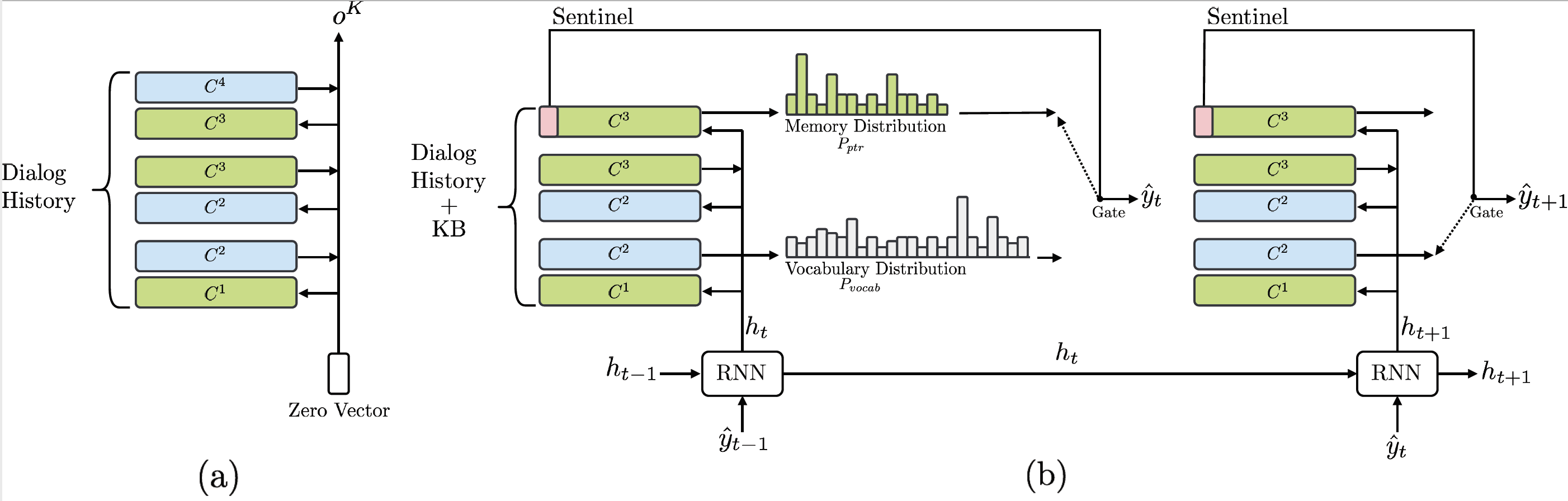
Mem2Seq
Mem2Seq: Effectively Incorporating Knowledge Bases into End-to-End Task-Oriented Dialog Systems (ACL 2018). Andrea Madotto, Chien-Sheng Wu, Pascale Fung. Accepted at ACL 2018. [PDF] in ACL anthology. Andrea Madotto and Chien-Sheng Wu contribute equally at this work.
This code has been written using Pytorch 0.3, soon we will update the code to Pytorch 0.4.
If you use any source codes or datasets included in this toolkit in your work, please cite the following paper. The bibtex are listed below:
@InProceedings{P18-1136,
author = "Madotto, Andrea
and Wu, Chien-Sheng
and Fung, Pascale",
title = "Mem2Seq: Effectively Incorporating Knowledge Bases into End-to-End Task-Oriented Dialog Systems",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
year = "2018",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
pages = "1468--1478",
location = "Melbourne, Australia",
url = "http://aclweb.org/anthology/P18-1136"
}
Mem2Seq in pytorch
In this repository we implemented Mem2Seq and several baseline in pytorch (Version 0.3). To make the code more reusable we diveded each model in a separated files (obviusly there is a large code overlap). In the folder models you can find the following:
- Mem2Seq: Memory to Sequence (Our model)
- Seq2Seq: Vanilla seq2seq model with no attention (enc_vanilla)
- +Attn: Luong attention attention model
- Ptr-Unk: combination between Bahdanau attention and Pointer Networks (Point to UNK words)
All of these file share the same structure, which is: a class that builds an encoder and a decoder, and provide training and validation methods (all inside the class).
Import data
Under the utils folder, we have the script to import and batch the data for each dataset.
Basic example
Mem2Seq can be considered as a general sequence to sequence model with the ability to address external memories. We prepared a very basic implementation (including data preprocessing and model) for a English to France translation task. Obviusly there is not much to copy from the input in this small corpus, so it is just to show how the model works in a general sequence to sequence task. Run:
❱❱❱ python3 main_nmt.pyThis version uses a flat memory instead of triple as described in the paper.
