Table of Contents generated with DocToc
LSF Git Operation
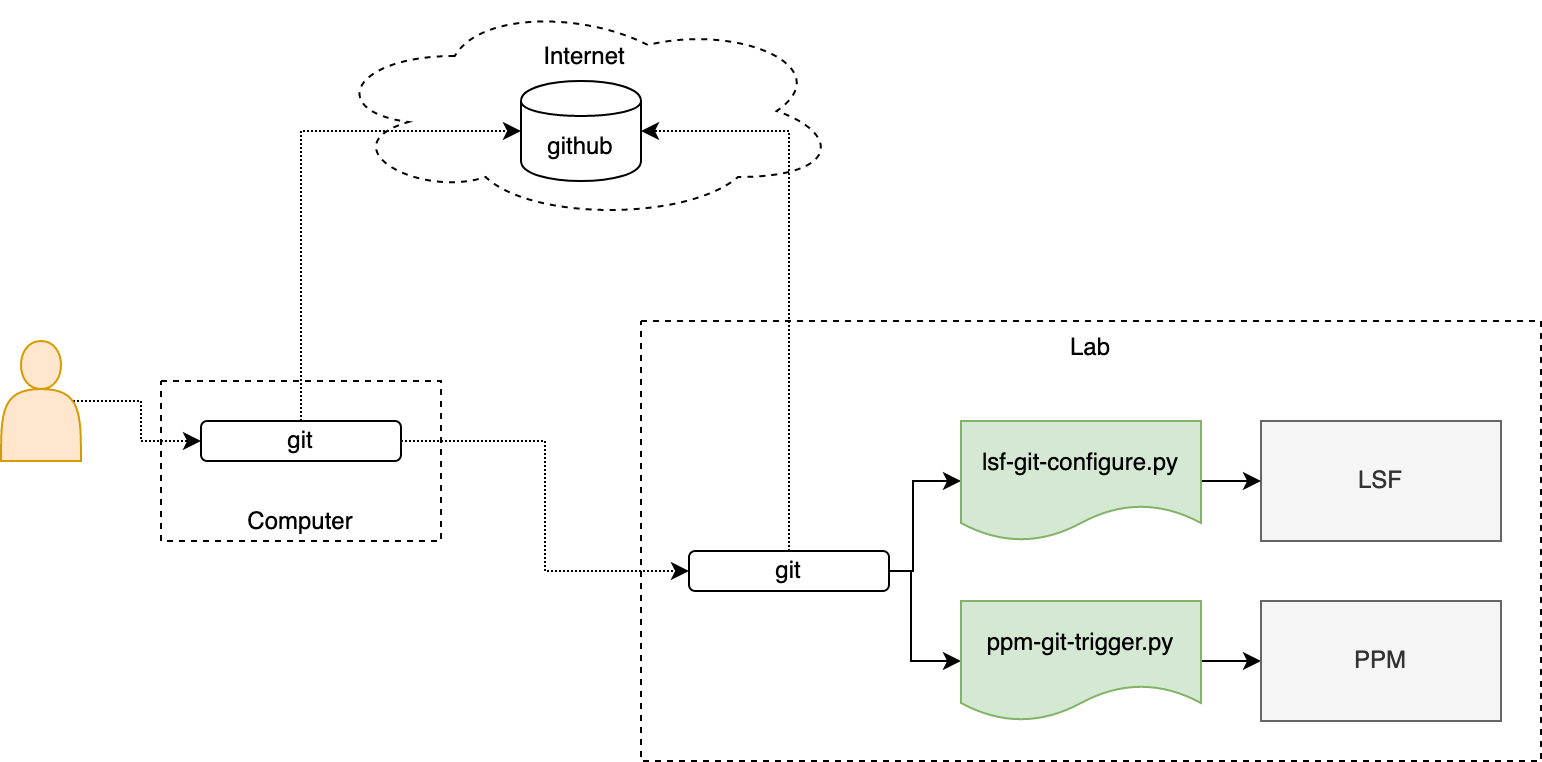
LSF git operation script tools make git changes automatically trigger LSF opeartions.
Git operation scripts monitor git repo to apply file changes in local LSF and PPM.
LSF configurations and PPM workflows/data can be managed by git with advantages:
- versioned data for LSF configurations, PPM workflow, etc.
- attached history information as submission user account, commit message, etc.
- access anywhere by git(hub)
NOTE: git and python should be installed to make script tools work.
LSF Configuration Manager
The general steps to use LSF git operation are:
- Manage your LSF configuration files in
git - Run
lsf-git-configure.py - Modify your LSF configuration files in local repository and
git pushyour change
You can use pre-receive as git pre-receive hook. It is used to check a commit
change to see if there is warning/error introduced in LSF. The commit will be rejected
if checking fails. This is not mandatory to use LSF git operation tool but perfered to
to have to make your LSF configuration as clean as possible.
