Note
TL;DR: Portable and easy-to-use C++ library which provides clean input/output operations.
C++'s native input/output library (iostream) doesn't provide the kind of high-level functions that you might like to use in your own projects, such as clearing the console, or stopping the natural control flow until a given key is pressed. This library aims to solve that in an beginner-friendly approach!
Tip
The simplest way to implement this library in your projects would be by fetching the library as a subdirectory of a given project's CMake script, and ultimately, make use of include_directory() to execute this directory's CMakeLists.txt, which makes it possible to use target_link_libraries() with your executable and the CPP_SAFE_IO variable, as follows:
Your project's directory structure:
./project
CMakeLists.txt
src/
CppSafeIO/
Your project's main CMakeLists.txt:
...
add_subdirectory(CppSafeIO)
target_link_libraries(YourExecutable ${CPP_SAFE_IO})
...
Note
This approach is used by this project's tests directory.
Nonetheless, I highly recommend making use of a second, cleaner approach where you don't have to directly include the library as one of your project's subdirectories:
Important
For this approach, your CMake script should use at least CMake 3.14.
You can just fetch it using FetchContent, and then link the library as follows:
Your project's main CMakeLists.txt:
...
include(FetchContent)
FetchContent_Declare( cppsafeio
GIT_REPOSITORY https://github.com/DanielRamirez404/CppSafeIO.git
GIT_TAG v2.0.0
GIT_SHALLOW TRUE
)
FetchContent_MakeAvailable(cppsafeio)
target_link_libraries(YourExecutable ${CPP_SAFE_IO})
...
Note
You can optionally change the value of the CPP_SAFE_IO variable before the FetchContent_MakeAvailable() call, if you wish so, since it won't be overwritten and it'll show up when building the project.
