Rovers must explore unknown terrains in search for precious Mars materials (gold and diamonds). With finite energy, efficient search and collection routes are imperative. This repository contains one approach to the aforementioned problem. Built using JASON, Agentspeak and Java coding languages, rover agents collaborate to overcome various challenges across multiple environments.
AgentSpeak is an agent-oriented programming language. It is based on logic programming and the belief–desire–intention software model (BDI) architecture for (cognitive) autonomous agents.
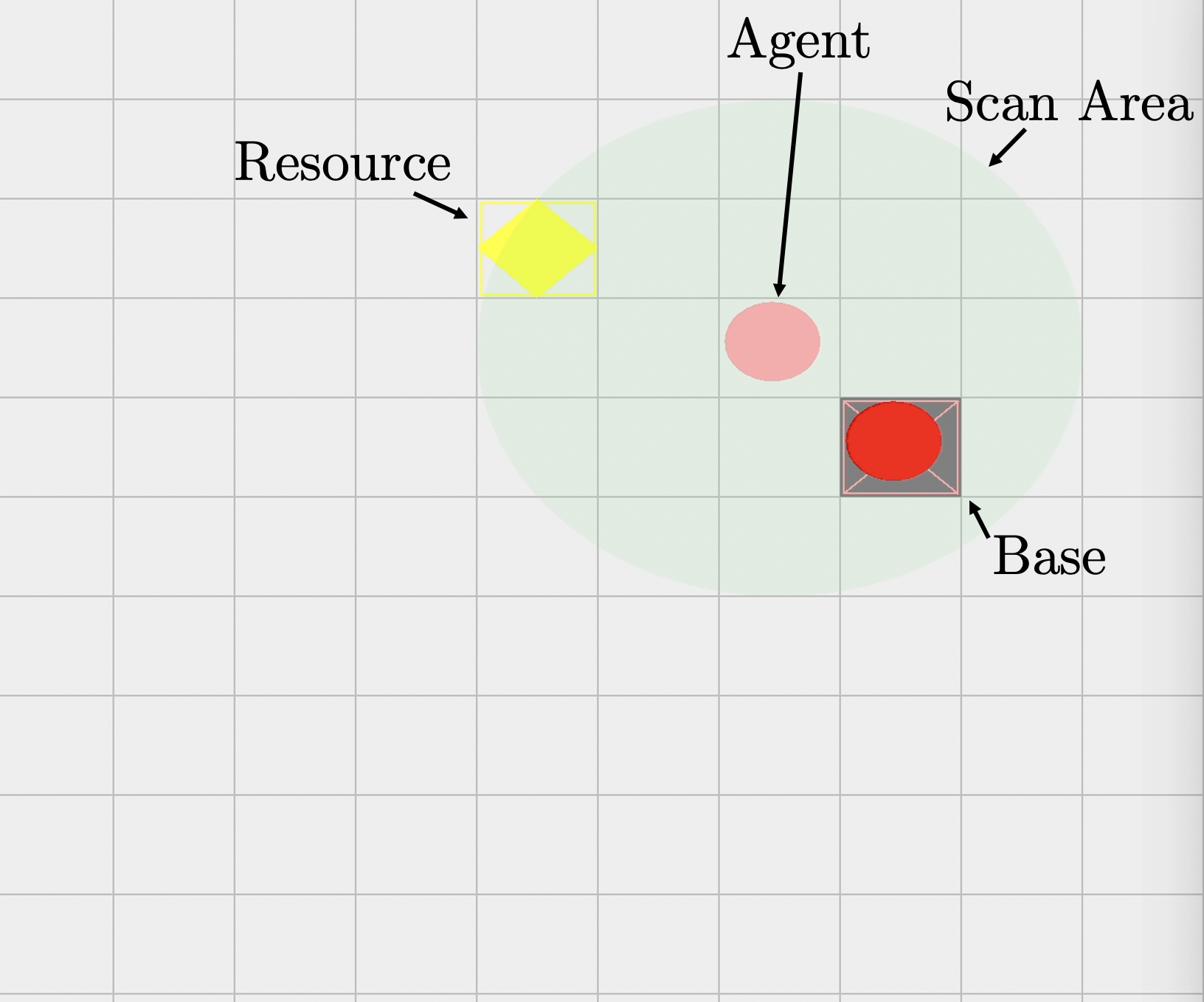
Agent (pink) starts at base (grey square) with a finite number of energy points and a specific scan area (transparent green circle). When resources are found (gold: yellow, diamond: blue), they are collected and transported back to the base before the energy runs out.
