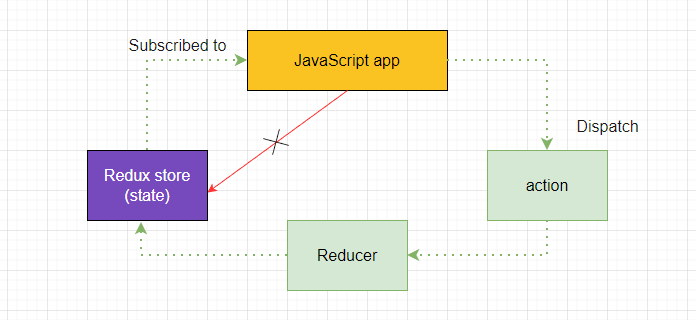
Redux is a predictable state management library for JavaScript applications. It can be used with any front-end JavaScript framework or library, such as React, Angular, or Vue.js.
Redux is designed to help manage the state of an application by providing a single, centralized store for all of the application's data. It uses a unidirectional data flow and a set of strict rules to ensure that the state of the application can only be modified in a predictable way. This makes it easier to understand and debug the application, as well as to implement features such as time travel debugging and hot reloading.
Redux is often used in conjunction with React because it works well with the declarative nature of React components. However, it is not limited to React and can be used with any front-end framework or library.
The core idea behind Redux is that the state of an application should be managed in a single, immutable store. This store can only be modified through the use of specific actions, which are dispatched to the store and processed by reducer functions. These reducer functions update the state of the store in a predictable, deterministic way, based on the type of action that was dispatched.
You are correct that both useReducer and useContext can be used as alternatives to Redux in some cases. useReducer is a hook that allows you to manage state in a React component, and useContext allows you to pass data down the component tree without the need for props drilling.
However, there are still a few reasons why you might want to consider using Redux in your application:
Centralized state management: Redux allows you to store all your application's state in a single, immutable store, which can make it easier to manage complex state, especially in larger applications.
-
Predictable state updates:
Redux uses a strict unidirectional data flow, which means that state updates only happen in a predictable way. This can make it easier to debug and test your application. -
Easy to implement undo/redo:
Because all state updates in Redux are stored in an array of previous states, it is easy to implement undo/redo functionality. -
Community support:
Redux is a widely-used library, and as such has a large community of developers who can provide support and resources.
That being said, it's important to choose the right tool for the job. In some cases, using useReducer or useContext may be sufficient for your needs, and using Redux may be unnecessary. It's always a good idea to carefully consider the trade-offs of each approach before making a decision.
Single source of truth:
The state of your entire application is stored in a single object, called the "store." This makes it easier to understand the state of your application and debug problems.State is read-only
The only way to change the state of your application is to dispatch an action, an object that describes a change to the state. This makes it easier to understand how the state of your application is being modified and allows you to implement logic to handle different types of actions.Changes are made with pure functions
In Redux, you define "reducers" to handle the logic for updating the state based on an action. Reducers are pure functions, which means they do not have side effects and always return the same output for a given input. This helps to ensure that the state of your application is predictable and easy to test.In Redux, a reducer is a function that takes in the current state of an application and an action, and returns a new state. Reducers are the way that you update the state of your application in response to actions.
Here is an example of a simple reducer function:
function reducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return { count: state.count + 1 };
case 'DECREMENT':
return { count: state.count - 1 };
default:
return state;
}
}In this example:
In this example, the reducer function has a switch statement that checks the type property of the action. Depending on the type of the action, the reducer returns a new state object with an updated count property. If the action type is INCREMENT, the count is incremented by 1. If the action type is DECREMENT, the count is decremented by 1. If the action type is not recognized, the reducer returns the current state.Reducers are important in Redux because they are the only way to update the state of your application. They are also pure functions, which means they do not have any side effects and always return the same output for a given input. This helps to ensure that the state of your application is predictable and easy to test.
In Redux, the state of your entire application is stored in an object tree within a single store. This single state tree makes it easy to keep track of changes over time and debug issues, as the entire state of the application is contained in a single store.
The state tree is made up of small, simple objects, and each piece of state is contained within its own property on the state tree.
For example:
if you are building a to-do list app, the state tree might contain a property called "todos" that stores an array of to-do objects, and another property called "visibilityFilter" that stores a string representing the current visibility filter for the to-do list.In Redux, the state of the application can only be modified through a process called dispatchinng an action. An action is a plain JavaScript object that describes the change that needs to be made to the state tree. For example, to add a new to-do to the list, you might dispatch an action with a type of "ADD_TODO" and a payload that includes the text of the new to-do.
Redux provides a way to manage the state of your application in a predictable, transparent way, making it easier to understand and debug the behavior of your app.
In Redux, an action is a plain JavaScript object that represents an intention to change the state of the application. Actions are the only way to trigger a state change in a Redux application, and they are the result of user input, network responses, or application logic.
More About State:
Actions are very simple objects that must have a type property to describe the type of action being performed. They may also include a payload of data that provides additional information about the action. For example, an action to add a new to-do item to a list might have a type of "ADD_TODO" and a payload that includes the text of the to-do item.Here is an example of a simple action object:
{
type: 'ADD_TODO',
payload: {
text: 'Write a Redux tutorial'
}
}In a Redux application, actions are dispatched using the store's dispatch method. When an action is dispatched, it is passed to the root reducer function, which then determines how the state should be updated based on the type of action that was dispatched.
For example, if the action above were dispatched, the reducer function might update the state tree by adding a new to-do item to the list of to-dos.