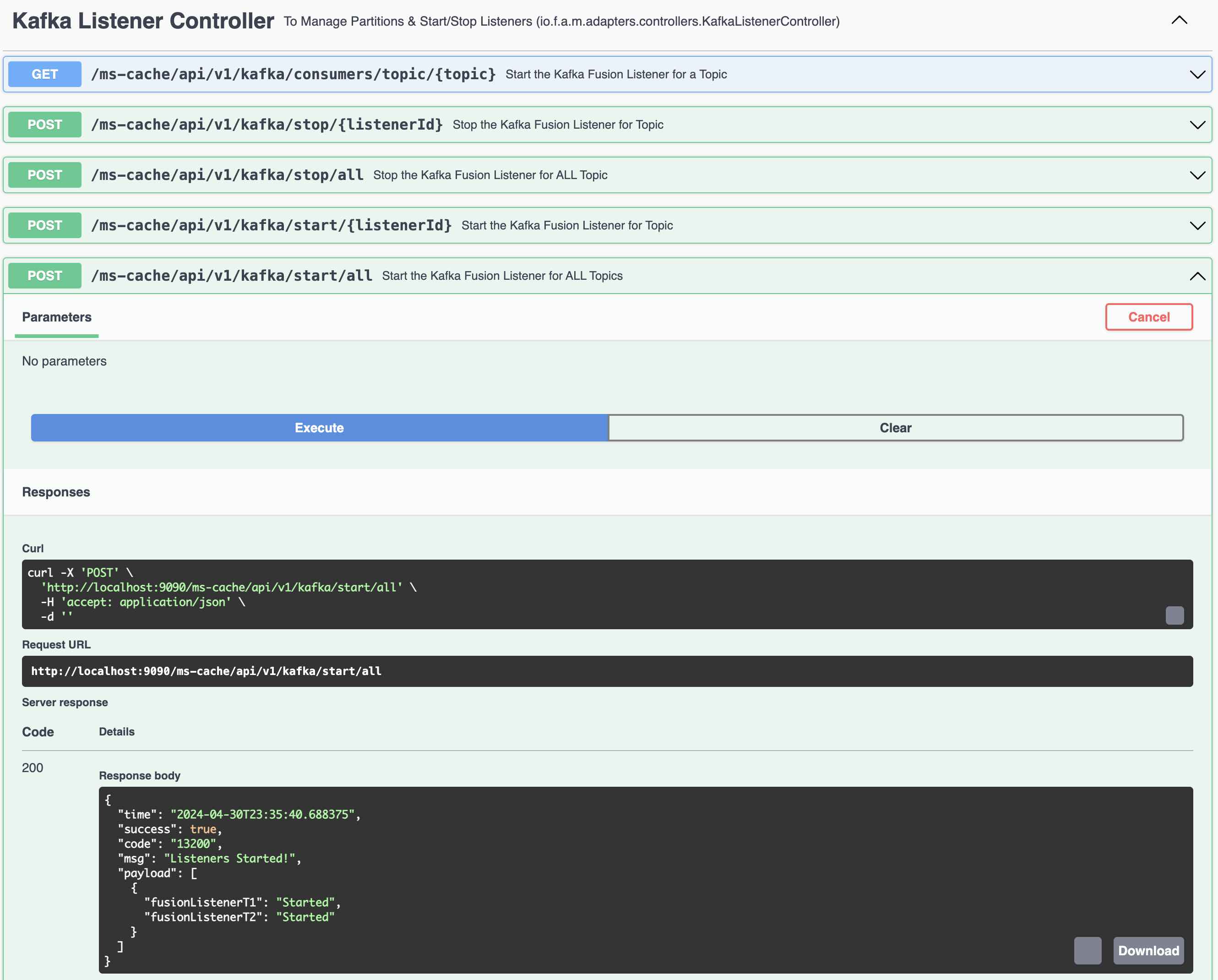
You can programatically Start and Stop the listeners (Consumers) using REST Endpoints (This is for demo purpose ONLY)
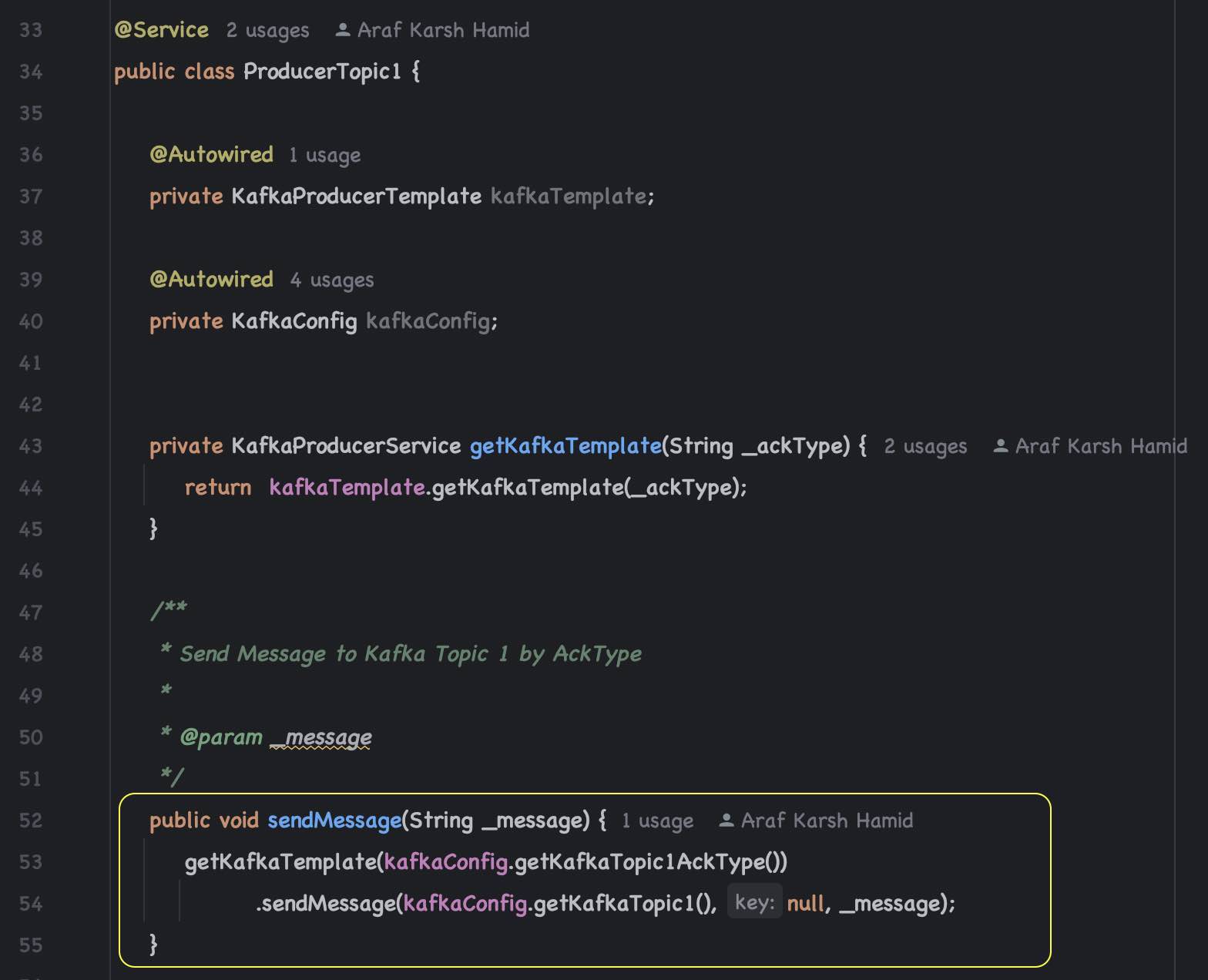
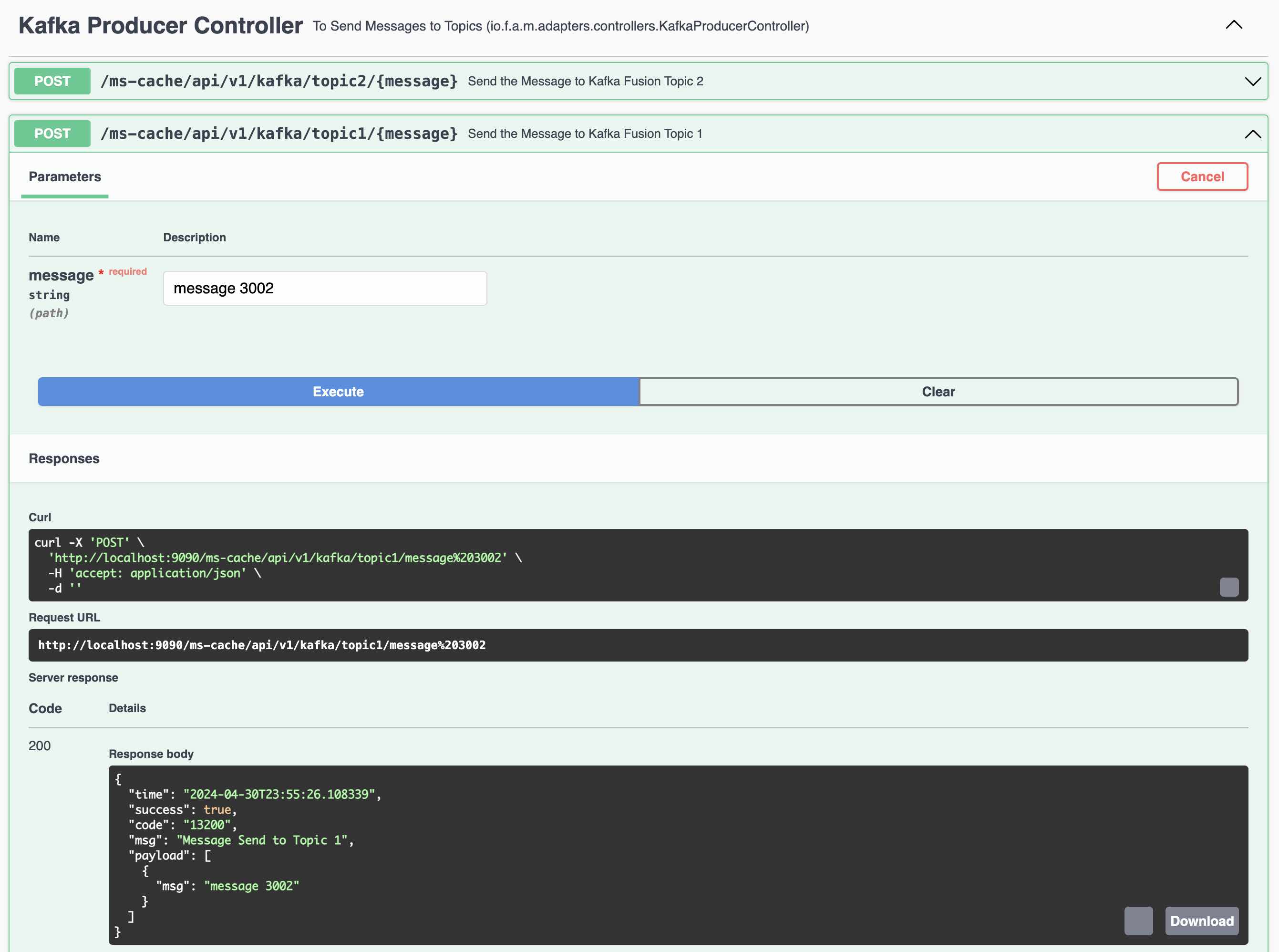
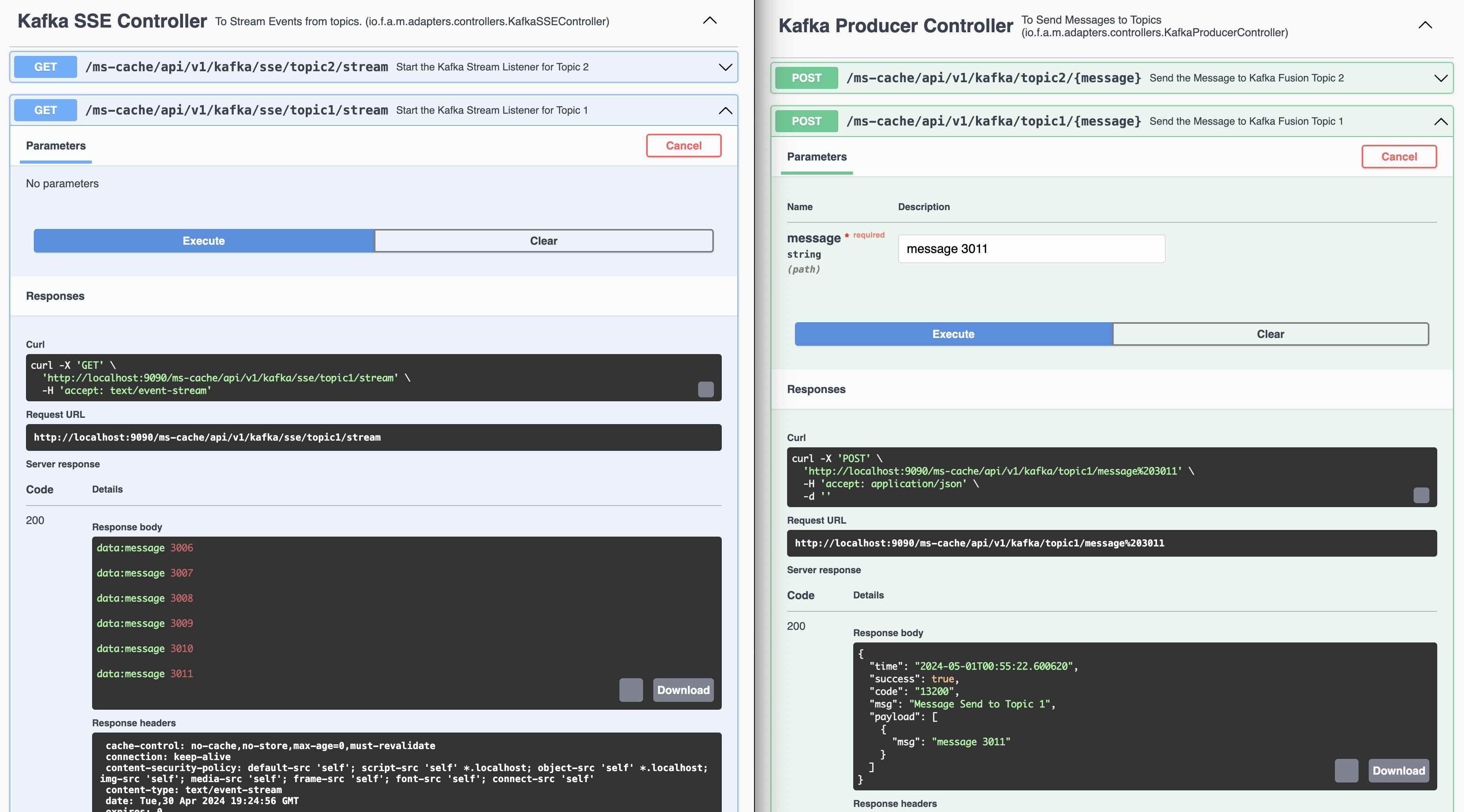
Kafka Producer 1 to send messages to Topic 1 (fusionTopic1)
REST Endpoint to send messages to Topic 1
Demo of Server Side Events using Kafka Listener (Topic 1). Ideally Web Sockets should be used instead of REST Endpoints. Spring provides the SseEmitter class which is useful for sending SSE events to clients. It can be returned from a controller method to handle the stream of server-sent events.
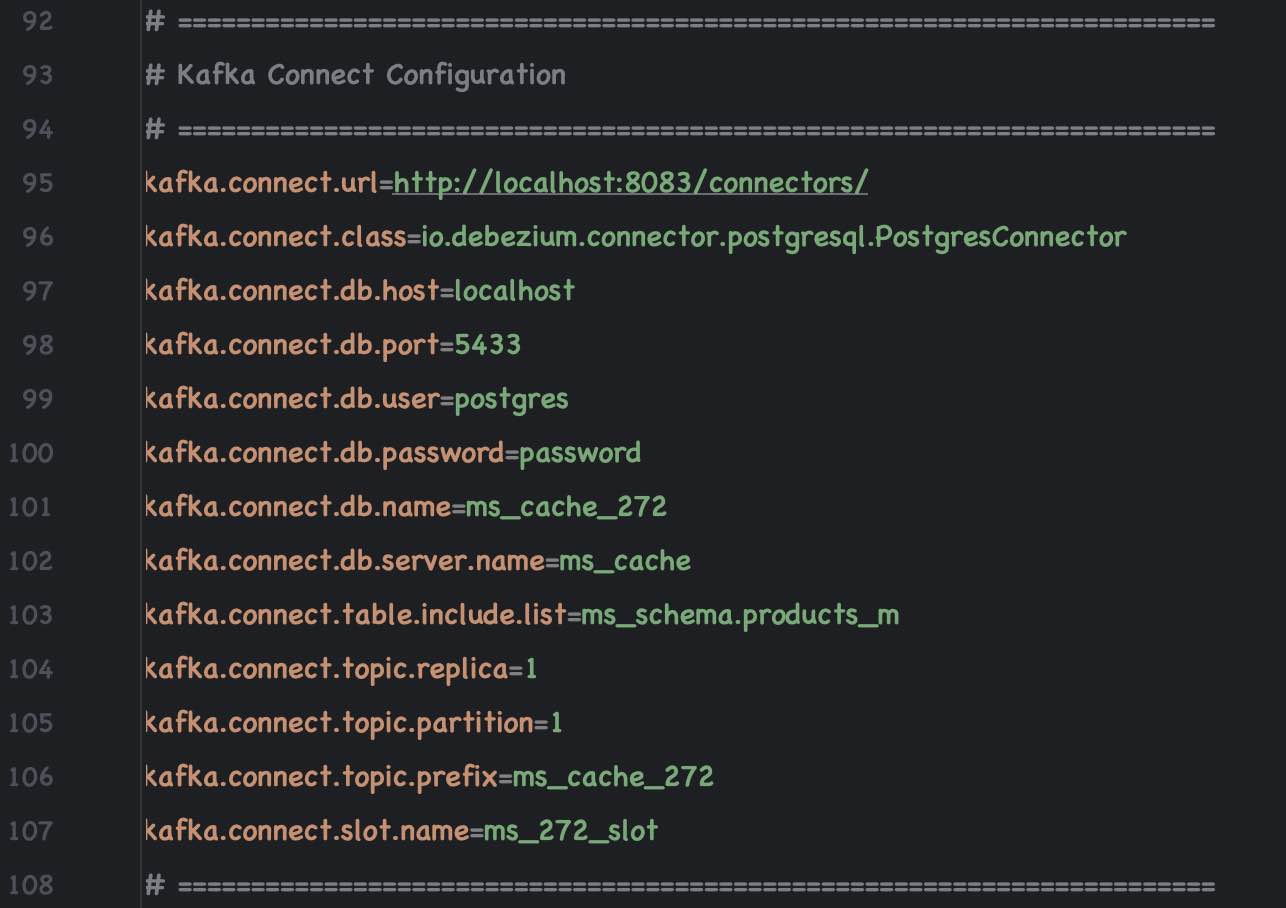
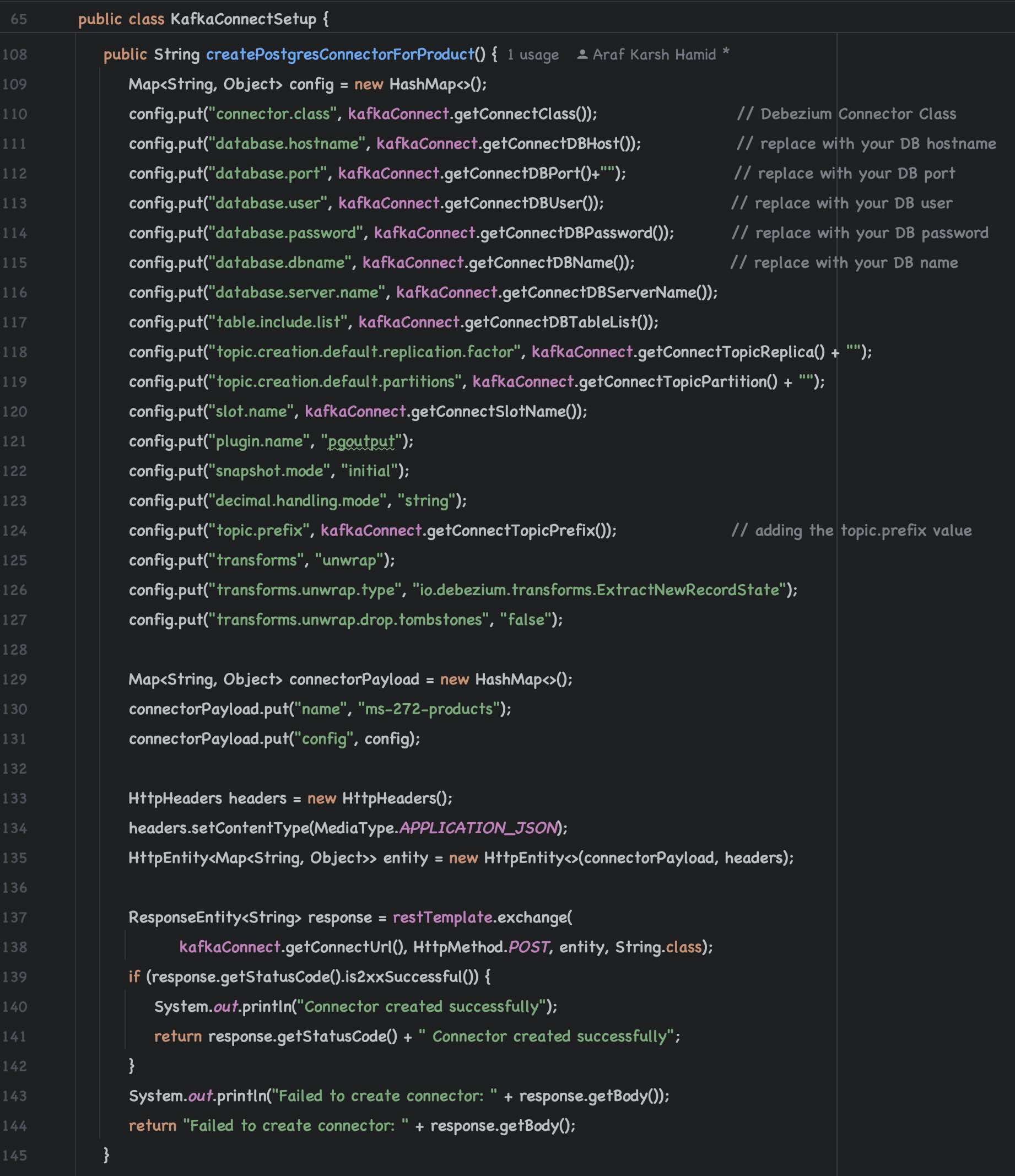
PostgreSQL Debezium driver is already available in kafka-connect directory.
To install the debezium drivers for any database, Download the driver from debezium site.
- Install these under plugins directory in the Kafka installation
- Open the config connect-distributed.properties and add following towards the end of the file