Both moving and scanning cost energy so it is imperative to make efficient use of each action. By remembering which regions have been scanned, and communicating with other allied agents, the most efficient approach is achieved.
Development setup for JASON & Agentspeak requires the following configurations:
- Java JDK click_here
- Install Eclipse IDE click here
- Install JASON click here
- Install JASON eclipse plugin click here
- After install, in Eclipse: Right Click on Project > Build Path > Configure Build Path > Add External Jars... > Replace the Jars in directory showing errors
(Note: The versions in provided links are the same as for the presented works.)
Credit to Fahid Mohammed, @fahidRM for creating the testing environment and project description below...
- The Environment
- The Agent
- Action Feedback
- All Actions
- Specific Feedback: Scanning
- Specific Feedback: Moving
- Extending agents capabilities using Internal actions
- Making your own maps
The RoverWorld environment is provided as a component of the jason-rover-environment.jar file.
To use this environment, set the environment entry of your mas2j file to:
__ environment: rover.RoverWorld("mas2j_file=<mas2j_file_name>", "scenario_id=<scenario_id>")__
where;
mas2j_file: Name of mas2j file or its path if it's located elsewhere.
_scenario_id: An string representing the id of the scenario to load.
example;
environment: rover.RoverWorld("mas2j_file=scenario_1.mas2j", "scenario_id=graded-scenario-1")
NOTE: This has already been done for you in the attached mas2j files
Agents are loaded via the mas2j file and each agent is expected to be configured before connecting to the environment.
Configuring an agent involves specifying its capacity, scan_range and where necessary resource_type.
You have 6 points to share between capacity and scan_range.
i.e. capacity can not have a value below 0 or above 6 and where capacity is 6, scan_range must be 0.
The environment would confirm all agent configurations are valid. Where a violation is detected, an adequate error message would be displayed and the affected agent(s) would be reconfigured as follows:
capacity = 3 and scan_range = 3
Adding an Agent to the environment requires the following line to be present in your coursework's mas2j file(s);
agents: <agent_name> [capacity=< val >, scan_range=< val >"] #< instances >;
where;
agent_name: Name of agent to add. This is the same name as the Agent's .asl file
instances: A positive non-zero integer that specifies the instances of that agent to add to the environment.
