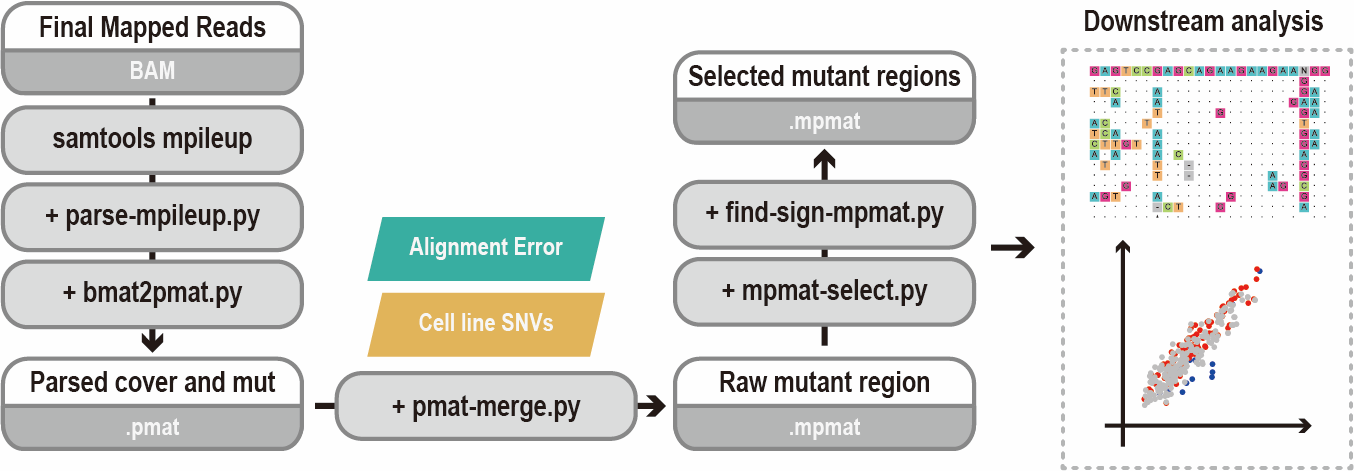
Detect-seq is a method performs the genome-wide identification of CBE-induced off-targets in the cellular context.
This technique is developed by YiLab @ School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing, China.
For full informations please click www.detect-seq.com
Detect-seq tools are a collection of Python scripts, which is designed for the analysis of Detect-seq data. The tools can help to perform Detect-seq analysis including but are not limited to off-targets finding sgRNA alignment, and visualization of results.
- Python = 2.7x
- Biopython >= 2.2.4
- pysam >= 0.15
- pandas >= 0.24.2
- numpy >= 1.16.2
- matplotlib >= 1.74
- scikit-learn >= 0.20.3
All Python code in this repertory can be directly downloaded and used like:
python + sepecific_cmd
We are going to distribute Detect-seq tools on pip, which will be coming soon!
We provide some test data in the test dir. So you can download the BAM files and find Detect-seq signal with the following steps.
- 0. A general analysis pipeline
- 1. From .BAM to .mpileup file
- 2. From .mpileup to .pmat file
- 3. Merge .pmat file into .mpmat file
- 4. Run enrichment test with .mpmat file
- 5. Select signicicant regions and run sgRNA alignment
- 6. Plot sgRNA alignment results
When you obtain the BAM files, you can follow this analysis pipeline to get your final off-target list and make a sgRNA alignment plot.