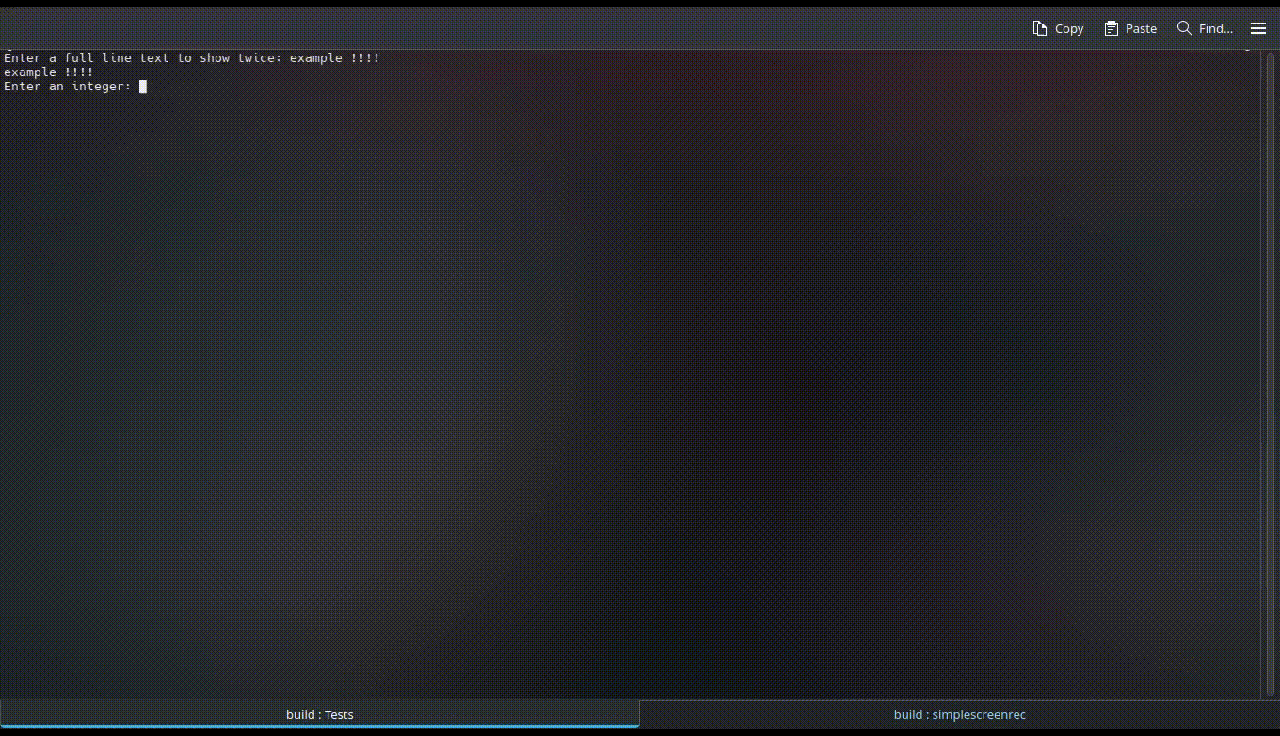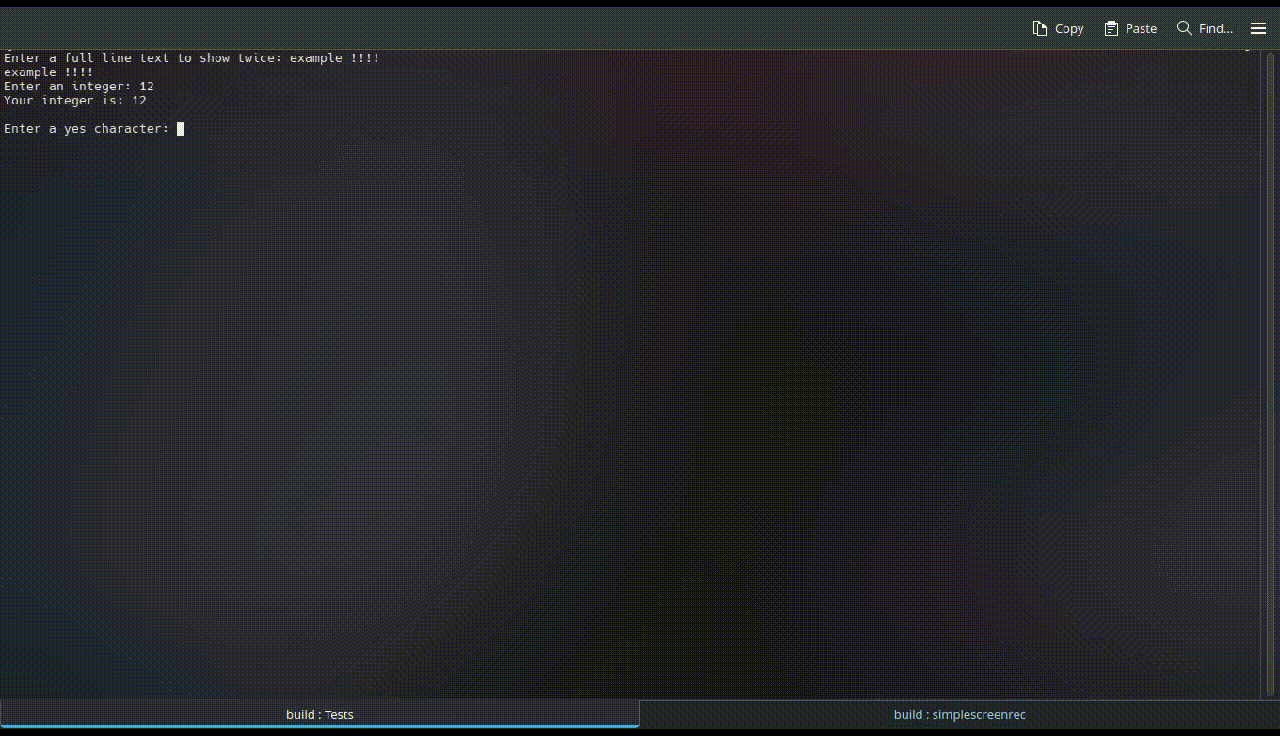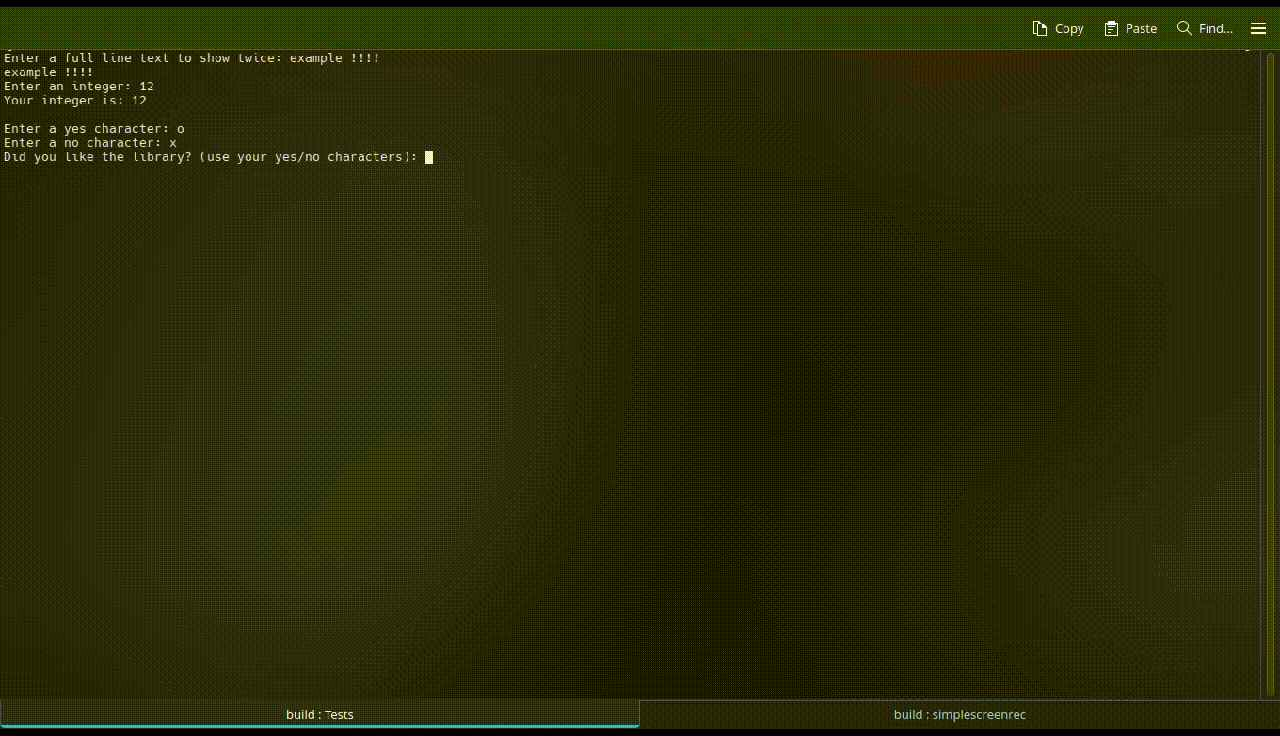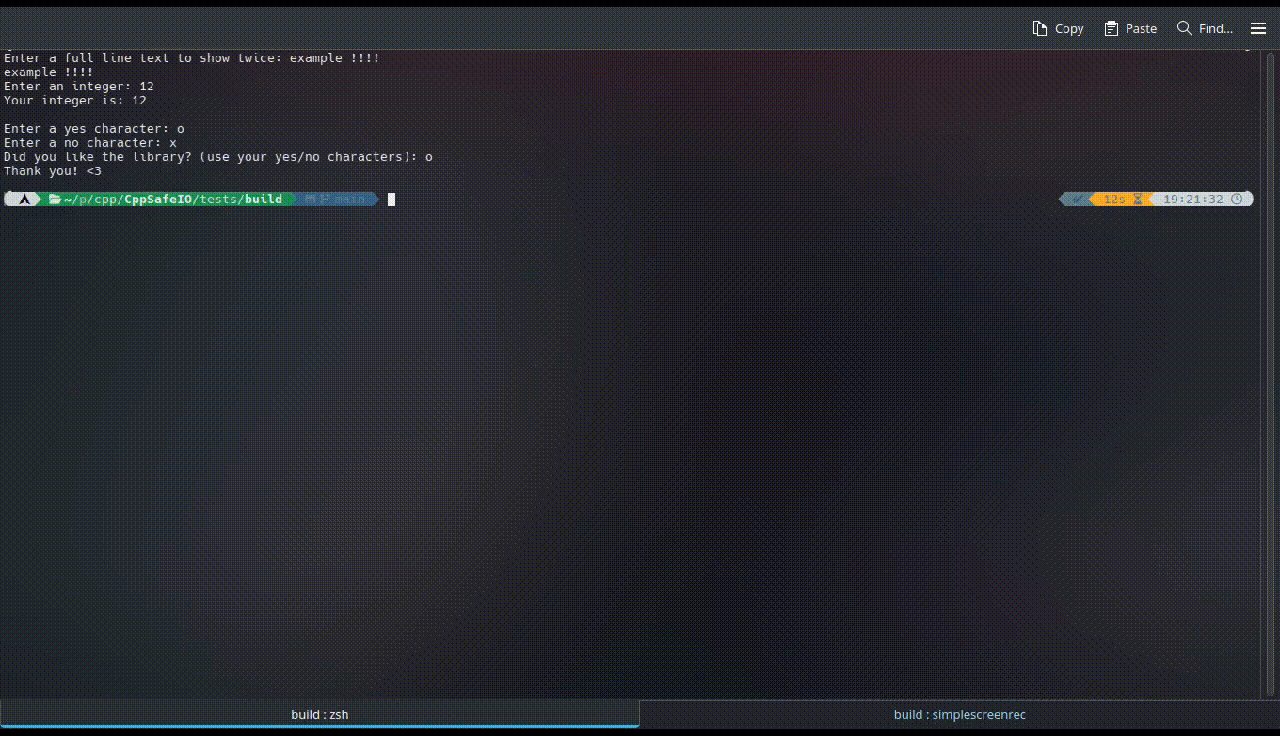
You only need to include the cppsafeio.h header file. Henceforth, all of the library's functions will be available inside of the CppSafeIO namespace, similarly to the std namespace of the C++ Standard Library. Here's a simple example showcasing a program that won't exit until the Enter key is pressed.
Tip
You can also add the using namespace CppSafeIO; statement if you wish to use this library's functions without needing to write the namespace, although that's usually considered a bad practice.
main.cpp:
#include "cppsafeio.h"
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "press the enter key to finish\n";
CppSafeIO::pressEnterToContinue();
return 0;
}
Warning
Don't forget to add the CppSafeIO namespace if you want to try out any of these functions.
<typename T> T getInput(): gets the input from the user as the provided datatype as the template argument (<T>). On failure, it throws astd::runtime_error.void clearConsole(): clears the console where the program is executed if the OS is supported (namely,Windows,LinuxorMacOS).void pressEnterToContinue(): waits until the user presses theEnterkey and ignores all input previously entered.void ignoreExceedingInput(): clearsstd::cin's buffer.bool parseYesNoInput(char yesChar, char noChar): gets one character input and returns true or false if it matches theyesCharornoCharvariables, respectively (case insensitive). On failure, it throws astd::runtime_error, or if both yesChar and noChar are the same letter.bool parseYesNoInput(): Overloaded version of the previous function with bothyandnas yesChar and noChar, respectively.std::string getInputLine():gets all entered input until a line break, as astd::string.
Tip
You can test this library's functions in the tests subdirectory.