example;
dummy_bot [capacity=3, scan_range=3] #1;
In this example, one instance of the agent dummy_bot defined in the file dummy_bot.asl would be added into the environment. It would have a capacity of 3 and a scan range of 3.
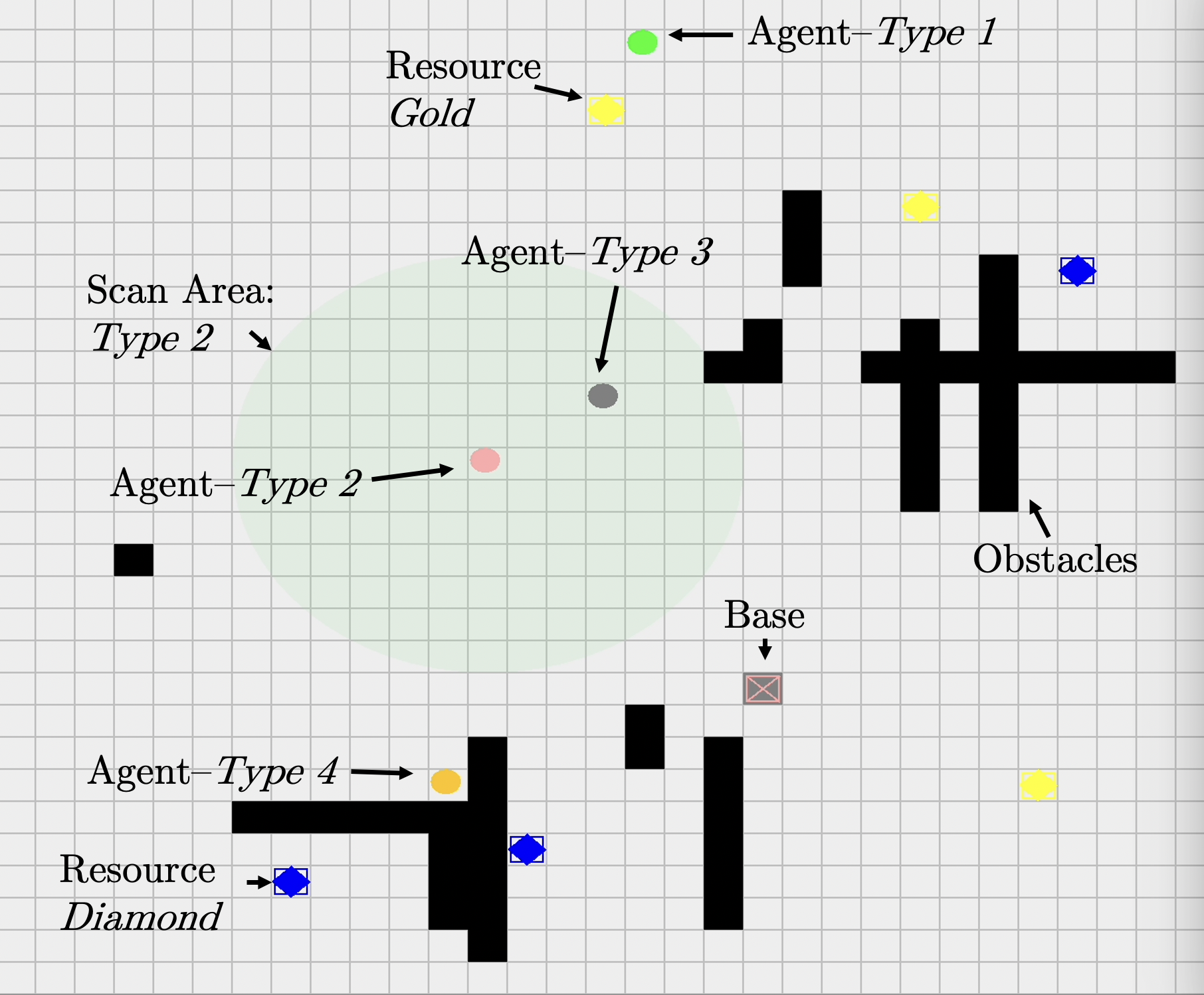
In certain scenarios, there would be multiple resource types available on the map (Gold & Diamond). Agents may only collect resources of a particular type and this can be specified in the mas2j file. Where unspecified, the type of the first resource collected by the agent would be the only type it can collect.
To specify resource type, add the resource_type attribute to the agent declaration as shown below;
example;
dummy_bot [capacity=3, scan_range=3, resource_type="gold"] #1;
The available options are Gold and Diamond.
Within the environment, an Agent would be able to scan the map, move around the map, collect resources and deposit collected resources.
All actions cost energy and would result in a feedback indicating the success or failure fo the action execution which would be delivered to agents in the form of percepts.
Note: Staying idle also costs energy.
Below are the syntax for the above stated actions;
Example: scan(3)
Example note: This would allow an Agent scan the map with a scan range of 3
move: move(<x-displacement>, <y-displacement>)
Example: move(3, 3)
Example note: This would allow an agent to move 3 steps away from its current possition along the x-axis and 3 steps away from its current position along the y-axis.
More info:
x-displacement:- Distance away from current position to travel along the x-axis
y-diaplacement:- Distance away from current position to travel along the y-axis
deposit: deposit(<resource_type>)
Example: deposit("gold")
Example note: This would allow an Agent to deposit a gold resource it's currently holding on the map.
collect: collect(<resource_type>)
Example: collect("gold")
Example note: Collects a single resource of the specified type from the map.
Kindly note that making an agent collect("gold") at one time and collect("diamond") at another would not
enable it to collect both. While running, an agent may only pick one type of resource.
Performing any of the allowed actions (move, collect and deposit) may result in any of the following feedback
When an Agent successfully performs an action, a feedback is returned to inform it of the success.
Format: action_completed(<action_name>);
Example: action_completed(move);
Example note: Informs the agent that it has successfully moved.
