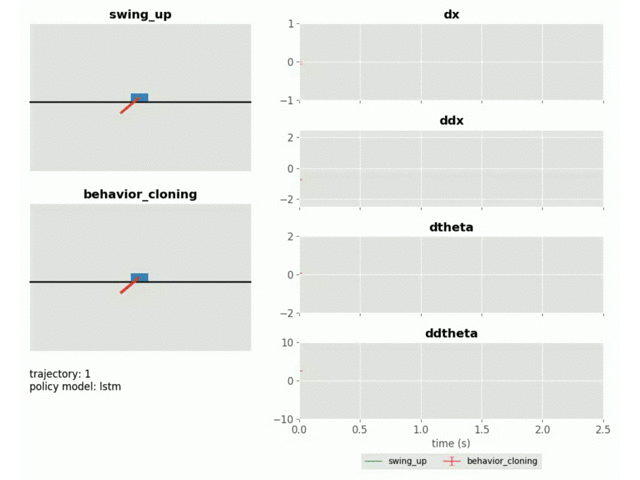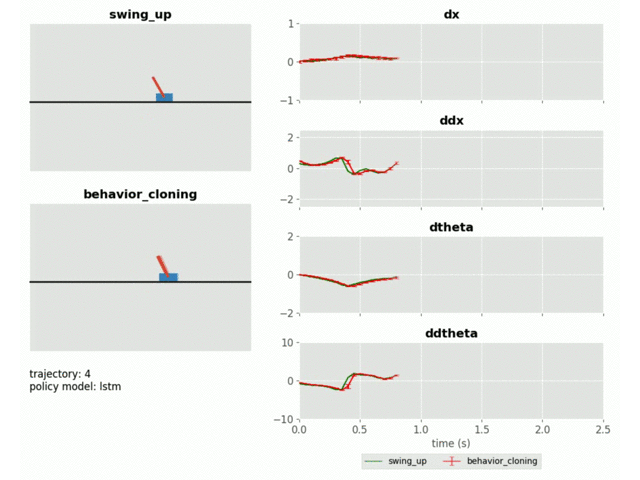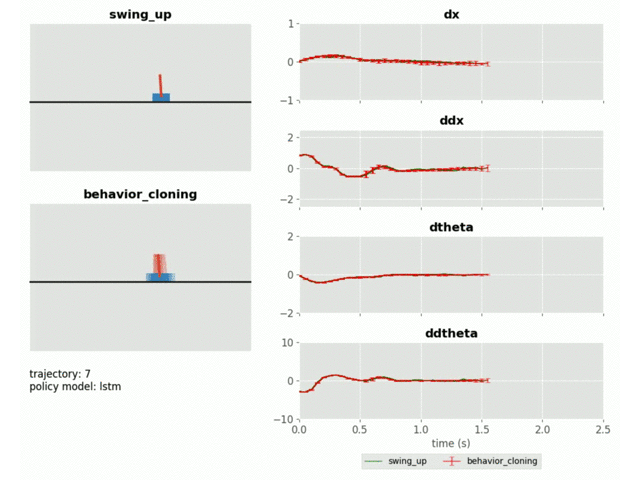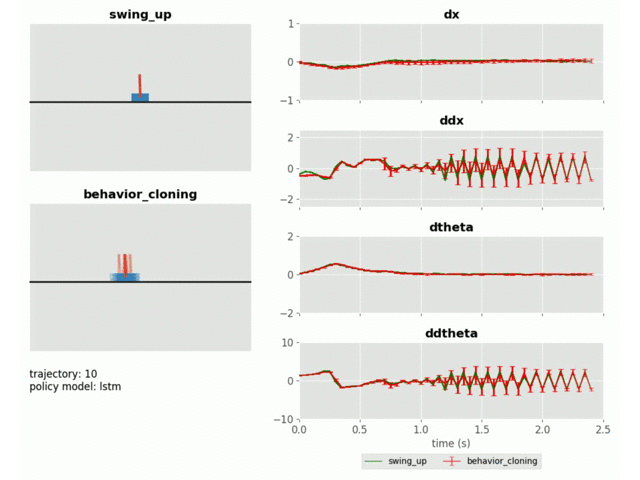
Behaviour Cloning of Cartpole Swing-up Policy with Model-Predictive Uncertainty Regularization
(UW CSE571 Guided Project 1)
By Kuo-Hao Zeng, Pengcheng Chen, Mengying Leng, Xiaojuan Wang
Introduction
In this project, we adopt the idea of uncertainty regularization [1] to learn a swing-up policy via behaviour cloning without interacting with the simulator. We make several modifications to adapt the learning framework for our focused task. We make several modifications to adapt the learning framework for cartpole swing-up task:
- Since our policy learning entirely relies on BC, our policy network does not need to interact with the environment during the training phase. Therefore, we remove the simulator from our learning framework, except for the data collection process.