- FILE: sorted
BAM - FILE: reference genome
FASTA(Here we usehg38.faas an example, and this ref file have to match yourBAM) - CMD:
samtoolsand version >= 1.9
You can generate .mpileup file from a sorted .BAM file with the following command:
samtools mpileup -q 20 -Q 20 --reference hg38.fa -o detect_seq.mpileup detect_seq.sort.bam
The output file will be like:
chr1 1302588 G 1 ^K. e
chr1 1302589 T 1 . j
chr1 1302590 G 1 . o
chr1 1302591 T 1 . o
chr1 1302592 G 1 . o
chr1 1302593 T 1 . s
chr1 1302594 C 1 . s
chr1 1302595 C 1 . s
chr1 1302596 A 1 . s
chr1 1302597 T 1 . s
The .mpileup format explain please check the HTML
mpileup explain
- FILE:
.mpileup - CMD:
parse-mpileup-V04.py(* This command support multiple threads.) - CMD:
bmat2pmat-V02.py
You can generate .bmat file from a .mpileup file with the following command:
parse-mpileup-V04.py -i detect_seq.mpileup -o detect_seq.bmat -p 1 -n 0
For help info, please run python parse-mpileup-V04.py -h:
python parse-mpileup-V04.py -h
usage: parse-mpileup-V04.py [-h] -i INPUT [-o OUTPUT] [-p THREADS] [-n MUTNUM]
[--TempDir TEMPDIR]
convert mpileup file to info file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT, --Input INPUT
samtools mpileup format file
-o OUTPUT, --Output OUTPUT
Output parsed file
-p THREADS, --Threads THREADS
Multiple threads number, default=1
-n MUTNUM, --MutNum MUTNUM
Only contain mutation info go to the output, set 0
mean output all site, default=0
--TempDir TEMPDIR Where to keep temp files, default is the same dir with
--Input
The .bmatformat will looks like:
chr_name chr_index ref_base A G C T del_count insert_count ambiguous_count deletion insertion ambiguous mut_num
chr1 1307722 G 0 77 0 1 0 0 0 . . . 1
chr1 1307723 C 0 0 78 0 0 0 0 . . . 0
chr1 1307724 G 0 79 0 0 0 0 0 . . . 0
chr1 1307725 A 70 0 0 0 0 0 0 . . . 0
chr1 1307726 C 0 0 75 0 0 0 0 . . . 0
chr1 1307727 G 0 74 0 0 0 1 0 . C . 0
chr1 1307728 C 0 0 76 0 0 0 0 . . . 0
chr1 1307729 C 0 0 75 0 0 0 0 . . . 0
chr1 1307730 C 0 0 75 0 0 0 0 . . . 0
chr1 1307731 C 0 0 74 0 0 0 0 . . . 0
As we all know, BAM files convert all sequence information into the reference strand, which also called forward strand (+). So if a CBE edit occurs on the reverse strand (-), BAM file record that information as G-to-A rather than C-to-T. So it is necessary to split results into two parts, a C-base part and the other is G-base part, represent forward strand (+) edits and reverse strand (-) edits respectively.
# select C-base info (possible foward strand edits)
awk '$3 == "C" {print $0}' detect_seq.bmat > detect_seq.C.bmat
# select G-base info (possible reverse strand edits)
awk '$3 == "G" {print $0}' detect_seq.bmat > detect_seq.G.bmat
.bmat and .pmat files are presented with a little difference. You can generate .pmat file from a .bmat file with the following command:
# For C-base info
bmat2pmat-V02.py -i detect_seq.C.bmat -o detect_seq.C.pmat --InHeader False --InLikeBED False --OutHeader True
# For G-base info
bmat2pmat-V02.py -i detect_seq.G.bmat -o detect_seq.G.pmat --InHeader False --InLikeBED False --OutHeader True
For help info, you can run python bmat2pmat-V02.py -h
usage: bmat2pmat-V02.py [-h] -i INPUT [-o OUTPUT] [-c COVERNUMCUTOFF]
[-m MUTNUMCUTOFF] [-r MUTRATIOCUTOFF] [-t MUTTYPE]
[--InHeader INHEADER] [--InLikeBED INLIKEBED]
[--OutHeader OUTHEADER]
convert bmat file to pmat file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT, --Input INPUT
Input bmat file
-o OUTPUT, --Output OUTPUT
Output BED format file
-c COVERNUMCUTOFF, --CoverNumCutoff COVERNUMCUTOFF
Site coverage number cutoff default=0
-m MUTNUMCUTOFF, --MutNumCutoff MUTNUMCUTOFF
Site mutation number cutoff default=0
-r MUTRATIOCUTOFF, --MutRatioCutoff MUTRATIOCUTOFF
Site mutation ratio cutoff default=0
-t MUTTYPE, --MutType MUTTYPE
Select mutation type, ALL means no selection, can set
like CT, default=ALL
--InHeader INHEADER If contain header line in input file, default=True
--InLikeBED INLIKEBED
If input bmat file looks like bed file, default=False
--OutHeader OUTHEADER
If contain header line in output file, default=True
- FILE: reference genome
FASTA(Here we usehg38.faas an example, and this ref file have to match yourBAM) - FILE:
.pmatfile - FILE: SNP annotation as
.vcfformat (not necessary) - CMD:
pmat-merge-V04.py
The pmat file only records single site information on each line, so we next try to search the tandem C-to-T (as G-to-A for reverse strand) pattern in the whole genome by pmat-merge-V04.py command.