Insufficent energy feedback is returned when an Agent did not have sufficient energy to complete the action it just attempted. An insufficient energy feedback is a sign of action execution failure.
Format:insufficient_energy(<action_name>);
Example: insufficient_energy(move);
Example note: Infroms the agent that it was unable to move due to insufficient energy.
When an Agent attempts to perform an action that has not been properly specified or an action that is not permitted within the environment, a failure feedback is returned indicting the invalid action.
Format: invalid_action(<action_name>, <reason>);
Example: invalid_action(jump, unpermitted);
Example note: Informs the agent that the action jump is not permitted in the environment.
The three possible reasons are unpermitted, invalid_param and unmet_requirement
The unpermittedreason informs us that the an Agent is trying to perform an action that is not permitted in the environment.
The invalid_param reason informs us that an invalid parameter was passed to an action. For instance trying to move with a non-numberic coordinate.
The unmet_requirement reason informs us that a requirement to perform the stated action has not been met. For instance, an agent trying to deposit a resource when it does not have any or when it has not be configured to carry a resource.
Note: An invalid action feedback would be raised for known action types in the following events;
- scan: If the Agent does not have the ability to scan or tries to scan an invalid range such as a negative range or a non numeric range.
- move: If the Agent does not have the ability to move or tries to move to an invalid location (non numeric coordinate).
- collect: If the Agent tries to collect resource from a tile that has no resoure or if the Agent has no space to carry another resource.
If an Agent scans and doesn't find any resource, a resource_not_found feedback is returned.
Format: resource_not_found
Example: resurce_not_found
Example note: An agent scanned a portion of the map and found nothing.
If an Agent scans a portion of the map and finds one or more resources.
Format: resource_found(<artefact_type>, <artefact_qty>, <x_dist>, <y_dist>)
where;
artefact_type: Item found on map such as "Gold", "Diamond" or "Obstacle".
artefact_qty: The qty found at that location.
x_dist: Artefact distance away from agent on the x-axis.
y_dist: Artefact distance away from agent on the y-axis.
Example: resource_found("Gold",10,1,1)
Example note: The Agent found 10 deposits of gold 1 step away on the x-axis and 1 step away on the y-axis.
If an Agent runs into another Agent on it's way, this would result in an obstructed feedback
Format: obstructed(<x_travelled>,<y_travelled>,<x_left>, <y_left>)
where;
x_travelled: Distance travelled along the x-axis before the collission.
y_travelled: Distance travelled along the y-axis before the collission.
x_left: Distance from destination along the x-axis.
y_left: Distance from destination along the y-axis.
Example: obstructed(1,1,3,4)
Example note: The Agent successfully travelled 1 step on both its x and y axis and the distance away from its initial destination is 3 steps away on the x-axis and 4 steps away on the y-axis.
Apart from the actions listed above, an Agent may extend its capability via internal actions. Some internal actions have been provided for you such as;
- usage: rover.ia.check_status(X)
This would store the Agent's current energy of type double in the variable X.
NOTE: For this coursework, you are limited to create internal actions for navigation purposes only. A very basic implementation of this has been made available in the libs/jason-rover-environment.jar jar file under the package rover.ia. This implementation is made available to get you started and is not optimised (unsuitable for submission). These internal actions would be demonstrated during the lab sessions and are briefly discussed below;
- log_movement: Keeps track of movement made by the Agent.
usage: rover.ia.log_movement (Xdist, Ydist) - clear_movement_log: Clears the map the Agent built.
usage: rover.ia.clear_movement_log - get_distance_from_base: Retrieves the location of the base.
usage: rover.ia.get_distance_from_base(Xdist,Ydist)Forget_base_locationto work, all movements performed by an agent needs to be logged using thelog_movementinternal action. Note: this is not optimised and you will have to either implement yours or optimise the output you've gotten from this. - get_config: Retrieves the agent's configuration (capacity, scan range and preferred resource type)
usage: rover.ia.check_config(Capacity,Scanrange,Resourcetype) - get_map_size: Retrieves the map's size as (Width, Height)
usage: rover.ia.get_map_size(Width,Height)
Custom maps allow you to test your agents' performance under certain conditions. To create custom maps, use the browser based tool available here.