This project aims to create a CNN model to classify German traffic signs.
This project requires:
- Introduction
- Data Set Summary & Exploration
- Preprocess data set
- Design, train and test a model architecture
- Use the model to make predictions on new images
- Analyze the softmax probabilities of the new images
---
The goal of this project is to succesfuly classify the german traffic sign dataset provided from the following repository: https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/udacity-selfdrivingcar/traffic-signs-data.zip
- succesfutlly classify means in this scope reach at least 93% in the validation and testing datasets.
The project's development takes place in the following jupyter notebook: Traffic_Sign_Classifier.ipynb
First we load the data, divide them in training, validation and testing data sets. The size of each of the data sets is as follows:
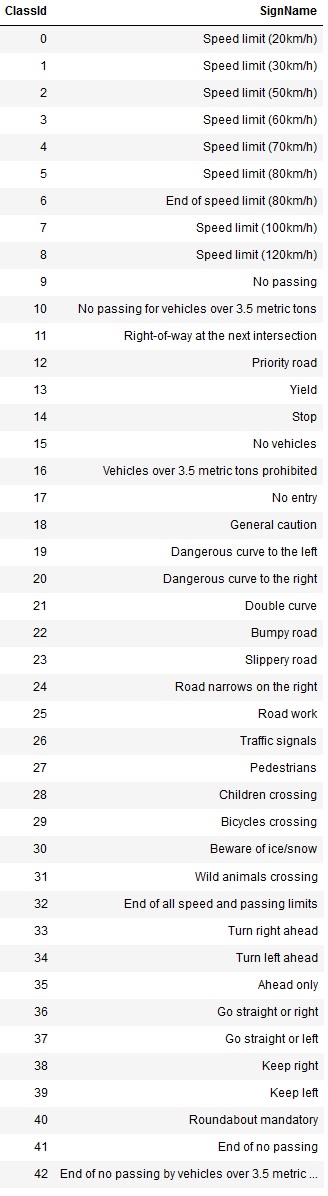
First thing I noticed is that the classes were encoded in an ordinal way and that there are 43 classes in total, as shown below:
Then I process to one hot encode the data to give all classes and equally chance while training since ordinal data tend to bias the model to go for the higher number. Therefore, the shape of the labels changed from [samples, 1] to [samples, 43].
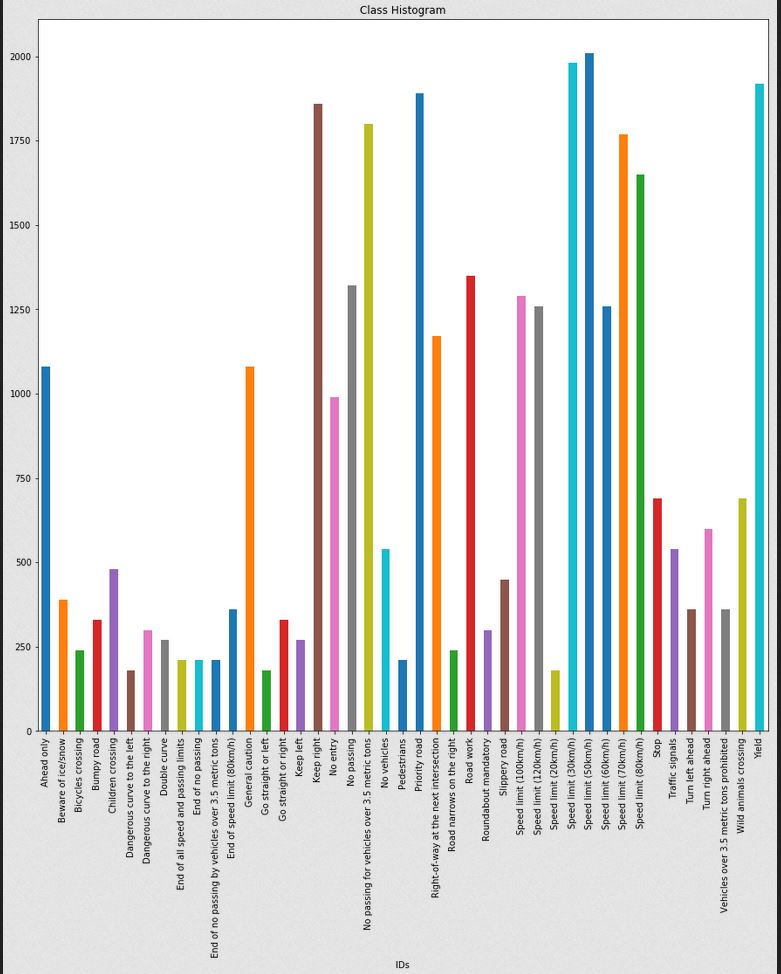
After that I created a histogram of the whole data class by class to quantify how much data I have for each class. The result was the following:
As we can see above the data is uneven. That might be an issue because the model won't be able to train on all the whole classes equally. Therefore we requirede to augment the data to get an even number of data in all the classes.