- plugin.path=/kafka/plugins (The directory you have downloaded the debezium driver)
-
Logical Replication Setup: Debezium leverages PostgreSQL's logical replication feature, which allows changes to the database (DML statements) to be streamed in real-time to external systems. Logical replication works by decoding the write-ahead log (WAL) of PostgreSQL, which records all changes to the database's data.
-
Replication Slot: Debezium establishes a replication slot on PostgreSQL, which is a stable store for WAL changes that the database maintains until the consuming application (Debezium) confirms their processing. This ensures that all changes can be captured without loss, even if the consuming application temporarily disconnects.
-
Snapshot (Initial Sync): On first run, Debezium can perform an initial snapshot of the entire database (or specific tables), exporting existing records before it starts streaming changes. This is useful for initializing the Kafka topics with the current state of the database.
To enable Debezium to capture changes from PostgreSQL (running on Machine C), you need to configure several components:
- PostgreSQL Configuration Changes:
- wal_level set to logical to enable logical decoding.
- max_wal_senders and max_replication_slots set to appropriate values to handle connections and replication slots.
- Replication User:
- A dedicated database user with replication privileges.
- Publication (For PostgreSQL 10+):
- Publications aren't strictly necessary for Debezium but are part of PostgreSQL's logical replication capabilities, allowing control over which tables are replicated
- Capture of Changes: As changes occur in the PostgreSQL database:
- Inserts generate new WAL entries, which are then converted into Create events.
- Updates are converted into Update events, capturing the old and new values (depending on the configuration).
- Deletes produce Delete events, with options to include the deleted data in the event payload.
-
Streaming to Kafka: Debezium reads these events from the replication slot and sends them to Kafka Connect, which in turn publishes them onto Kafka topics (running on Machine B). Each type of change (insert, update, delete) can be configured to go to the same or different topics based on the setup.
-
Serialization: The events are serialized (commonly using JSON or Avro formats) and include metadata such as the source database, table, and timestamp, along with the actual data change.
Modify the PostgreSQL configuration files (postgresql.conf) to enable logical replication:
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Kafka Connect Settings
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REPLICATION
wal_level = logical
max_wal_senders = 4
max_replication_slots = 4
Allow Replication Connections: Modify the pg_hba.conf file to allow the Debezium user to connect for replication purposes:
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
local all all trust
local all postgres trust
local all youruser trust
# Allow replication connections from localhost, by a user with the
# replication privilege.
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
local replication all trust
host replication all 127.0.0.1/32 trust
host replication all ::1/128 trust
Create Role in the PostgreSQL Database
CREATE ROLE name WITH REPLICATION LOGIN PASSWORD 'password';
Restart the PostgreSQL database.