- We use state observation instead of image observation to ease the learning of dynamic model. In this case, we are able to focus on the effectiveness of uncertainty regularization approach.
- We slightly modify the learning framework by changing the policy cost to behaviour cloning objective to fit our problem setting.
- To make the focused task simple, we do not adopt the z-dropout technique proposed by original authors, we rather directly utilize the simplest dropout technique to perform Bayesian Neural Network (e.g., generate sub-network on-the-fly by different dropout masks).
Check out our introduction video, final report, and some qualitative results.
Set Up
-
Clone this repository
git clone git@github.com:KuoHaoZeng/cartpole_model_based_control.git -
Using
python 3.6, create avenvNote: The
pythonversion needs to be above3.6to match the original carpole codebase provided by ETAs# Create venv and execute it python -m venv venv && source venv/bin/activate -
Install the requirements with
# Make sure you execute this under (venv) environment pip install -r requirements.txt
Train and evaluate it!
You can always change or adjust the hyperparameters defined in the config file to change the setting such as how often you want to store a checkpoint, how large the initial learning rate you are going to use, what batch size you are going to use etc.
Pretrain a dynamic model
# Train and test
python main.py --config configs/dm_state.yaml
The default model is dropout LSTM with dropout rate = 0.05. You can change them in the config file:
model:
...
backbone: dlstm # {fc, gru, lstm, dfc, dgru, dlstm} <--- change the model backbone here
...
dropout_p: 0.05 # only work for the model has dropout layer <--- change the dropout rate here
Main Results for dynamics model
| Model | L2 difference with simulator |
|---|---|
| FC | 0.528±0.079 |
| GRU | 0.354±0.063 |
| LSTM | 0.229±0.058 |
| Dropout FC | 0.559±0.114 |
| Dropout GRU | 0.416±0.064 |
| Dropout LSTM | 0.252±0.040 |
Learn a swing-up by uncertainty regularization with the pretrained dynamic model
# Train and test
python main.py --config configs/mp_state.yaml
Note: you need to make sure the dynamics model defined in the mp_state.yaml pointing to the correct pretrained dynamics model:
dm_model:
......
model:
protocol: state
backbone: dlstm # {fc, gru, lstm, dfc, dgru, dlstm} <--- change the model backbone here
...
dropout_p: 0.05 # only work for the model has dropout layer <--- change the dropout rate here
Do experiments on policy learning with a pretrained drop LSTM model with various experimental settings
Assuming you have pretrained the dynamics model with dlstm, the following script performs experiments with different hyparparameters setting defined in experiment.py.
# Train and test model with different experimental settings
# --n: indicates how many workers (n) you want to spawn for doing the experiments
python experiment.py --config configs/mp_state.yaml --n 4
You can change the hyparparameters which you would like to try in the experiment.py:
if __name__ == "__main__":
options = {
"framework.seed": [12345], # <--- indicates what are the random seeds you want to try
"dm_model.model.backbone": ["dlstm"], # <--- indicates what are the backbones for dynamics model you want to try
"model.backbone": ["fc", "dfc", "gru", "dgru", "lstm", "dlstm"], # <--- indicates what are the backbones for policy network you want to try
"train.LAMBDA": [0.0, 0.01, 0.1, 0.15], # <--- indicates what are the lambda for policy learning you want to try
}
You can easily add experimental options based on the hyperparameters defined in the config files. For example, do experiments with different initial learning rate:
if __name__ == "__main__":
options = {
"train.lr": [0.1, 0.01, 0.001],
}
Main Results for policy learning with uncertainty regularzation
| Dynamics Model \ Policy Network | FC | GRU | LSTM | Drpopout LSTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dropout LSTM w/ λ = 0 (original behaviour cloning) | 0.649 | 0.537 | 0.534 | 0.539 |
| Dropout LSTM w/ λ = 0.01 | 0.629 | 0.543 | 0.516 | 0.527 |
| Dropout LSTM w/ λ = 0.1 | 0.631 | 0.540 | 0.527 | 0.554 |
| Dropout LSTM w/ λ = 0.15 | 0.646 | 0.550 | 0.510 | 0.539 |
Reference
[1] Mikael Henaff, Alfredo Canziani, and Yann LeCun. Model-predictive policy learning with uncertainty regularization for driving in dense traffic. In ICLR, 2019.