The augmentation consisted of the following steps:
- Rotation
- Translation
- Shear
It was decided Augmenting the data up to 2500 samples on each class to match the low quantity class samples to the high quantity class samples. The result wast the following:
As shown above, now all data is even thanks to the augmented data.
Finally, some visualization of the data was done. In this case we saw a sample of each one of the classes to get an intuition of the image data set, as shown below:
In this stage of the project we try two basic preprocessing steps.
- The 1st one was to grayscale the image. An example of a grayscale image is shown below:
- Second one was to implement a min max normalization, which follow the below equation:
The reason to apply min-max normalization is because we want our data well conditioned as explained below:
As shown in the figure above, this will help the optimizer minimizing the cost more evenly as the variance is equal in both directions.
Note: At the end I make use of the normalized rgb data, since performance was better by feeding the model with color images rather than grayscale images.
The architecture selected for this task was a LeNet-like model, the reason was that there are similar applications for traffic sign classification using the LeNet model and also is one of the basic networks designed and I tought it was a great idea to start from the basics. An illustration of the whole model is shown below:
In summary the model consists of the following layers:
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Input | 32x32x3 RGB image |
| Convolution 5x5 | 1x1 stride, VALID padding, 6 filters. Outputs 28x28x6 |
| RELU | |
| Dropout | keep probability = 0.7 |
| Max pooling | 2x2 stride, filter 2x2. Outputs 14x14x6 |
| Convolution 5x5 | 1x1 stride, VALID padding, 16 filters. Outputs 10x10x16 |
| RELU | |
| Dropout | keep probability = 0.7 |
| Fully connected | input: 400 output: 120 |
| RELU | |
| Dropout | keep probability = 0.7 |
| Fully connected | input: 120 output: 84 |
| RELU | |
| Dropout | keep probability = 0.7 |
| Fully connected | input: 84 output: 43 |
| Softmax |
- The optimizer used to minimize was an ADAM optimizer. Diffent learning rates were tested and the one that seems to behave better was 1e-3.
- The number of epochs decided were 30 since more than that would've make the process of calibration very time consuming. Nevertheless if time were not a limited resource a lerning rate of 1e-4 and epochs: 100 seemed very promising to increase even more the accuracy of the model.
- Since data was augmented I also decided to increase the batch size to 256 so that the optimizer can do more informed updates in the weights.
- One of the best features in the model that helped inproving performance was the dropout layer, which turned to be a very good regularization approach.
At the end the model reached the following accuracy for each dataset:
- Training: 98.62%
- Validation: 94.92%
- Testing: 93.20%
BTW the whole model was saved at the following location checkpoints/trained_model2.ckpt
Thus, no need to retrain the model each we wanted to reuse the model. After in the notebook I also restore this model with all its weight to predict in 5 new images, which is better explained in the next section.
This section of the project was very fun since we now used the CNN we trained to predict real random images from internet. The images randomly chosen for this task were the following:
Here are the results of the prediction:
As you can see above 4 out of 5 were predicted, which gives an accuracy of 80%, not bad at all. I thought it might be a little lower. The 1st one was misclassified, maybe the reason is that it has a different perspective that most of the images from this class the model has seen in the training stage. To mitigate this problem we might need to add a preprocess step or augment the data with images that have a random perspective transform.
The next step was to look at the top 5 softmax results of each prediction to see the performance of the classifier in terms of how confident it was selecting the final outcome.
An illutration of the process is shown below:
- For the first image, we can now notice that at least the correct class was in the top 3 options. That means that the classifier was not that really sure in picking the class.
- Second one also shows that the classifier almost selects the wrong class. The similarity between a no entry sign and a stop sign seemed to affect in this case
- 3rd, 4rd and 5th were very confident selections by the classfier since they almost reach the 100%
In conclusion, this project was very fun to tackle. There is some future work that can be done such as trying other regularization methods, for instance, L2 regularization. We can also improve by trying other architectures or enhancing the dataset to make the current CNN learn other types of situations. Definitely there is still room for improvement which I plan to get better at.