Currently, we only support local checking. That means you need to make your git repo
on LSF master host and set your cluster installation path into the pre-receive hook.
# clone or download this repo and edit pre-receive to define LSF path correctly
cp lsf-git-ops/src/lsf/pre-receive [your-git-repo]/.git/hooks/Single Cluster Deployment
Below is a step to step example.
- prepare git environment to manage LSF configuration
# create a working git repository environment as bare repo
cd /usr/local/work/lsfconf
git init --bare
git config receive.denyCurrentBranch ignore
# configure lsf configruation git repo and make it connect to the bare repo
cd $LSF_ENVDIR
git init
git add .
git commit -m 'manage lsf configuration in git'
git remote add upstream /usr/local/work/lsfconf
git push --set-upstream upstream master- start up LSF git opeartion script for configuration on master host
# clone or download this repo and navigate to repo root directoy, then run below command
src/lsf/lsf-git-configure.py- manage LSF configuration in client
git clone [git-host]:/usr/local/work/lsfconf
cd lsfconf/
vi lsf.conf # add LSB_ENABLE_HPC_ALLOCATION=N
git add .
git commit -m 'add parameter LSB_ENABLE_HPC_ALLOCATION=N'
git push- check LSF configuration on master
# before manage LSF configuration in client
badmin showconf mbd | grep HPC # old display
# after manage LSF configuration in client
badmin showconf mbd | grep HPC # updated displayMulti-cluster Deployment
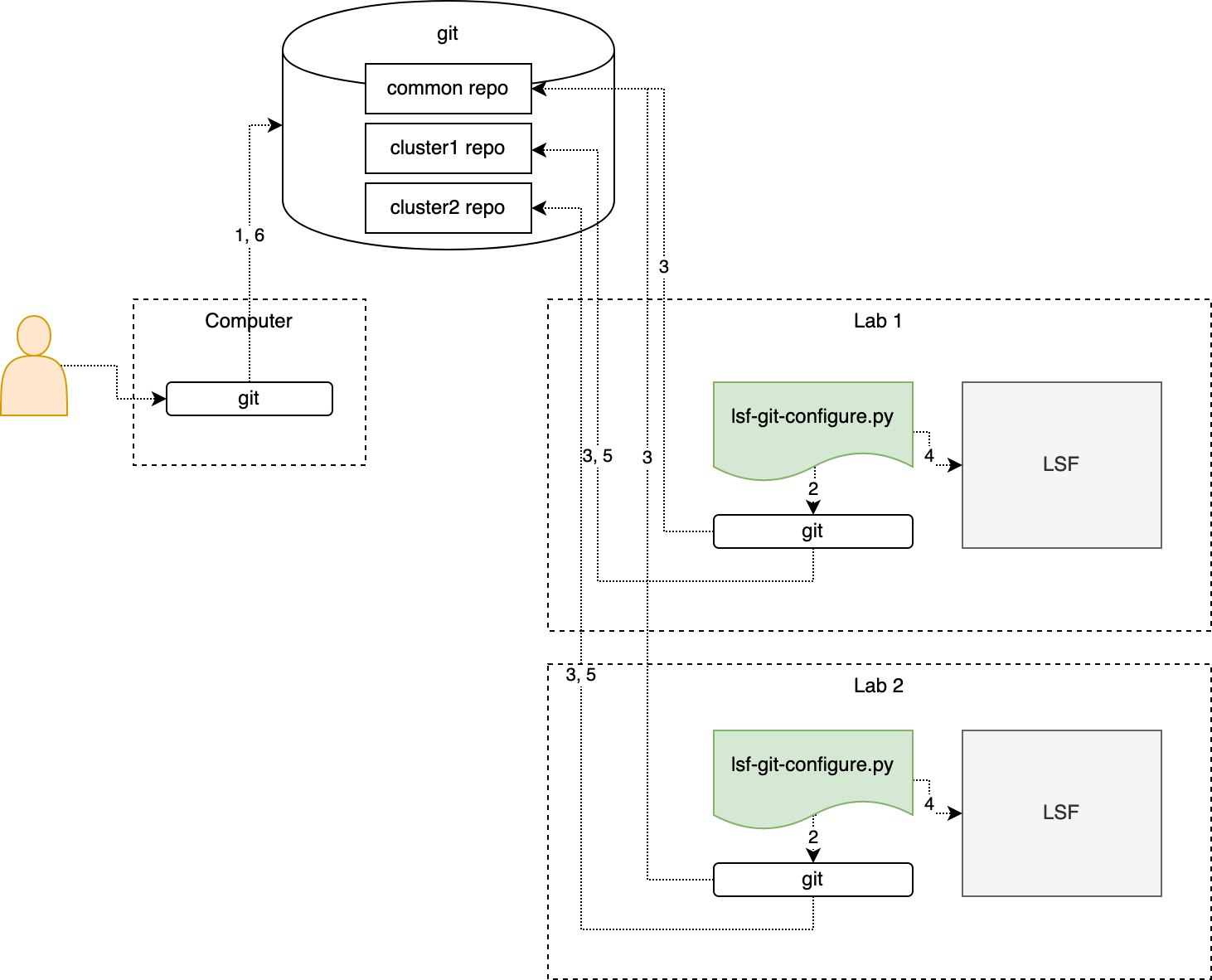
For multi-cluster configuration management, it works as:
- Modify and push cluster private and common repos from local
- Periodically check new commits for private and common repos
- Retrieve commits for private and common repos
- Take corresponding LSF operations
- (optionally) Push the operation result to
git-configuration.logfor private repo - (optionally) Get the response from private repo
Below is a step to step example.