Kafka Connect requires Java 17+
To Start the Kafka Connect Server
$ kafka-scripts/start-kc.sh
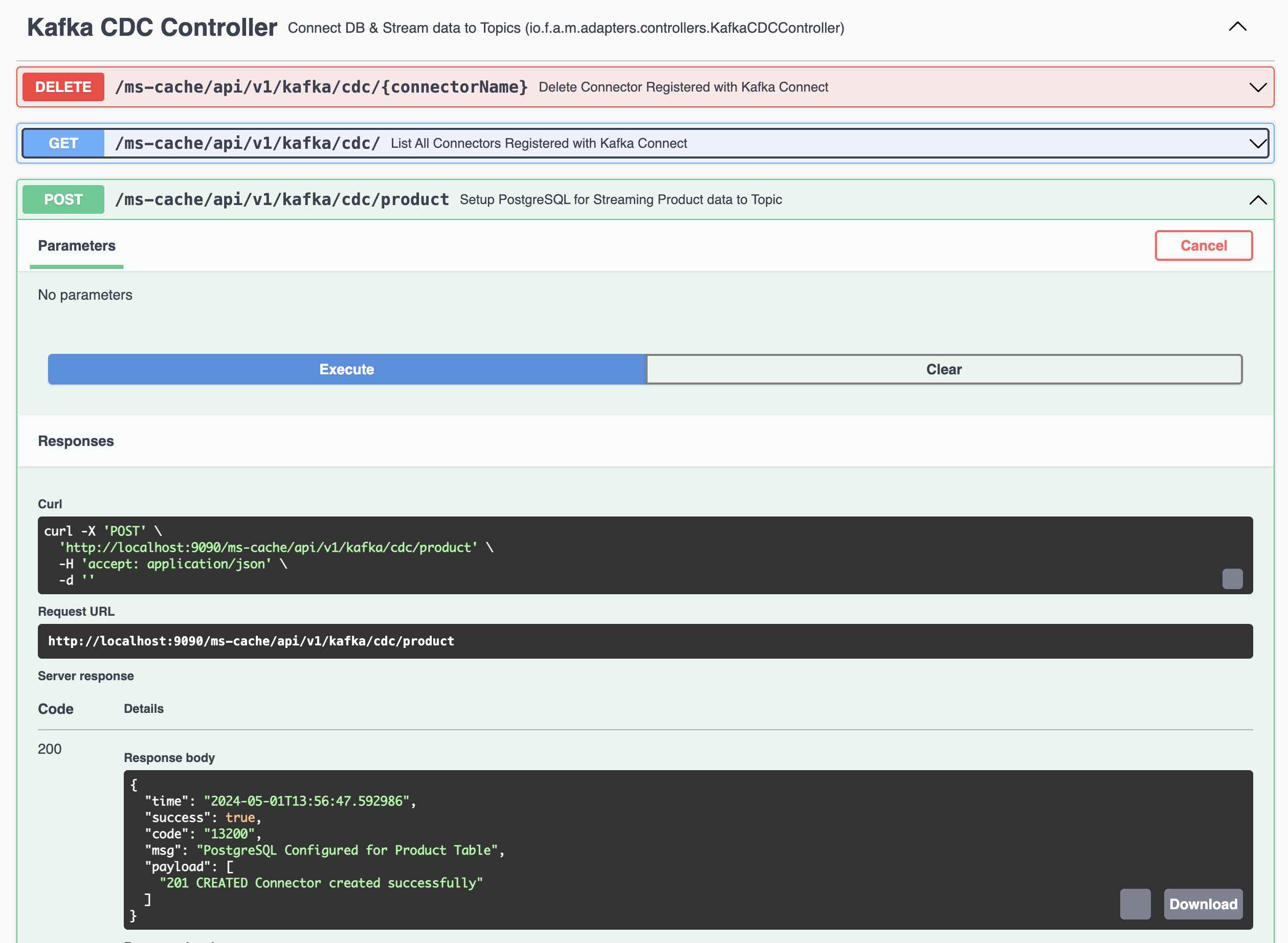
Kafka Connect - List the Connectors
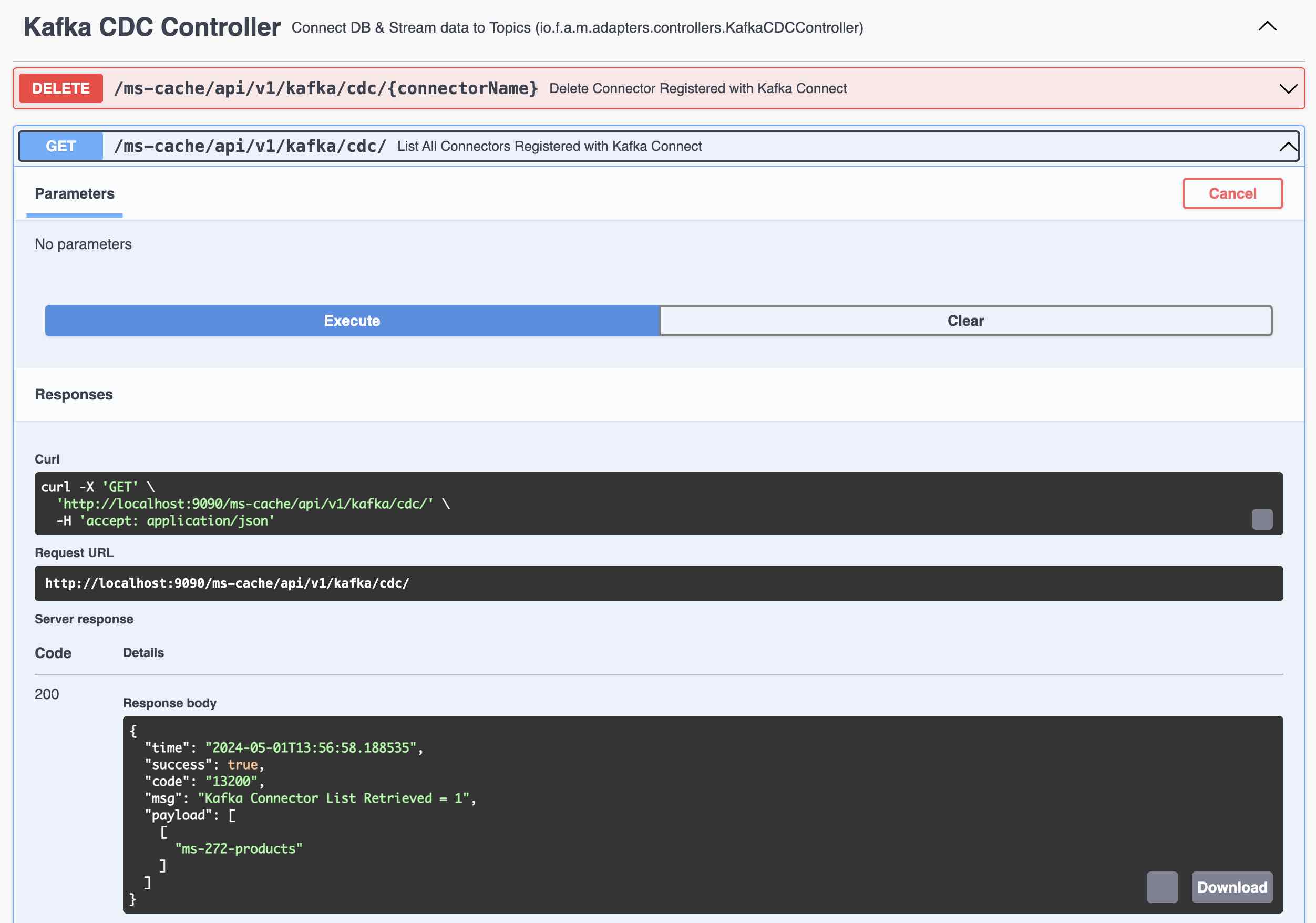
Following Steps involved in Testing the Kafka Connect and Streams.
