Moving forward: QA analyst - fundamentals, tools (sql, linux), automation(optional), finance, interview -> market (80-110) QA Engineer/Analyst - fundamentals, tools (sql, linux), automation, finance, interview -> market (90 - 110) QA Engineer - fundamentals, tools (sql, linux), automation(some additional), finance, interview (ask Akmal) -> market (95-120)
BA/QA or BA - fundamentals, tools (sql, linux), automation(optional), BA class, finance, interview -> market (100-150) - automation is optional more concentrate to BA ( ask Said)
- Full stack development?
- Top 10 programming languages: https://www.northeastern.edu/graduate/blog/most-popular-programming-languages/
- What is http?
- What is API?
- in linux: VI editor, Nano etc. (editors for code)
Applications that helps to write a code (IDE - integrated development Environment): PyCharm (Jet Brains), IntellijIdea (java, Jet Brains), Eclipse (java ) VisualStudio Code(), Visual Studio (for c#)
- help you write a code, help you to complete your syntax
- assist in idenfying syntax errors, importing (usage of external files)
https://www.wired.com/story/health-fitness-data-privacy/
-
Code refactoring In computer programming and software design, code refactoring is the process of restructuring existing computer code—changing the factoring—without changing its external behavior. Refactoring is intended to improve the design, structure, and/or implementation of the software, while preserving its functionality.
-
Pycharm shortcuts: Autoformating: ctrl + Alt + L based on PEP-8 Style Guide: https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that enables efficient access and modification.[1][2][3] More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data.
A data structure is a particular way of organizing data in a computer so that it can be used effectively.
Reading on Data structures:
https://www.integralist.co.uk/posts/data-types-and-data-structures/
https://towardsdatascience.com/8-common-data-structures-every-programmer-must-know-171acf6a1a42
For example, we can store a list of items having the same data-type using the array data structure.
odds = [1, 3, 5, 7 ]
new variable
vowels = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u']
working with lists create, edit, remove, access
Temporary sorting:
- new_list = sorted(list)
- new_list_rev = sorted(list, reverse=True)
Permanent sorting:
- list.sort()
- list.sort(reverse=True)
- list.reverse()
Types of Errors we can see dealing with list? IndexError: list index out of range What is object? What is iterable? what is return statement? why I have None on print() functions?
Looping through the list: for odd in odds: print(odd)
concatenate in the loop
-
Indentation Errors in the loop outside the loop not a loop
-
colons
Next class Agenda:
-
Making Numerical lists: range() list(range(1, 5))
-
Statistics: min(), max(), sum()
-
list comprehensions
PEP 8 -- Style Guide for Python Code autoformatting in pycharm - ctrl + alt + L Line Length
Slicing Copying the list
- various expression that we can use in if statement
- using simple comparison (numbers, strings, etc)
- using 'in' operator with range() function
- using 'in' operator with lists
- if statement in for loop
- if statement with multiple conditions
- if statement with multiple 'elif' statements
- using multiple lists (using pizza example)
- Some problem solving examples
Implement sum() with for loop Double characters in a string (e.g. “abc” => “aabbcc”) for letter in "hello": print(letter) Prove that a number is a prime Prove that a string is a palindrome (mom, dad, madam, kayak etc)
- dictionaries - new data structure (1-2)
- looping in dictionary
- dictionary/list with list/dictionary as a value
- 6-6. Polling:
- print multiplication table
- 6-7 to 6-12
- Keywords to note: stack, buffer
- while loop ( 0.5)
a. exercises for problem solving:
-
How to swap 2 variable values. e.g.: a=45 b=78 >> a=78 b=45
-
Count the vowels ('aeuoi') in any phrase/sentence/word. user enters any phrase, you return: print(f"number of {vowels}'s is : {count}")
-
Count each letter in any phrase
Pseudocode:
-
loop through the text
-
create a dictionary for this letters
-
add each letter to the dictionary as a key and count (starting from 0) as a value
-
every time you add a letter to a dictionary check if dictionary has the same key, if dictionary has a key you increment the valeu if dictionary does not have you create new element and value = 1 a: 1+1, d: 1+1, e: 1
-
how to find mostly used letter in the text: you have a dictionary now, you need find out what is the largest value(count) and print/return the key of that value
-
-
Find the first mostly used letter in a phrase. (max(), dictionary, add to dictionary, if the key is in the dictionary, increment)
b. Exercise from the book: 7-8. Deli: 7-9. No Pastrami: 7-10. Dream Vacation:
- 8-3. T-Shirt:
- 8-4. Large Shirts:
- 8-5. Cities:
Agenda: Functions Return values (ignore arbitrary arguments) method is the same thing as function Method is used in the context of Java, C++, C#
- 8-6. City Names:
- 8-7. Album:
- 8-8. User Albums:
Agenda:
- Functions
|-3| = 3 >>> abs(-3) =3
Primitive data type: float, integer, string, boolean Data structures: dictionary, list, tuples
Modules
- files containing your python functions
Importing modules to reuse your function anywhere in the project Packages ctrl + alt + o - to optimize the imports in the module
Imports:
import time
import functions_pkg.functions_return
import functions_pkg.functions_return as ft
from time import sleep
from functions_pkg.functions_return import print_formatted_name
from module_name import function_0, function_1, function_2
from time import *
from functions_pkg.functions_return import *Agenda:
- Classes and object (Chapter 9)
Object-oriented programming concepts:
-
class - blueprint or template code for replicating real-world things or situation, it will have state (attributes) and behavior (methods - functions)
-
object - instance of the class; it is a variable that will have an access to class state and behavior, this is used to execute the class functions
-
constructor - it is _init_() method(function), it is initializing method in the class, this will help python to define the class on execution
-
self - this is the keyword that identifies current class, it shows that attributes and functions are class level or belongs to class. super() - refers to parent class (when inheritance is used).