- prepare git environment to manage LSF configurations
# create working git repository environments as central repos.
#
# for cluster native configuration file, it has same preparation steps in single cluster case
# take LSF_CLUSTER_NAME=cluster1 as example, you can do below for all clusters individually
cd /usr/local/work/lsf-conf-cluster1
git init --bare
git config receive.denyCurrentBranch ignore
# for shared common configuration file
# make sure the common repo can be accessed from all clusters
cd /home/test/repo/common
git init --bare
git config receive.denyCurrentBranch ignore
# clone common repository for local cluster use
# take LSF_CLUSTER_NAME=cluster1 as example, you can do below for all clusters
cd /tmp
git clone git-host:/home/test/repo/common
cd common
echo "# the file can be included by lsb.queues " >>lsb.queues.common
git add .
git commit -m 'initialize an included configuration file'
cd $LSF_ENVDIR
# modify lsb.queues to add the common conf
echo "#INCLUDE \"/tmp/common/lsb.queues.common\" " >> lsbatch/cluster1/configdir/lsb.queues
git init
git add .
git commit -m 'manage lsf configuration in git'
git remote add upstream /usr/local/work/lsf-conf-cluster1
git push --set-upstream upstream master- start up LSF configuration git opeartion script on the master of each cluster
# clone or download this repo and navigate to repo root directoy, then run below command
src/lsf/lsf-git-configure.py --shared_envdir=/tmp/common- manage LSF configuration in client
git clone git-host:/home/test/repo/common
cd common
# add a new queue "common" for all clusters
cat << EOF > lsb.queues.common
Begin Queue
QUEUE_NAME = common
PRIORITY = 30
INTERACTIVE = NO
FAIRSHARE = USER_SHARES[[default,1]]
End Queue
EOF
git add .
git commit -m "update lsb.queues.common to add a new queue"
git push
- check LSF configuration on master
# take cluster1 as example, you can do below for all clusters
[user@test ~]# lsid
IBM Spectrum LSF Standard 10.1.0.6, Oct 10 2019
Copyright International Business Machines Corp. 1992, 2016.
US Government Users Restricted Rights - Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp.
My cluster name is cluster1
My master name is test.ibm.com
[user@test ~]#
[user@test ~]#bqueues common
QUEUE_NAME PRIO STATUS MAX JL/U JL/P JL/H NJOBS PEND RUN SUSP
common 30 Open:Active - - - - 0 0 0 0
[user@test ~]#PPM Workload Manager
The general steps to use PPM git operation are:
- Manage your PPM flow definition and file dependences in
git - Run
ppm-git-trigger.py - Modify your flow definition file and the data in your local repository and
git pushthe changes
The managed git repo should have below conventions for PPM git opeartion script:
- root dir has
workflowsubdirectory. workflowincludes flow directory anddata(optionally).
/workflow/
flow-name-A/
my-flow-A.xml
data/
A.data
B.data
C.data
out/
A.out
status/
error.msg
flow-name-B/
flow-name-C/
/others
PPM Deployment
Workflow can be submitted when it is pushed to the git repository. The workflow can also be designed to depend on the data to trigger the flow and continue the job.
Below is a step to step example.
Here just take samples in this repo as example, you also can create your flows on demand.