And you can use the --SNP option to set SNP information to ignore SNP or SNV signals during your Detect-seq analysis.
# For C-to-T .pmat merge
pmat-merge-V04.py -f C -t T -r hg38.fa --OutHeader False \
-i detect_seq.C.pmat -o detect_seq.CT.mpmat \
-d 50 -D 100 --NoMutNumCutoff 2 --OmitTandemNumCutoff 2 --SNP SNP_info.vcf &
# For G-to-A .pmat merge
pmat-merge-V04.py -f G -t A -r hg38.fa --OutHeader False \
-i detect_seq.G.pmat -o detect_seq.GA.mpmat \
-d 50 -D 100 --NoMutNumCutoff 2 --OmitTandemNumCutoff 2 --SNP SNP_info.vcf &
For help info, you can run python pmat-merge-V04.py -h
usage: pmat-merge-V04.py [-h] -i INPUT [-o OUTPUT] [-f FROMBASE] [-t TOBASE]
-r REFERENCE [-d MAXSITEDISTANCE]
[-D MAXREGIONDISTANCE]
[--NoMutNumCutoff NOMUTNUMCUTOFF]
[--OmitTandemNumCutoff OMITTANDEMNUMCUTOFF]
[--SNP SNP] [--OutHeader OUTHEADER]
[--InHeader INHEADER]
merge pmat file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT, --Input INPUT
Input bmat file
-o OUTPUT, --Output OUTPUT
Output BED format file
-f FROMBASE, --FromBase FROMBASE
Ref base, accept A,G,C,T default=C
-t TOBASE, --ToBase TOBASE
Mut base, accept A,G,C,T default=T
-r REFERENCE, --reference REFERENCE
Reference genome fasta file
-d MAXSITEDISTANCE, --MaxSiteDistance MAXSITEDISTANCE
Max distance between two sites in one region,
default=50
-D MAXREGIONDISTANCE, --MaxRegionDistance MAXREGIONDISTANCE
Max length of a mutation region, default=100
--NoMutNumCutoff NOMUTNUMCUTOFF
The number of site without mutation --ToBase signal in
a mutation region, default=2
--OmitTandemNumCutoff OMITTANDEMNUMCUTOFF
The omit tande site cutoff, default=2
--SNP SNP SNP file with vcf or bed format, if use multiple file,
use ',' to separate, default=None
--OutHeader OUTHEADER
If contain header line in output file, default=True
--InHeader INHEADER If contain header line in input file, default=True
- FILE:
.mpmat - FILE: Genome background file in
.jsonformat - CMD:
calculate-mut-stats-V02.py(* This command support multiple threads.) - CMD:
find-significant-mpmat-V02.py
In this step, we should merge two strands .mpmat file together.
# merge file
cat detect_seq.CT.mpmat detect_seq.GA.mpmat > detect_seq.merge.mpmat
# sort file
bedtools sort -g hg38.fa.fai -i detect_seq.merge.mpmat > detect_seq.merge.sort.mpmat
Next to calculate genome background before running a statistical test.
# ctrl sample
calculate-mut-stats-V02.py -i Full.Ctrl.bam -r hg38.fa -p 1 -o background_ctrl.json
# treat (PD) sample
calculate-mut-stats-V02.py -i Full.Treat.bam -r hg38.fa -p 1 -o background_treat.json
This step has to provide a full-size bam with all genome mapping reads into a script, so here we just show a pretend demo. And you can find background_ctrl.json and background_treat.json files in the test dir.