Train a model for task-oriented dialog datasets
We created main_train.py to train models. You can see there is a notation, globals()[args['decoder']], it is converting a string into a fuction. So to train a model you can run:
Mem2Seq bAbI t1-t6:
❱❱❱ python3 main_train.py -lr=0.001 -layer=1 -hdd=128 -dr=0.2 -dec=Mem2Seq -bsz=8 -ds=babi -t=1
❱❱❱ python3 main_train.py -lr=0.001 -layer=1 -hdd=128 -dr=0.2 -dec=VanillaSeqToSeq -bsz=8 -ds=babi -t=1
❱❱❱ python3 main_train.py -lr=0.001 -layer=1 -hdd=128 -dr=0.2 -dec=LuongSeqToSeq -bsz=8 -ds=babi -t=1
❱❱❱ python3 main_train.py -lr=0.001 -layer=1 -hdd=128 -dr=0.2 -dec=PTRUNK -bsz=8 -ds=babi -t=1or Mem2Seq In-Car
❱❱❱ python3 main_train.py -lr=0.001 -layer=1 -hdd=128 -dr=0.2 -dec=Mem2Seq -bsz=8 -ds=kvr -t=
❱❱❱ python3 main_train.py -lr=0.001 -layer=1 -hdd=128 -dr=0.2 -dec=VanillaSeqToSeq -bsz=8 -ds=kvr -t=
❱❱❱ python3 main_train.py -lr=0.001 -layer=1 -hdd=128 -dr=0.2 -dec=LuongSeqToSeq -bsz=8 -ds=kvr -t=
❱❱❱ python3 main_train.py -lr=0.001 -layer=1 -hdd=128 -dr=0.2 -dec=PTRUNK -bsz=8 -ds=kvr -t=the option you can choose are:
-tthis is task dependent. 1-6 for bAbI and nothing for In-Car-dschoose which dataset to use (babi and kvr)-decto choose the model. The option are: Mem2Seq, VanillaSeqToSeq, LuongSeqToSeq, PTRUNK-hddhidden state size of the two rnn-bszbatch size-lrlearning rate-drdropout rate-layernumber of stacked rnn layers, or number of hops for Mem2Seq
While training, the model with the best validation is saved. If you want to reuse a model add -path=path_name_model to the function call. The model is evaluated by using per responce accuracy, WER, F1 and BLEU.
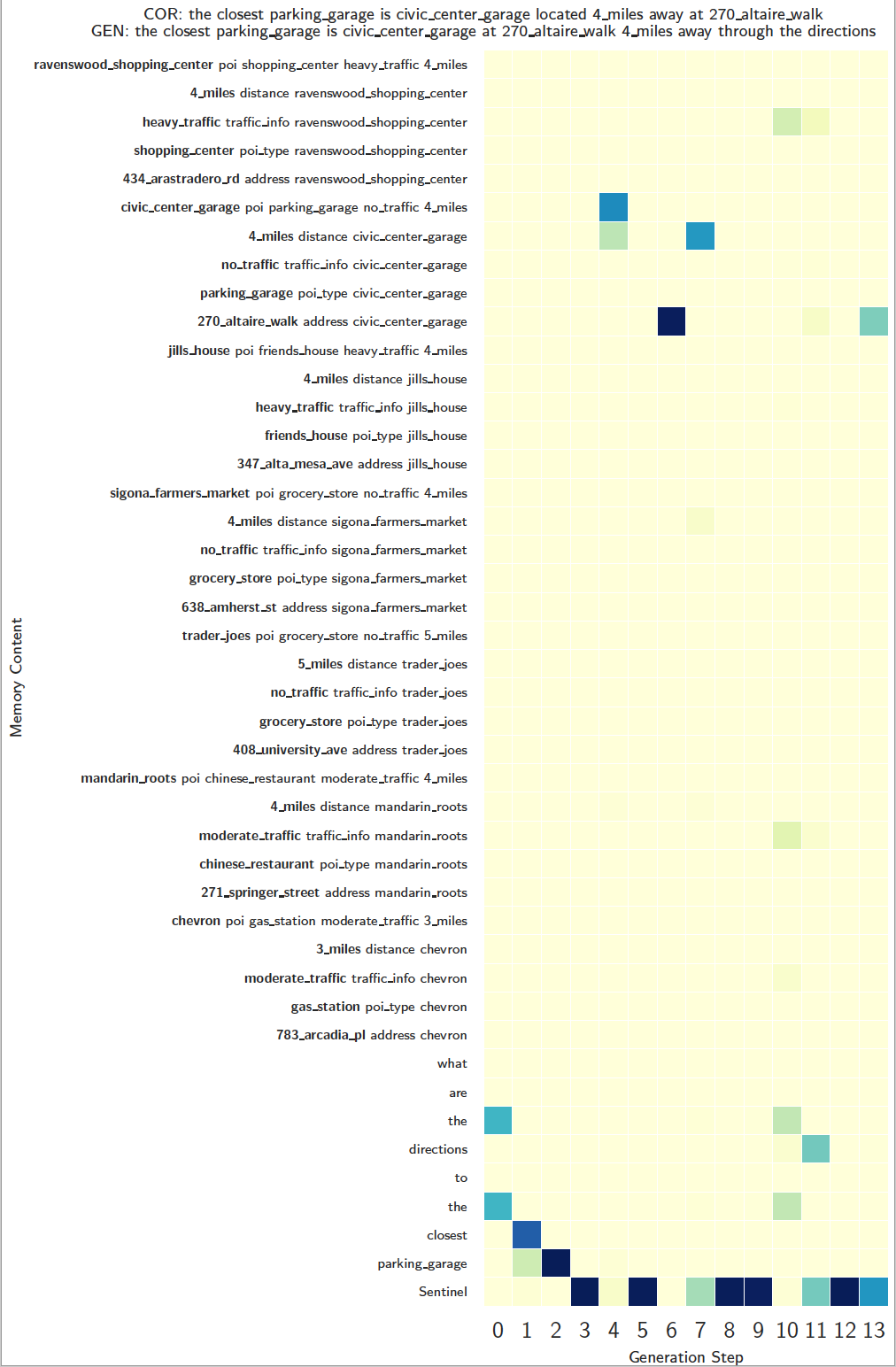
Visualization Memory Access
Notes
For hyper-parameter search of Mem2Seq, our suggestions are:
- Try to use a higher dropout rate (dr >= 0.2) and larger hidden size (hdd>=256) to get better performance when training with small hop (H<=3).
- While training Mem2Seq with larger hops (H>3), it may perform better with smaller hidden size (hdd<256) and higher dropout rate.
- Since there are some variances between runs, so it's better to run several times or run different seeds to get the best performance.