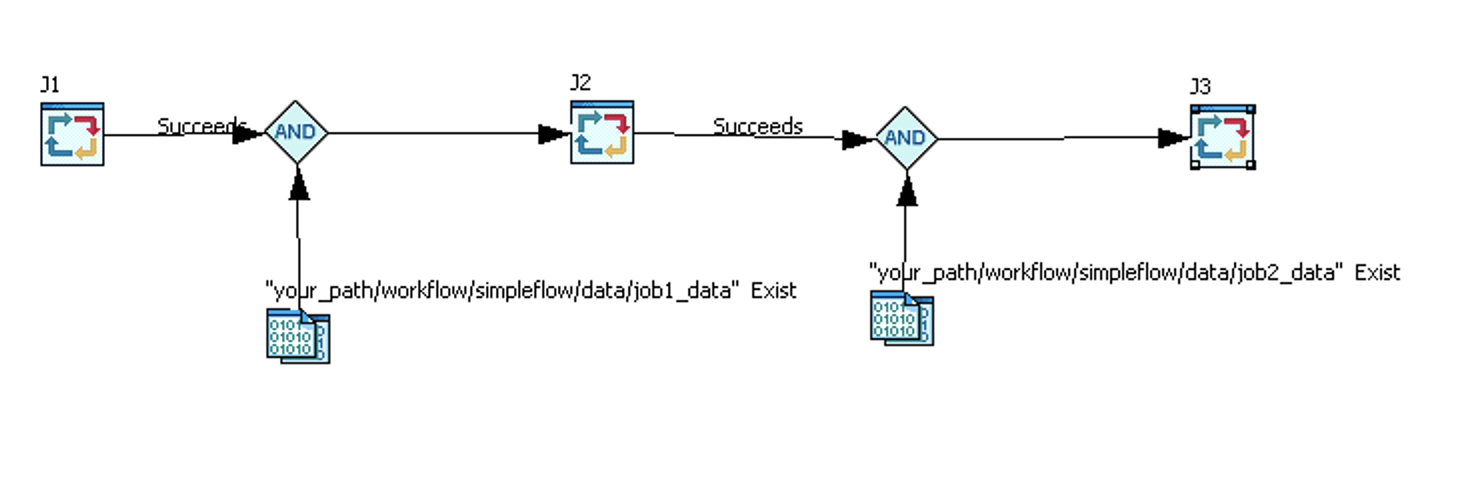
The simpleflow has three jobs:
- J1(command is "sleep 1") will run automaticlly after flow triggered
- J2(command is "sleep 2") will begin when all conditions are met(J1 is succeed and your_path/workflow/simpleflow/data/job1_data exist)
- J3(command is "sleep 3") will begin when all conditions are met(J2 is succeed and your_path/workflow/simpleflow/data/job2_data exist)
- prepare git environment to manage LSF configuration
# create a working git repository environment as bare repo
cd /usr/local/work/ppmworkflow/
git init --bare
git config receive.denyCurrentBranch ignore
# configure PPM data git repository and make it connect to the bare repo
cd /tmp
# clone or download this repo to /tmp
# copy samples directory in this repo to /tmp
cp -rf lsf-git-ops/src/ppm/samples ./
cd samples
# need replace the your_path (as a placeholder in workflow/simpleflow/simpleflow.xml) with /tmp/samples
# also need replace the user (as a placeholder in workflow/simpleflow/simpleflow.xml) with your name
sed -i 's/your_path/\tmp\/samples/g' workflow/simpleflow/simpleflow.xml
sed -i 's/user/your/g' workflow/simpleflow/simpleflow.xml
git init
git add .
git commit -m 'manage ppm flows in git'
git remote add upstream /usr/local/work/ppmworkflow
git push --set-upstream upstream master- start up LSF configuration git opeartion script
cd /tmp/lsf-git-ops/src/
# please make sure you have the permission to submit and trigger flows.
ppm/ppm-git-trigger.py -p /tmp/samples
# now the flow simpleflow in the /tmp/samples directory should be submitted and triggered
# J3 is under Waiting state due to not all the conditions are met
[user@test ~]# jflows 1
FLOW_ID: 1
USER NAME
user simpleflow
STATE START TIME END TIME
Running Thu Feb 27 23:20:48 GMT-05:00 2020
CURRENTLY-USED VERSION: 1.0
DETAILS:
NAME TYPE STATE JOBID JOBTYPE
1:user:simpleflow:J1 Job Done 2313
1:user:simpleflow:J2 Job Done 2314
1:user:simpleflow:J3 Job Waiting 0
[user@test ~]#- manage PPM workflow in client
git clone git-host:/usr/local/work/ppmworkflow
cd ppmworkflow
touch workflow/simpleflow/job2_data
git commit -m 'add job2_data for job3' -a
git push- check your PPM and LSF to see if workflow and job work as expected
[user@test ~]# jflows 1
FLOW_ID: 1
USER NAME
user simpleflow
STATE START TIME END TIME
Done Thu Feb 27 23:20:48 GMT-05:00 2020 Thu Feb 27 23:25:38 GMT-05:00 2020
CURRENTLY-USED VERSION: 1.0
DETAILS:
NAME TYPE STATE JOBID JOBTYPE
1:user:simpleflow:J1 Job Done 2313
1:user:simpleflow:J2 Job Done 2314
1:user:simpleflow:J3 Job Done 2315