Run Poisson test with find-significant-mpmat-V02.py and this idea refers to MACS2
find-significant-mpmat-V02.py \
-i detect_seq.merge.sort.mpmat \
-c detect_seq.ctrl.sort.bam \
-t detect_seq.sort.bam \
-r hg38.fa \
-m background_ctrl.json \
-n background_treat.json \
-g hg38.json \
-o detect_seq.StatsTest.table \
--region_mutation_min_cutoff 2 \
--query_mutation_type CT,GA \
--query_mutation_min_cutoff 2 \
--query_mutation_max_cutoff 18 \
--other_mutation_max_cutoff 12 \
--total_mutation_max_cutoff 26
Then you will have a test result like:
chr_name region_start region_end ctrl_count treat_count ctrl_mut_count treat_mut_countctrl_count.norm treat_count.norm ctrl_mut_count.norm treat_mut_count.norm log2_FC log2_FC_mut p_value FDR
chr1 1303462 1303462 5 3 0 0 0.0 0.0 3.60519843946 1.52868309363 NA -1.23778931409 0.9433256859064737 0.9433256859064737
chr1 1303610 1303612 2 4 0 1 0.0 0.50956103121 1.44207937578 2.03824412484 -0.972673143489 0.499176280075 0.8426930101168323 0.9433256859064737
chr1 1303615 1303615 2 4 0 0 0.0 0.0 1.44207937578 2.03824412484 NA 0.499176280075 0.9433256859064737 0.9433256859064737
chr1 1303634 1303637 2 4 0 1 0.0 0.50956103121 1.44207937578 2.03824412484 -0.972673143489 0.499176280075 0.8426930101168323 0.9433256859064737
chr1 1307688 1307704 0 108 0 105 0 53.50390828 0 55.03259137 5.741572374 5.782214359 1.50E-16 6.89E-14
chr1 93448687 93448710 6 85 1 75 0.721039688 38.21707734 4.326238127 43.31268765 5.727994971 3.323604715 6.58E-12 2.27E-09
chr1 109629398 109629446 6 157 0 144 0 73.37678849 4.326238127 80.0010819 6.197251858 4.208834528 1.42E-22 8.42E-20
chr2 396529 396546 5 36 0 31 0 15.79639197 3.605198439 18.34419712 3.981523167 2.347173187 2.27E-05 0.00471216
The output table column explain is:
ctrl_countreads count in controlBAMfiletreat_countreads count in treatBAMfilectrl_mut_countreads count in controlBAMfile with tandem mutation signalstreat_mut_countreads count in treatBAMfile with tandem mutation signalsctrl_count.normnomalized reads count in controlBAMfiletreat_count.normnomalized reads count in treatBAMfilectrl_mut_count.normnomalized mutation reads count in controlBAMfiletreat_mut_count.normnomalized mutation reads count in treatBAMfilelog2_FCcalculate aslog2_FC = log2(treat_count.norm / ctrl_count.norm)log2_FC_mutcalculate aslog2_FC_mut = log2(treat_mut_count.norm / ctrl_mut_count.norm)p_valuePoisson test pvalueFDRAdjust pvalue with Benjamini-Hochberg method.
- FILE:
detect_seq.StatsTest.table - CMD:
mpmat-to-art-V04.py
Related to our experience, the regions with the following criterion can be considered as enriched off-targets region:
FDR< 0.05;log2_FC_mut> 1;ctrl_mut_count< 3 ORctrl_mut_count.norm< 3;
After this select step, we can obtain detect_seq.StatsTest.Sign.table.
bedtools intersect -a detect_seq.merge.sort.mpmat -b detect_seq.StatsTest.Sign.table -wa > detect_seq.merge.sort.Sign.mpmat
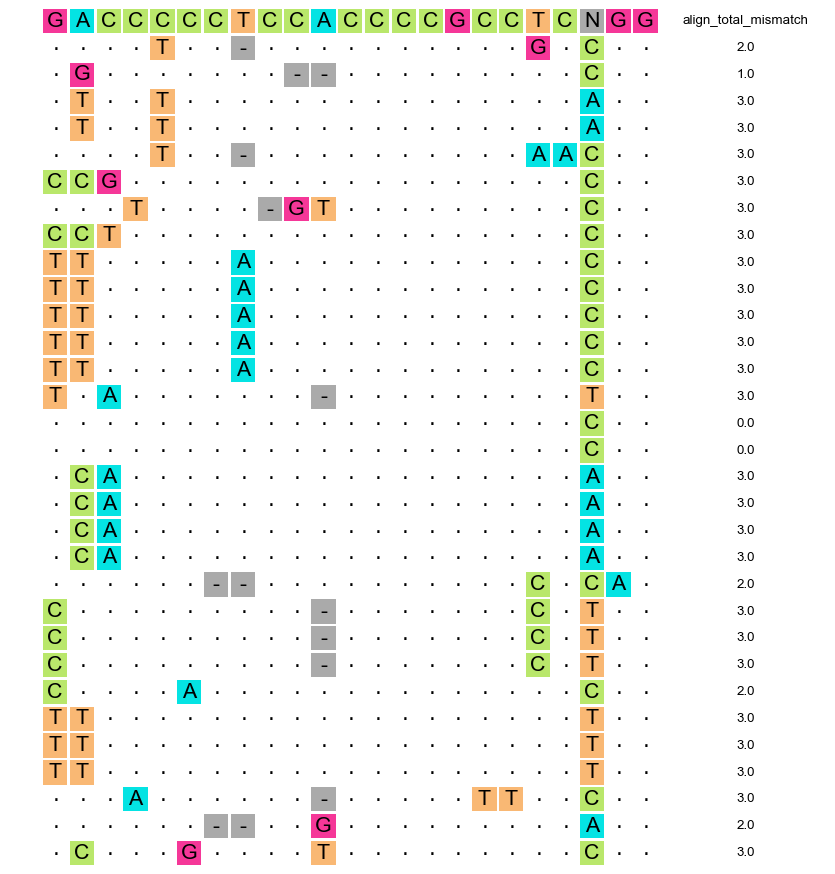
You can run sgRNA alignment as the following command. Only one thing you should take care of, the --sgRNA sequence has to include PAM info.
