Perceiver, Perceiver IO and Perceiver AR
This repository is a PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning implementation of
| Perceiver: General Perception with Iterative Attention (paper, video) | 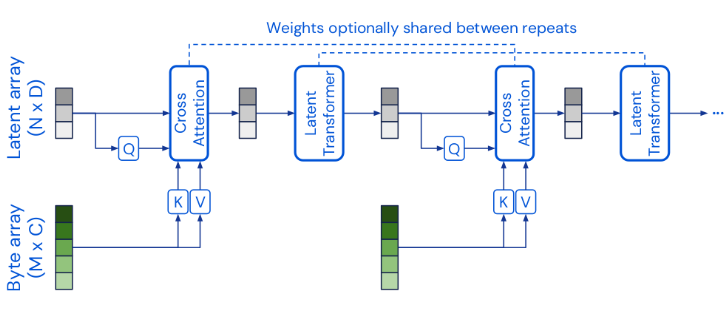 |
| Perceiver IO: A General Architecture for Structured Inputs & Outputs (paper, blog post) | 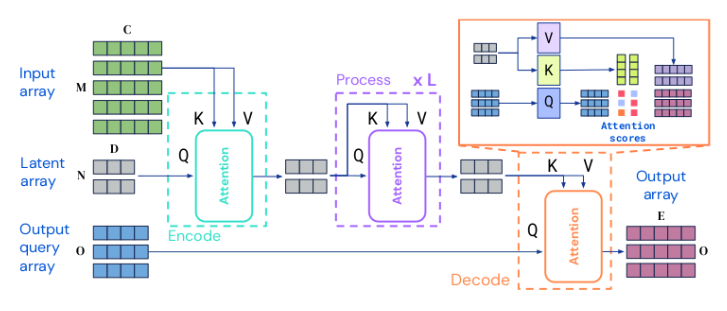 |
| General-purpose, long-context autoregressive modeling with Perceiver AR (paper, blog post) | 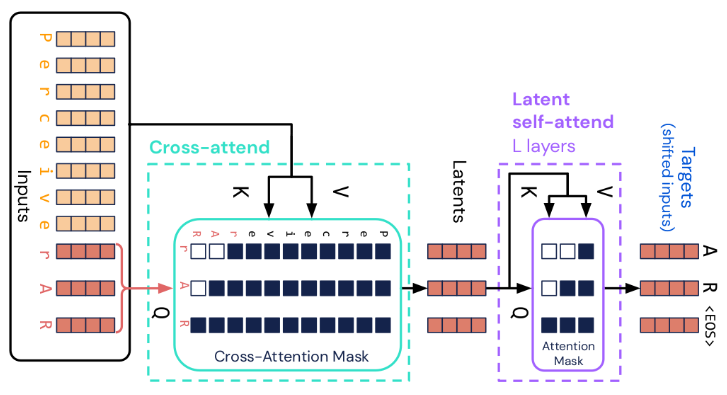 |
Models are written in plain PyTorch and can be trained at scale with PyTorch Lightning
and the Lightning CLI. Pretrained weights
of
Installation
Via pip
pip install perceiver-io[text,vision]From sources
Installation from sources requires a Miniconda and a Poetry (1.2.0 or higher) installation.
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate perceiver-io
poetry install --all-extrasDocker image
docker pull ghcr.io/krasserm/perceiver-io:latestSee Docker image for details.
Documentation
- Getting started
- Model construction
- Pretrained models
- Training examples
- Inference examples
- Building blocks
Getting started
Here's a minimal example for autoregressive language modeling with Perceiver AR. A small language model (30.7M parameters) is trained on the WikiText-103-raw dataset and then used to generate text from a prompt. Input text is tokenized into raw UTF-8 bytes and the model also generates raw UTF-8 bytes.
The PyTorch model class (CausalLanguageModel) and the corresponding PyTorch Lightning wrapper class
(LitCausalLanguageModel) are defined in perceiver/model/text/clm.py (see also
model construction for further details). The PyTorch Lightning data module
(WikiTextDataModule) is defined in perceiver/data/text/wikitext.py.
Training
Command line
The script for training a CausalLanguageModel on the command line is perceiver/scripts/text/clm.py.
The constructor signatures of LitCausalLanguageModel and WikiTextDataModule determine the available --model.* and
--data.* command line options. Command line options --optimizer.*, --lr_scheduler.* and --trainer.* configure
the optimizer, learning rate scheduler and the PyTorch Lightning Trainer,
respectively.
python -m perceiver.scripts.text.clm fit \
--model.num_latents=512 \
--model.num_channels=512 \
--model.num_self_attention_layers=8 \
--model.cross_attention_dropout=0.5 \
--data=WikiTextDataModule \
--data.tokenizer=deepmind/language-perceiver \
--data.add_special_tokens=false \
--data.max_seq_len=4096 \
--data.task=clm \
--data.batch_size=16 \
--optimizer=Adam \
--optimizer.lr=2e-4 \
--lr_scheduler.warmup_steps=200 \
--trainer.accelerator=gpu \
--trainer.devices=1 \
--trainer.max_epochs=5 \
--trainer.accumulate_grad_batches=4Supported optimizers are those packaged with PyTorch and pytorch-optimizer.