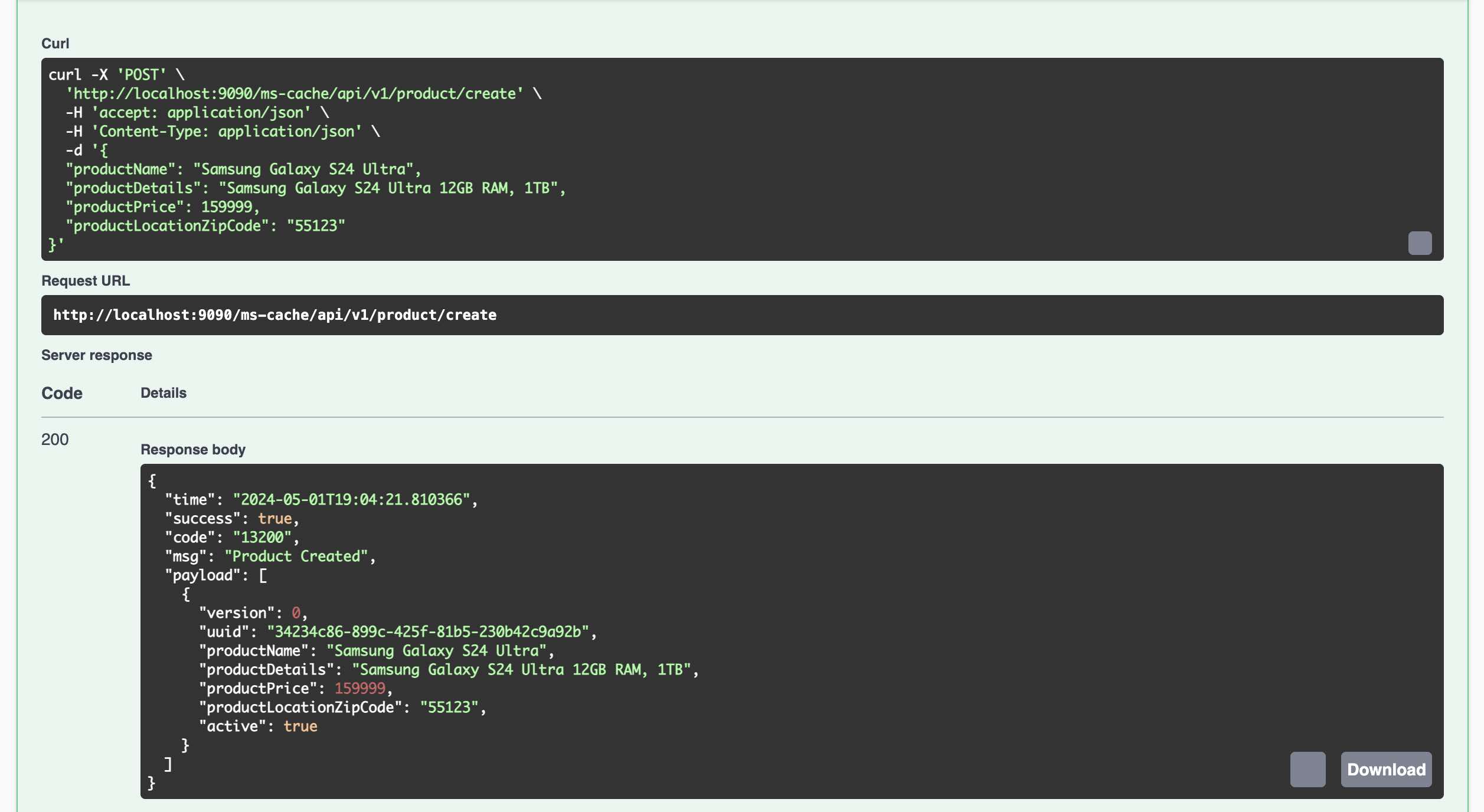
- Create a Product Using REST Endpoint and the Record is created in PostgreSQL Database
- Kafka Connect immediately sends the record to Kafka Topic
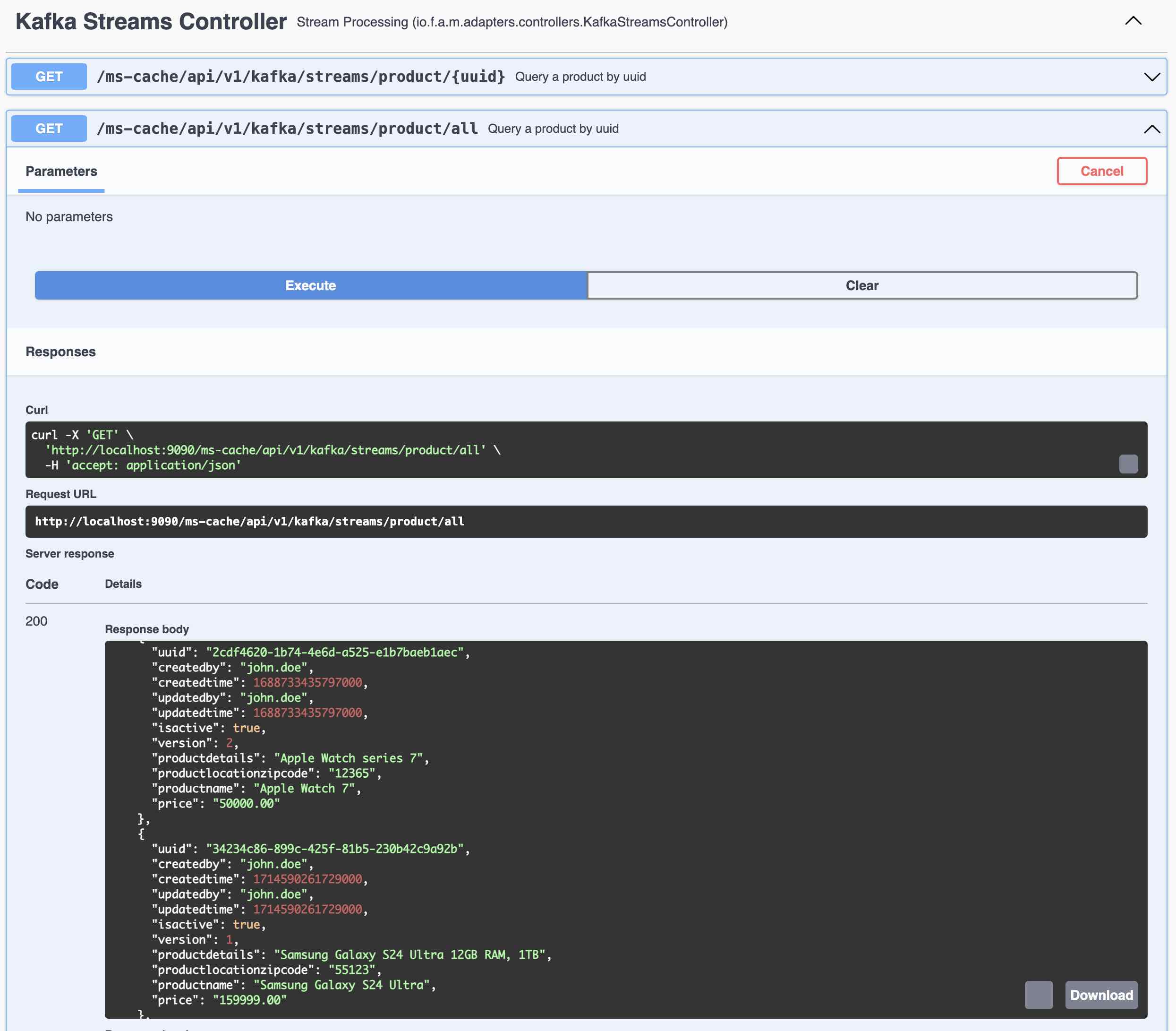
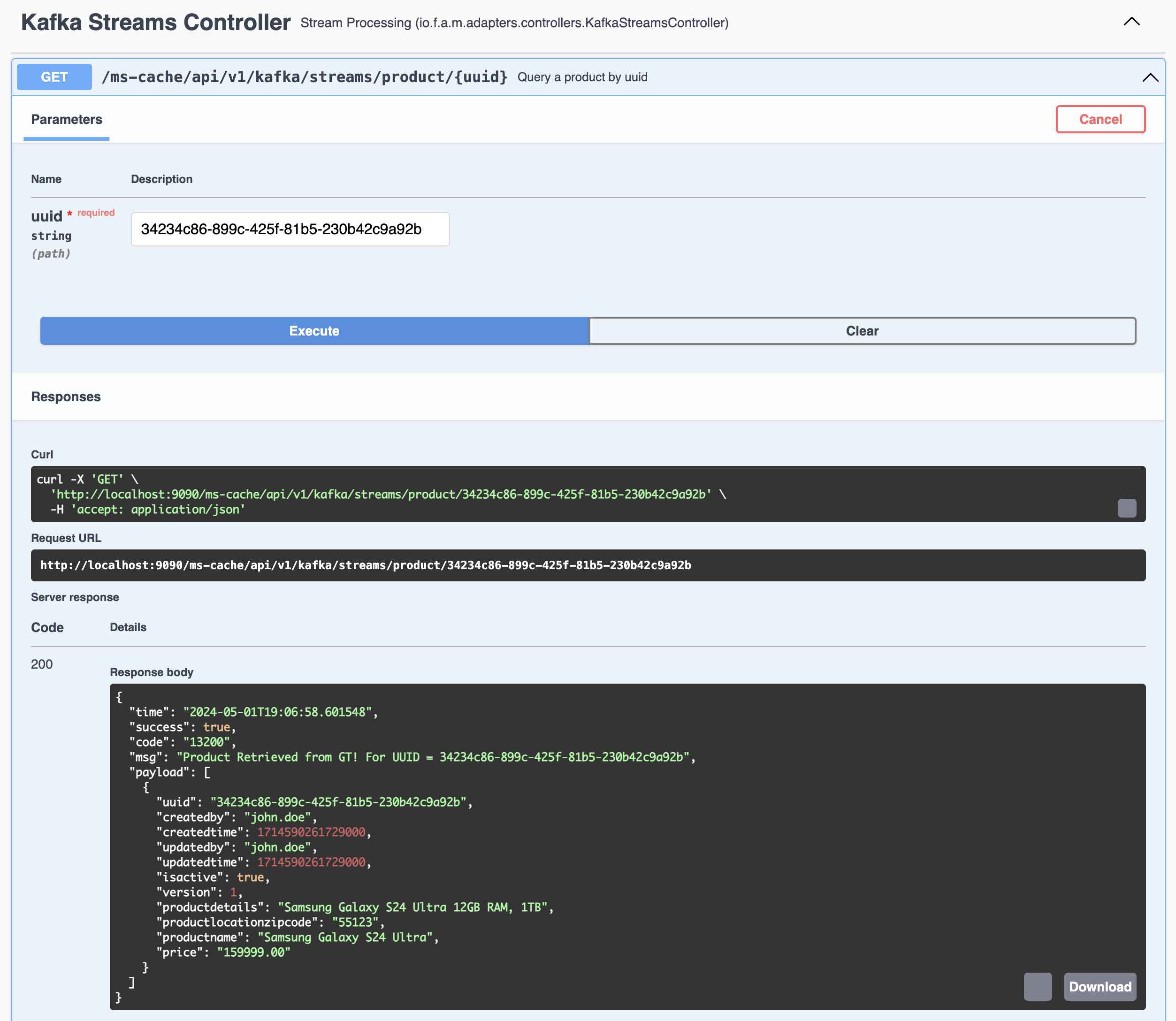
- Query all the records from Kafka Streams using Global Table
- Query a Specific Record by UUID of that Record from Kafka Streams Global Table
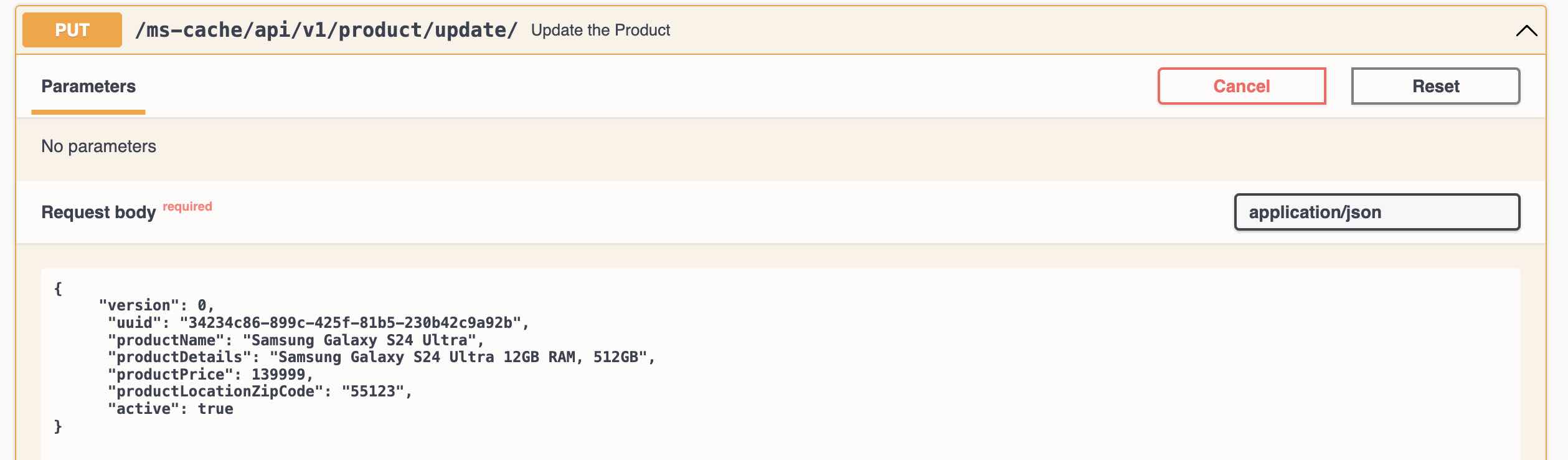
- Update the record in Product DB using Update Product REST Endpoint
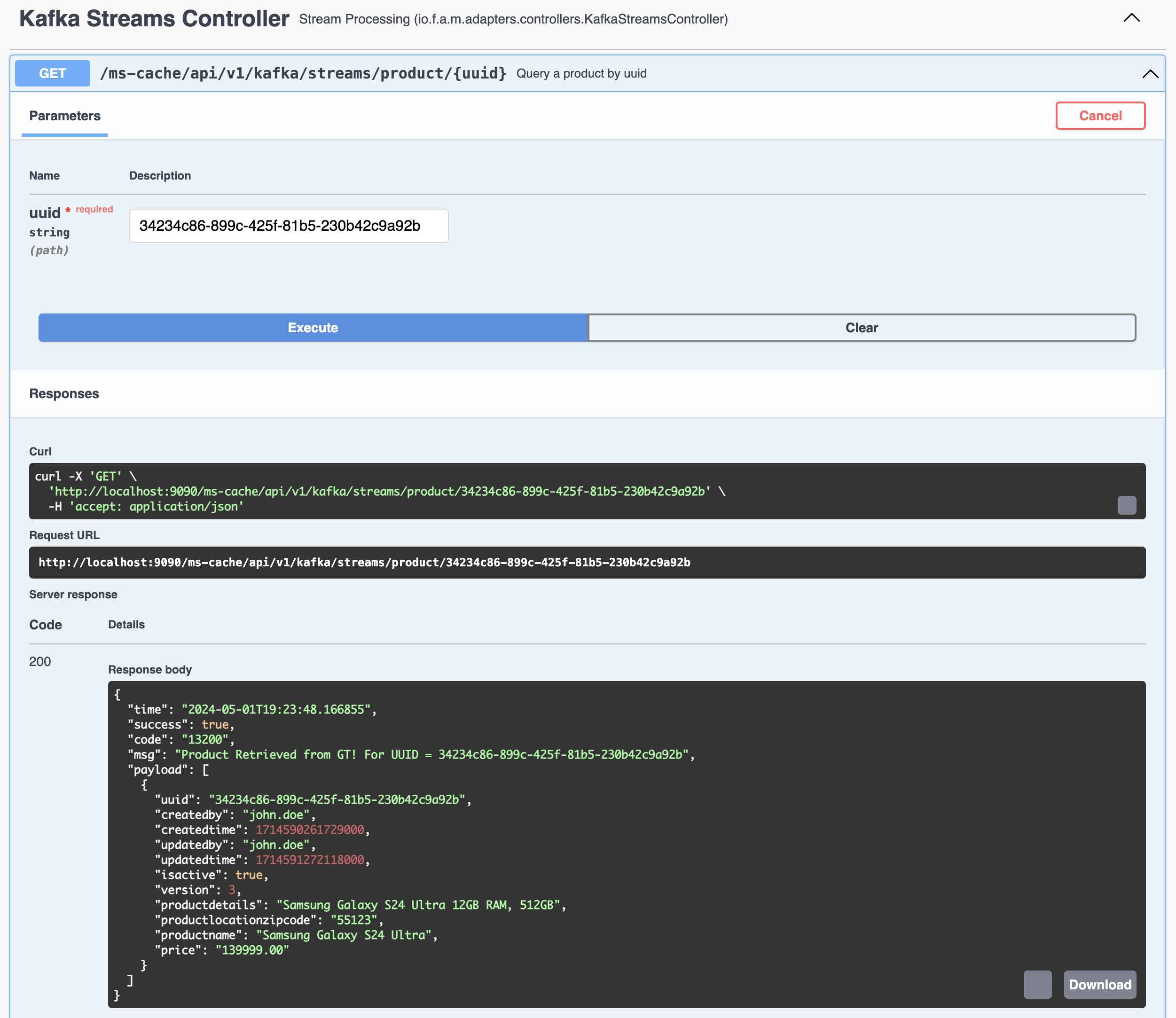
- Query the same record again using UUID from Kafka Streams Global Table
-
Kafka Connect immediately sends the record to Kafka Topic
-
Query a Specific Record by UUID of that Record from Kafka Streams Global Table
-
Update the record in Product DB using Update Product REST Endpoint
-
Query the same record again using UUID from Kafka Streams Global Table
- Verify the Org Name in src/main/resources/app.props.tmpl file (service.org)
- Verify the container name in src/main/resources/app.props.tmpl file (service.container)
- Verify the microservice name in src/main/resources/app.props.tmpl file (service.api.name)
- build (Build the Container)
- scan (Scan the container vulnerabilities)
- start (Start the Container)
- logs (to view the container logs) - Wait for the Container to Startup
- Check the URL in a Browser
Update the Org Name in src/main/resources/app.props.tmpl file (service.org) Setup the Docker Hub or any other Container Registry
- push (Push the Container to Docker Hub)
- stop (Stop the Container)
- stats (show container stats)
(C) Copyright 2021-24 : Apache 2 License : Author: Araf Karsh Hamid
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License.