mpmat-to-art-V04.py \
-i detect_seq.merge.sort.Sign.mpmat -r hg38.fa --sgRNA GACCCCCTCCACCCCGCCTCCGG > detect_seq.merge.sort.Sign.art
For more alignment options you can run python mpmat-to-art-V04.py -h
usage: mpmat-to-art-V04.py [-h] -i MPMAT_TABLE --sgRNA SGRNA
[-o OUT_ALIGNMENT_RESULT] -r REFERENCE
[-s SAMPLE_NAME] [--extend_method EXTEND_METHOD]
[--align_dist_to_signal ALIGN_DIST_TO_SIGNAL]
[--bedtools_path BEDTOOLS_PATH]
[--align_method ALIGN_METHOD]
[--align_settings ALIGN_SETTINGS]
[--align_min_score ALIGN_MIN_SCORE]
[--input_header INPUT_HEADER]
[--input_sep INPUT_SEP]
[--more_colname MORE_COLNAME]
From .mpmat to alignment result table (.art) file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i MPMAT_TABLE, --mpmat_table MPMAT_TABLE
.mpmat table file, generated from <pmat-merge.py> or
<mpmat-select.py>
--sgRNA SGRNA sgRNA sequence with PAM (NGG/NAG) sequence
-o OUT_ALIGNMENT_RESULT, --out_alignment_result OUT_ALIGNMENT_RESULT
Output alignment result table (.art) filename,
default=Stdout
-r REFERENCE, --reference REFERENCE
Reference genome fasta file
-s SAMPLE_NAME, --sample_name SAMPLE_NAME
Sample name of this .mpmat, default=run_mpmat
--extend_method EXTEND_METHOD
Select and extend region of mpmat file to get FASTA
file, <region> <upstream_site> <downstream_site>
<highest_site>, default=highest_site
--align_dist_to_signal ALIGN_DIST_TO_SIGNAL
If distance too far between mutation signal and
alignment, consider as there is no appropriate
alignment, default=20
--bedtools_path BEDTOOLS_PATH
Software <bedtools> PATH, default considered
<bedtools> is already included in current PATH
environment.
--align_method ALIGN_METHOD
Provide two methods, <PAM_first> <fair_align>,
'PAM_first' treat PAM region with a higher weight,
default=fair_align
--align_settings ALIGN_SETTINGS
Set <align_match_score> <align_mismatch_score>
<align_gap_open_score> <align_gap_extension_score>,
default=5,-4,-24,-8
--align_min_score ALIGN_MIN_SCORE
If alignment score lower than this, consider as no
appropriate alignment, default=15
--input_header INPUT_HEADER
If .mpmat file contain header, default=False
--input_sep INPUT_SEP
default=\t
--more_colname MORE_COLNAME
More info you want to include in output table, so you
can write the column names like col1,col2...
default=None
- FILE:
detect_seq.merge.sort.Sign.art - CMD:
plot-art-V01.py
plot-art-V01.py -i detect_seq.merge.sort.Sign.art --sgRNA GACCCCCTCCACCCCGCCTCCGG --out_figure_format png -o out.art.png
After a few seconds, you can obtain an image with a match and mismatch information between the sgRNA sequence and off-target region.