The --data.task=clm option configures the data module to produce data compatible with causal language modeling (other
possible values are mlm for masked language modeling and clf for sequence classification). When running this command
for the first time, the WikiText dataset is downloaded and preprocessed. To download and preprocess the dataset prior
to training, run
python -m perceiver.scripts.text.preproc wikitext \
--tokenizer=deepmind/language-perceiver \
--add_special_tokens=false \
--max_seq_len=4096 \
--task=clmwhich is usually faster.
Python code
Training on the command line uses the PyTorch Lightning Trainer under the hood. To run the Trainer directly from
a Python script, dynamically add a configure_optimizers method to LitCausalLanguageModel, create instances of
LitCausalLanguageModel and WikiTextDataModule and then call trainer.fit() with the model and data module as
arguments:
from torch.optim import Adam
from perceiver.data.text import WikiTextDataModule, Task
from perceiver.model.text.clm import LitCausalLanguageModel, CausalLanguageModelConfig
from perceiver.scripts.lrs import ConstantWithWarmupLR
import pytorch_lightning as pl
def configure_optimizers(self):
optimizer = Adam(self.parameters(), lr=2e-4)
scheduler = ConstantWithWarmupLR(optimizer, warmup_steps=200)
return {
"optimizer": optimizer,
"lr_scheduler": {"scheduler": scheduler, "interval": "step", "frequency": 1},
}
# # Add configure_optimizers method to LitCausalLanguageModel (not hard-coded there)
setattr(LitCausalLanguageModel, "configure_optimizers", configure_optimizers),
if __name__ == '__main__':
data = WikiTextDataModule(
tokenizer="deepmind/language-perceiver",
add_special_tokens=False,
max_seq_len=4096,
task=Task.clm,
batch_size=16,
)
config = CausalLanguageModelConfig(
vocab_size=data.vocab_size,
max_seq_len=data.max_seq_len,
num_latents=512,
num_channels=512,
num_self_attention_layers=8,
cross_attention_dropout=0.5,
)
# Create Lightning module of CausalLanguageModel from configuration object
lit_model = LitCausalLanguageModel.create(config)
# Instantiate PyTorch Lightning Trainer
trainer = pl.Trainer(accelerator="gpu", devices=1, max_epochs=5, accumulate_grad_batches=4)
# Train model (will also preprocess dataset if not already done yet)
trainer.fit(lit_model, datamodule=data)The trained PyTorch model can be accessed with lit_model.model. If you prefer to use a custom training loop without
using the PyTorch Lightning Trainer, create a plain PyTorch model with CausalLanguageModel.create(config=...) and
train it directly as shown in the following simple example:
from perceiver.model.text.clm import CausalLanguageModel
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.optim import Adam
data = ...
data.prepare_data()
data.setup()
model_config = ...
model = CausalLanguageModel(config=model_config)
model.train()
optim = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=2e-4)
# Simplified training loop compared to previous
# examples (no gradient accumulation, ...)
for epoch in range(5):
for labels_ids, input_ids, _ in data.train_dataloader():
logits = model(input_ids)
loss = F.cross_entropy(logits.permute(0, 2, 1), labels_ids[:, -model_config.num_latents:])
loss.backward()
optim.step()
optim.zero_grad()
# Save trained model
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "/path/to/model.pt")Inference
For generating text from a prompt via top-k sampling, CausalLanguageModel provides a generate() method. The following
example first loads a trained model from a checkpoint and then generates text from a short sample prompt. An interactive
demo is also available in the Colab notebook.
from perceiver.data.text import TextPreprocessor
from perceiver.model.text.clm import LitCausalLanguageModel
# Load model from a checkpoint that has been written by the PyTorch Lightning Trainer
model = LitCausalLanguageModel.load_from_checkpoint("/path/to/checkpoint").model.eval()
# Alternatively, load the model's state_dict directly
#model = CausalLanguageModel(config=model_config).eval()
#model.load_state_dict(torch.load("/path/to/model.pt"))
# Create a text preprocessor
preproc = TextPreprocessor(tokenizer="deepmind/language-perceiver", max_seq_len=4096, add_special_tokens=False)
# Convert text to model input
prompt, _ = preproc.preprocess("A man was reading a book on a sunny day until he sudden")
# Continue prompt via top-k sampling where k = f(vocab_size, threshold)
generated = model.generate(num=512, prompt=prompt[None, ...], threshold=0.9)
# Decode model output using preprocessor's tokenizer
generated_text = preproc.tokenizer.decode(generated[0])