-
instance variables - variable defined in the constructor (attributes)
-
class names should be with upper case: Car() is good, car() is not good
-
instantiation - process of creating an object of the class
-
encapsulation - hiding data from object (users)
- read chapter 9
- exercises: from 9-1 to 9-5
- Class: inheritance Inheritance works one way from parent class to child class, not other way around.
- we can reuse all attributes and methods from parent class
- we can create new attributes (available to child only)
- we can create new methods(functions, available to child only)
- we can override the method that parent had (OOPs - Method Overriding)
Agenda:
- Exercises and Q & A
- Working with Files
- Handling Exceptions
- all exercises in Chapter 11
- read about exception handling
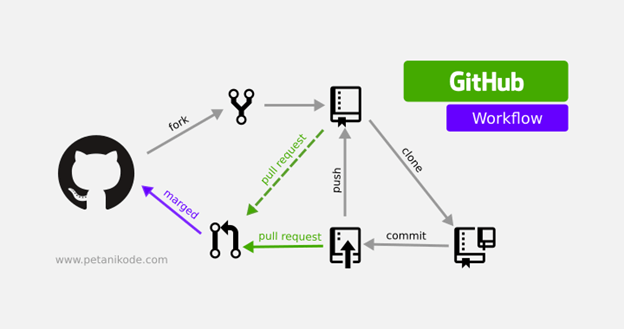
- sign up for GitHub and read about version control systems
Agenda: markdown language files and version control system
Current Class organization in the GitHub: https://github.com/2020Fall2
You can find detailed documentation here
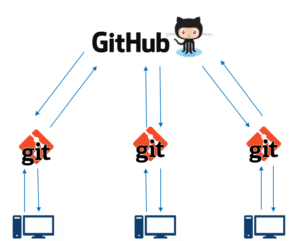
Version Control refers to a system that records changes to a file or set of files over time, called the ‘versions’. In other words, these versions help you in tracking the changes in your codes/project and if necessary, undo those changes as well.
There are three types of version control.
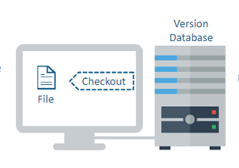
- Local Version Controls
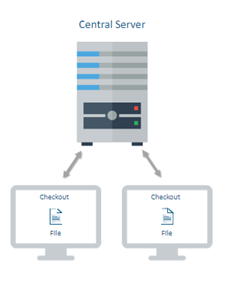
- Centralized Version Controls
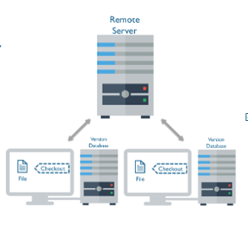
- Distributed Version Controls
Version database or file is present on a local computer. Multiple people cannot work parallelly on the same project.
In CVC, a central repository is maintained where all versions are kept and a user can check out and check-in files from their different computers at any time.
The issue with CVC is that in case of central server failure, the whole system goes down. However, the solution is a distributed Version Control.
Version database or file is stored at every user’s local system and at remote servers. If any of the servers dies, a client-server user can be used to restore the data.
Once saved, all the changes made in files are permanent and cannot revert back. There is no record what was done and by whom.
-
Install git system on your computer. go to this location to download the git. make sure you have git bash terminal (linux)
-
Go to github.com and create and account
You can print out this cheat-sheet for basic git command: cheat-sheet
Git is a distributed version control software which you need to install on your local system in order to use it. For an individual working on a project alone, Git proves to be excellent software.
GitHub is a web-based Git version control repository hosting service. It provides all of the distributed version control and source code management (SCM) functionalities of Git.
Users' active directory simply creates new files in this space and this will be tracked by the Git.
It is a place where all the modified files marked to be committed are placed.
User’s copy of the version database or file and access all the files through local repos and push the change made to remote
It is a server where all the collaborators upload changes made to files.
Creates a copy of an existing remote repository inside the local repository.
Commits all files from the staging area to local Repository
Pushes all the changes made in local to Remote Repository
Collects the changes from Remote Repository and copies them to Local Repository but doesn't affect our workspace
Collects the changes from Remote Repository and copies them to Local Repository along with merges to the current directory or our workspace
- https://learngitbranching.js.org/
- https://www.katacoda.com/courses/git
- github for previous class: spring 2020 repository
- Selenium WebDriver : working with automated browser